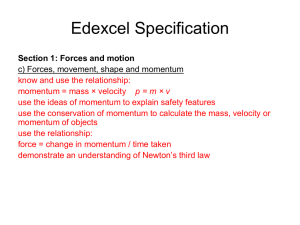
Impulse Momentum Wksheet
... small car. In physics terms, we say that the truck has greater momentum. We can find momentum using this equation: momentum = mass of object u velocity of object Velocity is a term that refers to both speed and direction. For our purposes we will assume that the vehicles are traveling in a straight ...
... small car. In physics terms, we say that the truck has greater momentum. We can find momentum using this equation: momentum = mass of object u velocity of object Velocity is a term that refers to both speed and direction. For our purposes we will assume that the vehicles are traveling in a straight ...
Ch11 - Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
... Answer: The maximum height reached by B is less than that reached by A. For A, all the kinetic energy becomes potential energy at h. Since the ramp is frictionless for B, all of the rotational K stays rotational, and only the translational kinetic energy becomes potential energy at its maximum ...
... Answer: The maximum height reached by B is less than that reached by A. For A, all the kinetic energy becomes potential energy at h. Since the ramp is frictionless for B, all of the rotational K stays rotational, and only the translational kinetic energy becomes potential energy at its maximum ...
IGCSE-14-Momentum
... total initial momentum = -12000 kg m/s Momentum is conserved in the collision so total momentum after collision = -12000 kg m/s total momentum = total mass x velocity -12000 kg m/s = 3000 kg x v -12000 ÷ 3000 = v common velocity = - 4 m/s The lorry/car combination will move in the original direction ...
... total initial momentum = -12000 kg m/s Momentum is conserved in the collision so total momentum after collision = -12000 kg m/s total momentum = total mass x velocity -12000 kg m/s = 3000 kg x v -12000 ÷ 3000 = v common velocity = - 4 m/s The lorry/car combination will move in the original direction ...
Drop Tower Physics
... drop including braking from magnetic damping or collision with an air bag system. ...
... drop including braking from magnetic damping or collision with an air bag system. ...
Chapters 1–5 Schedule of Crisis Centre
... • Elastic collision: the total kinetic energy after collision is equal ! to the total before collision. • Inelastic collision: the total kinetic energy is not conserved. If ! objects stick together after collision, the collision is “perfectly ! inelastic” – no bounce of one object from the other. Ex ...
... • Elastic collision: the total kinetic energy after collision is equal ! to the total before collision. • Inelastic collision: the total kinetic energy is not conserved. If ! objects stick together after collision, the collision is “perfectly ! inelastic” – no bounce of one object from the other. Ex ...
408 4 Biomechanics for the Speed and Power Events
... Directionality. In everyday speech, we may exchange the phrases displacement and distance traveled, and they are similar concepts. With displacement, a direction in which movement will be measured must be specified, or at least implied by context. For example, a body that moves directly north 20 mil ...
... Directionality. In everyday speech, we may exchange the phrases displacement and distance traveled, and they are similar concepts. With displacement, a direction in which movement will be measured must be specified, or at least implied by context. For example, a body that moves directly north 20 mil ...
Chapter 21 Rigid Body Dynamics: Rotation and Translation
... can be neglected (Figure 21.8). The Yo-Yo is released from rest. You will need to assume that the center of mass of the Yo-Yo descends vertically, and that the string is vertical as it unwinds. (a) What is the tension in the cord as the Yo-Yo descends? (b) What is the magnitude of the angular accele ...
... can be neglected (Figure 21.8). The Yo-Yo is released from rest. You will need to assume that the center of mass of the Yo-Yo descends vertically, and that the string is vertical as it unwinds. (a) What is the tension in the cord as the Yo-Yo descends? (b) What is the magnitude of the angular accele ...
5 The Physics of Rotating Bodies
... until the hanging mass would fall if only 1-2 g more were added. What is the relation between the hanging weight, the weight of the moving pulley and the tension in the string? Next, add about 200 g to the hanging mass so that it falls down, raising the moving pulley in the process. ...
... until the hanging mass would fall if only 1-2 g more were added. What is the relation between the hanging weight, the weight of the moving pulley and the tension in the string? Next, add about 200 g to the hanging mass so that it falls down, raising the moving pulley in the process. ...
Chapter 5 Rotational Motion File
... • Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction • When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular acceleration – The tangential (linear) speed ...
... • Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction • When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular acceleration – The tangential (linear) speed ...
Chapter 6: Momentum
... Twice as great force if you do it in 1s than if you do it in 2s, because change in momentum = impulse = FDt. (so half Dt means twice F) c) In a general situation, when does impulse equal momentum? If the object’s initial momentum is zero, then ...
... Twice as great force if you do it in 1s than if you do it in 2s, because change in momentum = impulse = FDt. (so half Dt means twice F) c) In a general situation, when does impulse equal momentum? If the object’s initial momentum is zero, then ...
Chapter 8: Rotational Motion
... A ladybug sits halfway between the rotational axis and the outer edge of the turntable. When the turntable has a rotational speed of 20 RPM and the bug has a tangential speed of 2 cm/s, what will be the rotational and tangential speeds of her friend who sits at the outer edge? A. ...
... A ladybug sits halfway between the rotational axis and the outer edge of the turntable. When the turntable has a rotational speed of 20 RPM and the bug has a tangential speed of 2 cm/s, what will be the rotational and tangential speeds of her friend who sits at the outer edge? A. ...
Rotational Motion
... the resulting acceleration, and the proportionality constant r ris the mass. Newton’s second law can also be expressed for objects undergoing angular motion - in this case, " = I# . The applied torque generates an angular acceleration, and the two quantities are linearly proportional with a proporti ...
... the resulting acceleration, and the proportionality constant r ris the mass. Newton’s second law can also be expressed for objects undergoing angular motion - in this case, " = I# . The applied torque generates an angular acceleration, and the two quantities are linearly proportional with a proporti ...
Rotational Dynamics and the Flow of Angular Momentum
... must be connected via a friction coupling. To this end, a short piece of garden hose can be afixed to one flywheel concentric to its axis and a bottle cork (which can be inserted into the hose) to the other flywheel (Figure la). For one experiment (Section II.11), the flywheels must be connected via ...
... must be connected via a friction coupling. To this end, a short piece of garden hose can be afixed to one flywheel concentric to its axis and a bottle cork (which can be inserted into the hose) to the other flywheel (Figure la). For one experiment (Section II.11), the flywheels must be connected via ...