title of video - Discovery Education
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
psy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the undergraduate level. The materials are from different sources including the internet and the contributors do not in any way claim authorship or ownership of them. The materials are also not to be used for any commerc ...
... The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the undergraduate level. The materials are from different sources including the internet and the contributors do not in any way claim authorship or ownership of them. The materials are also not to be used for any commerc ...
myers Chapter 02 review game
... 20. Curare is a poison people use to paralyze animals when hunting. It is therefore an ____ which inhibits the ...
... 20. Curare is a poison people use to paralyze animals when hunting. It is therefore an ____ which inhibits the ...
Chapter 8
... What kind of experiences do young children need to learn? What kind of activities ate best to involve children in? Mabel and Ian wanted their daughter Brianna to learn to read early so they began using flash cards with her when she was two years old. They found that Brianna's skills developed about ...
... What kind of experiences do young children need to learn? What kind of activities ate best to involve children in? Mabel and Ian wanted their daughter Brianna to learn to read early so they began using flash cards with her when she was two years old. They found that Brianna's skills developed about ...
The Brain** in Brain Computer Interface - CBMSPC
... Neurological Injury • Injury to the nervous system often causes irreversible damage – results in disability, sometimes devastating – occasionally results in very bizarre symptoms ...
... Neurological Injury • Injury to the nervous system often causes irreversible damage – results in disability, sometimes devastating – occasionally results in very bizarre symptoms ...
File
... information (except smell) goes here first 2. The Hypothalamus- monitors the internal systems to maintain the normal state of the body (homeostasis) by controlling the release of hormones it can moderate body functions (sleep, food intake, and liquid intake) WARNING- if out of balance difficult to c ...
... information (except smell) goes here first 2. The Hypothalamus- monitors the internal systems to maintain the normal state of the body (homeostasis) by controlling the release of hormones it can moderate body functions (sleep, food intake, and liquid intake) WARNING- if out of balance difficult to c ...
Nervous System
... It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. ...
... It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. ...
1244509Health Nervous System 2012
... 2% soluble organics, 1% inorganic salt. The brain can stay alive for 4 to 6 minutes without oxygen. After that cells begin die. The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph!!! ...
... 2% soluble organics, 1% inorganic salt. The brain can stay alive for 4 to 6 minutes without oxygen. After that cells begin die. The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph!!! ...
Secrets of the Teen Brain
... and mental activities maybe responsive to experience. • Development of brain generally proceeds from back to front. • 1st sensory functions, 2nd coordination of those sensory functions, 3rd prefrontal cortex. ...
... and mental activities maybe responsive to experience. • Development of brain generally proceeds from back to front. • 1st sensory functions, 2nd coordination of those sensory functions, 3rd prefrontal cortex. ...
Human Body Systems - Whitehall District Schools
... • Electrical impulse due to a chemical change along the membrane of a neuron • Resting Potential: electrical potential of the neural membrane (70mV), created by Na/K pump, creates charge difference • Threshold: Minimum level of stimulus to activate a neuron, a neuron is an all or nothing response • ...
... • Electrical impulse due to a chemical change along the membrane of a neuron • Resting Potential: electrical potential of the neural membrane (70mV), created by Na/K pump, creates charge difference • Threshold: Minimum level of stimulus to activate a neuron, a neuron is an all or nothing response • ...
The Emerging Nervous System
... Neurons • Neural Plate: A group of cells that form a flat structure three weeks after conception • At four weeks the neural plate folds to form a tube that than becomes the brain and spinal cord • Neurons begin to produce ten weeks after conception ...
... Neurons • Neural Plate: A group of cells that form a flat structure three weeks after conception • At four weeks the neural plate folds to form a tube that than becomes the brain and spinal cord • Neurons begin to produce ten weeks after conception ...
The Nervous System
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
TOC - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20005, phone 202-962-4000. Instructions for Authors are available at http://www.jneurosci.org/misc/itoa.shtml. Auth ...
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20005, phone 202-962-4000. Instructions for Authors are available at http://www.jneurosci.org/misc/itoa.shtml. Auth ...
The Journal of Neuroscience Journal Club SYMPOSIUM
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20005, phone 202-962-4000. Instructions for Authors are available at http://www.jneurosci.org/misc/itoa.shtml. Auth ...
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20005, phone 202-962-4000. Instructions for Authors are available at http://www.jneurosci.org/misc/itoa.shtml. Auth ...
Study Guide
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
Temprana Reflex Therapy Info
... Temprana Reflex therapy is a Brain-Based concept Temprana Reflex Therapy is brain-based concept based in the latest in specific analyzing and treatment. Temprana Reflex Therapy can increase the body's ability to heal itself by specifically analyzing and reversing neurological impairment. Treatments ...
... Temprana Reflex therapy is a Brain-Based concept Temprana Reflex Therapy is brain-based concept based in the latest in specific analyzing and treatment. Temprana Reflex Therapy can increase the body's ability to heal itself by specifically analyzing and reversing neurological impairment. Treatments ...
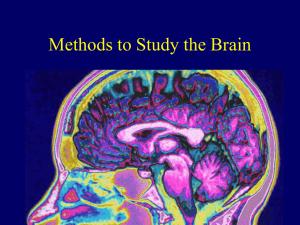
Module 11: Methods to Study the Brain
... • Reveal the activity of different areas • Shows consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
... • Reveal the activity of different areas • Shows consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
Module 11: Methods to Study the Brain
... • Reveal the activity of different areas • Shows consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
... • Reveal the activity of different areas • Shows consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
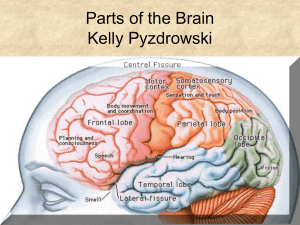
The Structures of the Brain
... Carries motor impulses from the brain to internal organs and muscles Carries sensory information from extremities and internal organs to the brain 400,000 people a year in US either partial or complete ...
... Carries motor impulses from the brain to internal organs and muscles Carries sensory information from extremities and internal organs to the brain 400,000 people a year in US either partial or complete ...
What” and ”where” – dynamic parallel processing of sound
... • Paralysis due to stroke may prevent early participation in a rehabilitation program • Similar network of cerebral structures (e.g., premotor cortex) is activated when normal control subjects execute physically or imagine a sequence of up-down foot movements mental practice with motor imagery can ...
... • Paralysis due to stroke may prevent early participation in a rehabilitation program • Similar network of cerebral structures (e.g., premotor cortex) is activated when normal control subjects execute physically or imagine a sequence of up-down foot movements mental practice with motor imagery can ...
X Period- Review for Brain test
... Upper brain- controls all human functions, example—thinking, personality ...
... Upper brain- controls all human functions, example—thinking, personality ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.