Physics Ch. 7 Rotational Motion
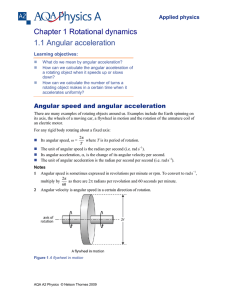
... speed, it still has an acceleration. Remember that acceleration can be produced by a change in magnitude or a change in direction. For an object traveling at a constant speed in a circular path, the acceleration is due to a change in direction, centripetal acceleration (center seeking). ...
... speed, it still has an acceleration. Remember that acceleration can be produced by a change in magnitude or a change in direction. For an object traveling at a constant speed in a circular path, the acceleration is due to a change in direction, centripetal acceleration (center seeking). ...
Rotational Motion
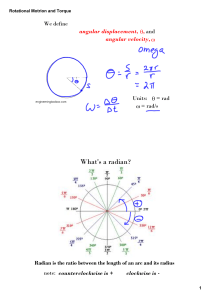
... For the motion of particles which are not a rigid body, the torque is defined about a point. If r is the vector from that chosen point to the point of application of a force F, the torque is defined as τ = r × F. Applying this definition to our rigid body rotation, if the chosen point is taken anywh ...
... For the motion of particles which are not a rigid body, the torque is defined about a point. If r is the vector from that chosen point to the point of application of a force F, the torque is defined as τ = r × F. Applying this definition to our rigid body rotation, if the chosen point is taken anywh ...
mv2 player plus
... The Swinging Door: (a) A man applies a force of F=3.00 × 102 N at an angle of 60.0° to the door of Figure 8.7a, 2.00 m from the hinges. Find the torque on the door, choosing the posi: ...
... The Swinging Door: (a) A man applies a force of F=3.00 × 102 N at an angle of 60.0° to the door of Figure 8.7a, 2.00 m from the hinges. Find the torque on the door, choosing the posi: ...
Use example problem 9-3 to solve practice problems 9-3
... Suppose you place several sugar cubes in a box and close it. We can call the box and the sugar in it a system, a defined collection of objects. Shake the box hard for several minutes. When you open it, you find that the shapes of the cubes have changed. In addition, there are sugar grains in the box ...
... Suppose you place several sugar cubes in a box and close it. We can call the box and the sugar in it a system, a defined collection of objects. Shake the box hard for several minutes. When you open it, you find that the shapes of the cubes have changed. In addition, there are sugar grains in the box ...
Lecture6
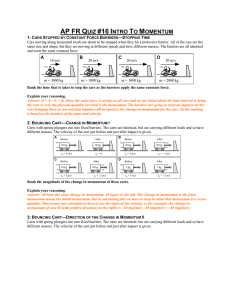
... m2 moving with known initial velocities v1i and v2i along a straight line. • They collide head-on and after the collision, they stick together and move with a common velocity vf. ...
... m2 moving with known initial velocities v1i and v2i along a straight line. • They collide head-on and after the collision, they stick together and move with a common velocity vf. ...
Parallel axis theorem
... In classical mechanics, the Parallel axis theorem can be generalized to calculate a new inertia tensor Jij from an inertia tensor about a center of mass Iij when the pivot point is a displacement a from the center of mass: Jij = Iij + M(a2δij − aiaj) Where a is the displacement vector from the cente ...
... In classical mechanics, the Parallel axis theorem can be generalized to calculate a new inertia tensor Jij from an inertia tensor about a center of mass Iij when the pivot point is a displacement a from the center of mass: Jij = Iij + M(a2δij − aiaj) Where a is the displacement vector from the cente ...
momentum
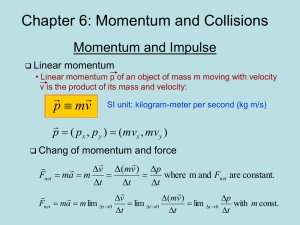
... The amount of momentum which an object has is dependent upon two variables: how much stuff is moving and how fast the stuff is moving. In other words: The size of the momentum is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the size of the object's velocity. ...
... The amount of momentum which an object has is dependent upon two variables: how much stuff is moving and how fast the stuff is moving. In other words: The size of the momentum is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the size of the object's velocity. ...
am-ii_unit-v-3
... If they are both released from rest at the top of the hill, which will reach the bottom the fastest? a) A will reach the bottom first b) B will reach the bottom first c) They will reach the bottom at the same time ...
... If they are both released from rest at the top of the hill, which will reach the bottom the fastest? a) A will reach the bottom first b) B will reach the bottom first c) They will reach the bottom at the same time ...
Ch12 Motion Notes and Practice problems with explanations
... The conservation of momentum only applies to systems that have no external forces acting upon them. We call such a system a closed or isolated system: objects within the system may exert forces on other objects within the system (e.g., the cue ball can exert a force on the eight ball and vice versa) ...
... The conservation of momentum only applies to systems that have no external forces acting upon them. We call such a system a closed or isolated system: objects within the system may exert forces on other objects within the system (e.g., the cue ball can exert a force on the eight ball and vice versa) ...
PSE4_Lecture_Ch10 - Rotational Motion
... angular acceleration have the same form as those for linear motion with constant acceleration. • Torque is the product of force and lever arm. • The rotational inertia depends not only on the mass of an object but also on the way its mass is distributed around the axis of rotation. • The angular acc ...
... angular acceleration have the same form as those for linear motion with constant acceleration. • Torque is the product of force and lever arm. • The rotational inertia depends not only on the mass of an object but also on the way its mass is distributed around the axis of rotation. • The angular acc ...