PowerPoint file of HBM_part 2
... the information carrying waves can follow. Similar features occur inside entangled systems. Due to the exclusion principle, observing the state of a sub-module has direct (instantaneous) consequences for the state of other sub-modules. ...
... the information carrying waves can follow. Similar features occur inside entangled systems. Due to the exclusion principle, observing the state of a sub-module has direct (instantaneous) consequences for the state of other sub-modules. ...
Introduction to First-Principles Method
... functions at k points that are very close together will be almost identical, hence it is possible to represent the electronic wave functions over a region of k space by the wave functions at a single k point. ...
... functions at k points that are very close together will be almost identical, hence it is possible to represent the electronic wave functions over a region of k space by the wave functions at a single k point. ...
4-Space Dirac Theory and LENR A. B. Evans Research Article ∗
... preferred frame of reference. In these models, the space-time coordinates X λ = (x k , ct) are all on an equal footing, i.e. both spatial position and time are regarded as observables. An invariant parameter (called τ below), corresponding to the proper time of classical relativity, is used instead ...
... preferred frame of reference. In these models, the space-time coordinates X λ = (x k , ct) are all on an equal footing, i.e. both spatial position and time are regarded as observables. An invariant parameter (called τ below), corresponding to the proper time of classical relativity, is used instead ...
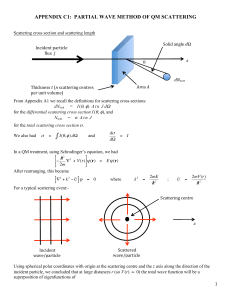
APPENDIX C1: PARTIAL WAVE METHOD OF QM SCATTERING
... because we now have identical particles, so the Pauli Exclusion Principle has to be taken into account when including the effects of spin. Also, in the case of p-p scattering there is the (repulsive) Coulomb repulsion in addition to the (attractive) potential well at small separations. At lower ener ...
... because we now have identical particles, so the Pauli Exclusion Principle has to be taken into account when including the effects of spin. Also, in the case of p-p scattering there is the (repulsive) Coulomb repulsion in addition to the (attractive) potential well at small separations. At lower ener ...
Symmetry in Electron-Atom Collisions and Photoionization Process
... that escapes the reaction zone as a result of photoionization did not really exist as a free electron in the initial state. It was an integral part of the neutral atom in the ‘nucleus + electron(s)’ bound system. Following the description in Reference [4,5] which is both the inspiration and the prim ...
... that escapes the reaction zone as a result of photoionization did not really exist as a free electron in the initial state. It was an integral part of the neutral atom in the ‘nucleus + electron(s)’ bound system. Following the description in Reference [4,5] which is both the inspiration and the prim ...
Kang_3
... What are the momentum distributions of quarks, antiquarks, and gluons? How are quarks and gluons distributed spatially? How do partons carry the proton spin-1/2? (spin and orbital angular momentum) How are these quark and gluon distributions correlated with overall nucleon properties, such as spin d ...
... What are the momentum distributions of quarks, antiquarks, and gluons? How are quarks and gluons distributed spatially? How do partons carry the proton spin-1/2? (spin and orbital angular momentum) How are these quark and gluon distributions correlated with overall nucleon properties, such as spin d ...
2010 Pacing Pacing Guide - High School Science Help
... Work is the mechanical transfer of energy to or from a system and is the product of a force at the point of application and the parallel component of the object’s displacement. The net work on a system equals its PH.6a The concepts developed in this standard include the following: Kinetic energy ...
... Work is the mechanical transfer of energy to or from a system and is the product of a force at the point of application and the parallel component of the object’s displacement. The net work on a system equals its PH.6a The concepts developed in this standard include the following: Kinetic energy ...
Physphax Review
... 25. Projectile fired at angle with initial speed vi: Symmetry as in straight-up case. See diagram 4. Velocity is tangent to path. Fx and ax = 0. Fnet = Fg = weight downward, so a is also. Still free fall. Horiz. comp.: vix=vicos stays same. Use TOTAL time to find range: dx = vix x ttotal Vert. c ...
... 25. Projectile fired at angle with initial speed vi: Symmetry as in straight-up case. See diagram 4. Velocity is tangent to path. Fx and ax = 0. Fnet = Fg = weight downward, so a is also. Still free fall. Horiz. comp.: vix=vicos stays same. Use TOTAL time to find range: dx = vix x ttotal Vert. c ...
New features of ion acoustic waves in inhomogeneous and
... a simultaneous presence of density gradient. A typical environment for this mechanism to work are solar magnetic structures where a density gradient should be ubiquitous in the direction perpendicular to the magnetic field. However, it should be stressed that the magnetic field plays no role in this ...
... a simultaneous presence of density gradient. A typical environment for this mechanism to work are solar magnetic structures where a density gradient should be ubiquitous in the direction perpendicular to the magnetic field. However, it should be stressed that the magnetic field plays no role in this ...
propagation of electromagnetic waves inside a
... One very interesting and, at the same time, very significant generalization of the above expression can be realized: ...
... One very interesting and, at the same time, very significant generalization of the above expression can be realized: ...
Factors Affecting Surface Wave Propagation Janice
... ground a potentially bound surface wave can exist. The higher the surface reactance, Xs the more tightly bound the surface wave is to the interface and the more of the field that is distributed within the surface wave region. The surface wave region can be defined as the region in which the surface ...
... ground a potentially bound surface wave can exist. The higher the surface reactance, Xs the more tightly bound the surface wave is to the interface and the more of the field that is distributed within the surface wave region. The surface wave region can be defined as the region in which the surface ...
6.Utilization of photon equation of motion to
... Light and electromagnetic waves, (E.M.W) play an important role in our daily life [1]. Light is the oldest known form of( E.M.W) Theories about the nature of light can be traced from the writing of ancient authors like Newton, who proposed that light behaves like the smallest of tiny particles. Its ...
... Light and electromagnetic waves, (E.M.W) play an important role in our daily life [1]. Light is the oldest known form of( E.M.W) Theories about the nature of light can be traced from the writing of ancient authors like Newton, who proposed that light behaves like the smallest of tiny particles. Its ...
Problems for the course FYS4130
... (i) s = R 1 + (u/u0 ) (v/v0 ) (ii) s = N0−1 R(uv/u0 v0 )2 (iv) s = N0−1 R(uv/u0 v0 )1/3 where u0 = E0 /N0 , v0 = V0 /N0 . These relations do not contradict general principles. ...
... (i) s = R 1 + (u/u0 ) (v/v0 ) (ii) s = N0−1 R(uv/u0 v0 )2 (iv) s = N0−1 R(uv/u0 v0 )1/3 where u0 = E0 /N0 , v0 = V0 /N0 . These relations do not contradict general principles. ...
Wave packet
.gif?width=300)
In physics, a wave packet (or wave train) is a short ""burst"" or ""envelope"" of localized wave action that travels as a unit. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, an infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere constructively only over a small region of space, and destructively elsewhere. Each component wave function, and hence the wave packet, are solutions of a wave equation. Depending on the wave equation, the wave packet's profile may remain constant (no dispersion, see figure) or it may change (dispersion) while propagating.Quantum mechanics ascribes a special significance to the wave packet; it is interpreted as a probability amplitude, its norm squared describing the probability density that a particle or particles in a particular state will be measured to have a given position or momentum. The wave equation is in this case the Schrödinger equation. It is possible to deduce the time evolution of a quantum mechanical system, similar to the process of the Hamiltonian formalism in classical mechanics. The dispersive character of solutions of the Schrödinger equation has played an important role in rejecting Schrödinger's original interpretation, and accepting the Born rule.In the coordinate representation of the wave (such as the Cartesian coordinate system), the position of the physical object's localized probability is specified by the position of the packet solution. Moreover, the narrower the spatial wave packet, and therefore the better localized the position of the wave packet, the larger the spread in the momentum of the wave. This trade-off between spread in position and spread in momentum is a characteristic feature of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle,and will be illustrated below.