Name Pd ____ Date Physics Unit 6: Rotational Inertia Math Problems
... 12. For the same mass and radius you would expect a solid sphere to have a smaller / larger rotational inertia than a hollow sphere. 13. For a hollow sphere and solid sphere made of the same material and with the same radius you would expect the hollow / solid sphere to have the larger rotational in ...
... 12. For the same mass and radius you would expect a solid sphere to have a smaller / larger rotational inertia than a hollow sphere. 13. For a hollow sphere and solid sphere made of the same material and with the same radius you would expect the hollow / solid sphere to have the larger rotational in ...
3. rotational motion - Mahesh Tutorials Science
... Moment of Inertia of a discreet particle system : Keep in mind that here the quantity r is the perpendicular distance to an axis, not the distance to an origin. To evaluate this integral, we must express m in terms of r. ...
... Moment of Inertia of a discreet particle system : Keep in mind that here the quantity r is the perpendicular distance to an axis, not the distance to an origin. To evaluate this integral, we must express m in terms of r. ...
Coriolis force, geometric phase, and spin
... reciprocal momentum space9. The associated covariant gauge field enters the equation of motion for the group velocity of a wave-packet and may affect the coherent transport properties of holes in valence subbands10 11 12. In this paper, we extend the results of these studies to the lowest conduction ...
... reciprocal momentum space9. The associated covariant gauge field enters the equation of motion for the group velocity of a wave-packet and may affect the coherent transport properties of holes in valence subbands10 11 12. In this paper, we extend the results of these studies to the lowest conduction ...
Momentum
... • A new fundamental quantity, like force, energy • The linear momentum p of an object of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined to be the product of the mass and velocity: ...
... • A new fundamental quantity, like force, energy • The linear momentum p of an object of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined to be the product of the mass and velocity: ...
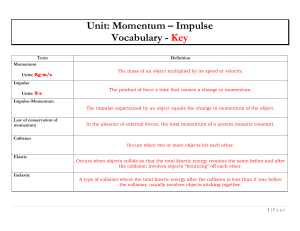
Momentum and Impulse
... Change In Momentum The change in momentum is the difference in momentum from when the object is moving at its initial speed until it reaches its final speed. The unit of change in momentum is kg ms-1. ...
... Change In Momentum The change in momentum is the difference in momentum from when the object is moving at its initial speed until it reaches its final speed. The unit of change in momentum is kg ms-1. ...
11. Kinematics of Angular Motion
... system fixed with respect to the moving object while for some other problems it was useful to have a coordinate system fixed with respect to the laboratory or the Earth. For angular motion, it is useful to have a coordinate system that is moving along with the object in angular motion. By convention ...
... system fixed with respect to the moving object while for some other problems it was useful to have a coordinate system fixed with respect to the laboratory or the Earth. For angular motion, it is useful to have a coordinate system that is moving along with the object in angular motion. By convention ...
Collision of a ball with a barbell and related impulse problems
... Secondly, the system’s angular momentum is conserved. In fact, an even stronger statement can be made by choosing to compute the angular momentum about the z-axis passing through the origin O rather than about the system’s CM [2]. In that case, the collisional impulses on the ball and barbell have z ...
... Secondly, the system’s angular momentum is conserved. In fact, an even stronger statement can be made by choosing to compute the angular momentum about the z-axis passing through the origin O rather than about the system’s CM [2]. In that case, the collisional impulses on the ball and barbell have z ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... – Include a coordinate axis and select the positive direction to be the direction of the velocity of the car. – Draw a vector diagram for momentum and impulse. ...
... – Include a coordinate axis and select the positive direction to be the direction of the velocity of the car. – Draw a vector diagram for momentum and impulse. ...
chapter09
... forces acting on the particles of the system. The forces are not specified as conservative or non-conservative. There is no indication if the forces are constant or not. The only requirement is that the forces must be internal to the system. This gives a hint about the power of this new model. ...
... forces acting on the particles of the system. The forces are not specified as conservative or non-conservative. There is no indication if the forces are constant or not. The only requirement is that the forces must be internal to the system. This gives a hint about the power of this new model. ...
Momentum and Collision
... Because the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant, the total initial momentum of the boater and the boat will be equal to the total final momentum of the boater and the boat. m1v1,i + m2v2,i = m1v1,f + m2v2,f ...
... Because the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant, the total initial momentum of the boater and the boat will be equal to the total final momentum of the boater and the boat. m1v1,i + m2v2,i = m1v1,f + m2v2,f ...
ClassicalMechanics_4..
... Energy in Rotation To get something moving, you do work on it, the result being kinetic energy. To get objects spinning also takes work, but what is the rotational equivalent of kinetic energy? Problem: in a rotating object, each bit of mass has the same angular speed , but different linear speed ...
... Energy in Rotation To get something moving, you do work on it, the result being kinetic energy. To get objects spinning also takes work, but what is the rotational equivalent of kinetic energy? Problem: in a rotating object, each bit of mass has the same angular speed , but different linear speed ...
Chapter 10 Momentum, System of Particles, and Conservation
... 10.2.1 Average Force, Momentum, and Impulse ................................................... 2 10.2.2 Non-Constant Force and Impulse................................................................. 2 Example 10.1 Impulse for a Non-Constant Force ........................................... ...
... 10.2.1 Average Force, Momentum, and Impulse ................................................... 2 10.2.2 Non-Constant Force and Impulse................................................................. 2 Example 10.1 Impulse for a Non-Constant Force ........................................... ...