Habitat Fragmentation
... Other Impacts • Fragmentation eliminates habitat for those species requiring large unbroken blocks of habitat (e.g., bobcats and grizzly bears, deer). • Additionally, the small habitat patches resulting from fragmentation often do not provide the food and cover resources for many species that do at ...
... Other Impacts • Fragmentation eliminates habitat for those species requiring large unbroken blocks of habitat (e.g., bobcats and grizzly bears, deer). • Additionally, the small habitat patches resulting from fragmentation often do not provide the food and cover resources for many species that do at ...
Extinction and Conservation
... ultimate extinction of the population (for very small fragments), or simply inhibit their ability to evolve in response to changing conditions ...
... ultimate extinction of the population (for very small fragments), or simply inhibit their ability to evolve in response to changing conditions ...
0 Science 10 - Chapter 1.2 Notes
... Photosynthesis (pg. 37) A chemical reaction converts solar energy into chemical energy used by plants (requires light) Soil (pg. 38) Is important because it 1) provides nutrients for plants and 2) supports many species of small organisms (some of these organisms (ex. bacteria) break down pollutants ...
... Photosynthesis (pg. 37) A chemical reaction converts solar energy into chemical energy used by plants (requires light) Soil (pg. 38) Is important because it 1) provides nutrients for plants and 2) supports many species of small organisms (some of these organisms (ex. bacteria) break down pollutants ...
3 - School-Portal.co.uk
... At a local level threats are likely to be associated with development and exploitation of resources (perhaps directly, or indirectly e.g. oil), possibly pollution. Tourism is a possibility, in terms of coral or forest destruction, plus urbanisation and other economic development. Expect marine or te ...
... At a local level threats are likely to be associated with development and exploitation of resources (perhaps directly, or indirectly e.g. oil), possibly pollution. Tourism is a possibility, in terms of coral or forest destruction, plus urbanisation and other economic development. Expect marine or te ...
Systems
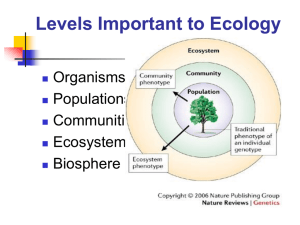
... These are large regions with a distinct climate and specific life forms. E.g. Desert, grassland. Each biome may have many ecosystems with communities adapted to the changes in soil, climate and other factors throughout the biome. The marine and freshwater portions of the biosphere are divided into a ...
... These are large regions with a distinct climate and specific life forms. E.g. Desert, grassland. Each biome may have many ecosystems with communities adapted to the changes in soil, climate and other factors throughout the biome. The marine and freshwater portions of the biosphere are divided into a ...
Ch 4 Ecosystems and Communites
... Predators can affect the size of prey populations in a community and determine the places prey can live and feed. ...
... Predators can affect the size of prey populations in a community and determine the places prey can live and feed. ...
4.2_Niches_and_Community
... Predators can affect the size of prey populations in a community and determine the places prey can live and feed. ...
... Predators can affect the size of prey populations in a community and determine the places prey can live and feed. ...
Ecosystems
... Greek word oikos, for “house,” eco-is the combining form meaning “environment or habitat.” ...
... Greek word oikos, for “house,” eco-is the combining form meaning “environment or habitat.” ...
Center for Community-Based Resource Management (CBRM) CBRM Database
... variance; Multivariate regression trees; Reef fish assemblage; North-western Mediterranean Marine protected areas (MPAs) are increasingly envisaged as a tool to manage coastal ecosystems and fisheries. Assessment of their performance with respect to management objectives is therefore important. A nu ...
... variance; Multivariate regression trees; Reef fish assemblage; North-western Mediterranean Marine protected areas (MPAs) are increasingly envisaged as a tool to manage coastal ecosystems and fisheries. Assessment of their performance with respect to management objectives is therefore important. A nu ...
COMMUNITY AND POPULATION ECOLOGY
... Two or more individuals scrambling or fighting for the same resource. Can be within the same species or between species. ...
... Two or more individuals scrambling or fighting for the same resource. Can be within the same species or between species. ...
biodiversity - Association of American Geographers
... All species, as well as all individuals within a species, have a finite life span. Radical changes to the habitat of a species over short periods of time, and subtler changes occurring steadily over longer periods, will cause that species to become either extinct or exotic. Both conditions are assoc ...
... All species, as well as all individuals within a species, have a finite life span. Radical changes to the habitat of a species over short periods of time, and subtler changes occurring steadily over longer periods, will cause that species to become either extinct or exotic. Both conditions are assoc ...
Species of the Day: Amami Rabbit
... Owing to widespread habitat degradation brought about by logging and development, the Amami Rabbit population has undergone a significant decline, with only four fragmented subpopulations remaining. Since 1980, the amount of old growth forest on the islands of Amami and Tokuno has declined by an ala ...
... Owing to widespread habitat degradation brought about by logging and development, the Amami Rabbit population has undergone a significant decline, with only four fragmented subpopulations remaining. Since 1980, the amount of old growth forest on the islands of Amami and Tokuno has declined by an ala ...
Name: Date - mrsholmeshaw
... 8. In the area where the students were digging out invasive plants, what was on that land originally, before it was a dump? ___________________ 9. The largest ecosystem (place where plants and animals live) in the world is the _____________ where 2/3 of all species live. 10. Name 5 things you can d ...
... 8. In the area where the students were digging out invasive plants, what was on that land originally, before it was a dump? ___________________ 9. The largest ecosystem (place where plants and animals live) in the world is the _____________ where 2/3 of all species live. 10. Name 5 things you can d ...
CHAPTER 4.2 EXAM REVIEW: 1. Give examples of both biotic and
... 10. A symbiotic relationship between a flower and the insect that feeds on its nectar is an example of what? Mutualism 11. How could a predator INCREASE the numbers of a certain species in a habitat? Killing and eating the competitors of other species 12. Define ecological succession The series of p ...
... 10. A symbiotic relationship between a flower and the insect that feeds on its nectar is an example of what? Mutualism 11. How could a predator INCREASE the numbers of a certain species in a habitat? Killing and eating the competitors of other species 12. Define ecological succession The series of p ...
ECOSYSTEMS ARE ALWAYS CHANGNING
... & left a barren area) • Pioneer Species: the first living things to move into a barren environment (moss & lichen are common when no topsoil is available- have tiny rootlike anchors) • As pioneers grow, they weaken rock, it breaks down & mixes with decaying plant matter to form soil. Now, new plants ...
... & left a barren area) • Pioneer Species: the first living things to move into a barren environment (moss & lichen are common when no topsoil is available- have tiny rootlike anchors) • As pioneers grow, they weaken rock, it breaks down & mixes with decaying plant matter to form soil. Now, new plants ...
Biomes Ice Tundra Taiga (Boreal Forest)
... Ecology of Ecosystems Biomes are large-scale, regional ecosystems ...
... Ecology of Ecosystems Biomes are large-scale, regional ecosystems ...
PowerPoint 7435KB
... 6-A-2: Identify high-risk species and ecosystems; work toward predicting changes in habitat types and extent. 6-A-3: Identify practices to enhance resilience 6-A-4: Identify priority conservation areas and corridors. 6-A-5: Avoid adverse effects on biodiversity from human responses to climate change ...
... 6-A-2: Identify high-risk species and ecosystems; work toward predicting changes in habitat types and extent. 6-A-3: Identify practices to enhance resilience 6-A-4: Identify priority conservation areas and corridors. 6-A-5: Avoid adverse effects on biodiversity from human responses to climate change ...
Topic 6 Succession and Change in Ecosystems
... an ecosystem) and some changes can be slow (IE: seeds being carried by the wind to a vacant lot introducing a new plant population) This gradual process by which some species replace other species in an ecosystem is called succession Two types of succession: 1. Primary Succession The gradual gro ...
... an ecosystem) and some changes can be slow (IE: seeds being carried by the wind to a vacant lot introducing a new plant population) This gradual process by which some species replace other species in an ecosystem is called succession Two types of succession: 1. Primary Succession The gradual gro ...
Appendix A: Pre/Post Test
... D. selective cutting. 2. The largest population that an environment can support is called its A. carrying capacity. B. limiting factor. C. birth rate. D. death rate. 3. A close relationship between two species that benefits at least one of the species is called A. natural selection. B. symbiosis. C. ...
... D. selective cutting. 2. The largest population that an environment can support is called its A. carrying capacity. B. limiting factor. C. birth rate. D. death rate. 3. A close relationship between two species that benefits at least one of the species is called A. natural selection. B. symbiosis. C. ...
Forest aims to cultivate kids` interest in nature
... third phases should remain on schedule with the third section completed in 2016. "It took longer than we thought … but another year or two, we're hoping to have the rest of it done," Idol said. The project would benefit the zoo's annual 750,000 visitors, teaching them about the importance of sustain ...
... third phases should remain on schedule with the third section completed in 2016. "It took longer than we thought … but another year or two, we're hoping to have the rest of it done," Idol said. The project would benefit the zoo's annual 750,000 visitors, teaching them about the importance of sustain ...
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project

The Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project, originally called the Minimum Critical Size of Ecosystems Project is a large-scale ecological experiment looking at the effects of habitat fragmentation on tropical rainforest; it is one of the most expensive biology experiments ever run. The experiment, which was established in 1979 is located near Manaus, in the Brazilian Amazon. The project is jointly managed by the Smithsonian Institution and INPA, the Brazilian Institute for Research in the Amazon.The project was initiated in 1979 by Thomas Lovejoy to investigate the SLOSS debate. Initially named the Minimum Critical Size of Ecosystems Project, the project created forest fragments of sizes 1 hectare (2 acres), 10 hectares (25 acres), and 100 hectares (247 acres). Data were collected prior to the creation of the fragments and studies of the effects of fragmentation now exceed 25 years.As of October 2010 562 publications and 143 graduate dissertations and theses had emerged from the project.