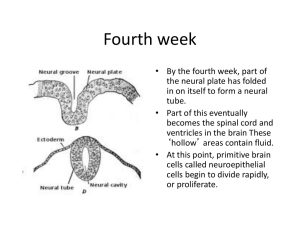
Fourth week
... • During the last phase of development, the earlier processes of cell proliferation and migration continue to some degree, and synapses continue to form all over the brain. • But two new processes begin in earnest: a pruning of unnecessary cells and connections - an active process, known as apoptosi ...
... • During the last phase of development, the earlier processes of cell proliferation and migration continue to some degree, and synapses continue to form all over the brain. • But two new processes begin in earnest: a pruning of unnecessary cells and connections - an active process, known as apoptosi ...
Brain Waves Parent Resource
... Adaptation is experienced when a stimulus is present for a long time. For example, after being in a freshly painted room for a while, the smell might not be as strong. However, someone entering the room for the first time will find the smell very strong because they are not adapted. If we smelled ev ...
... Adaptation is experienced when a stimulus is present for a long time. For example, after being in a freshly painted room for a while, the smell might not be as strong. However, someone entering the room for the first time will find the smell very strong because they are not adapted. If we smelled ev ...
Ch 10 Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity (pt2)
... Regrowth of damaged neurons Not as successful in mammals as in lower ...
... Regrowth of damaged neurons Not as successful in mammals as in lower ...
The Brain - Central Connecticut State University
... except smell and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, and touching. ...
... except smell and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, and touching. ...
Einstein`s Brain
... pathologist, who performed the autopsy. Harvey cut the brain into 240 pieces, which he kept in jars at his house. Harvey moved around the country but he always brought the brain with him. He eventually sent parts out to be studied to various researchers in the 1980s and 1990s. ...
... pathologist, who performed the autopsy. Harvey cut the brain into 240 pieces, which he kept in jars at his house. Harvey moved around the country but he always brought the brain with him. He eventually sent parts out to be studied to various researchers in the 1980s and 1990s. ...
einsteins-brain
... pathologist, who performed the autopsy. Harvey cut the brain into 240 pieces, which he kept in jars at his house. Harvey moved around the country but he always brought the brain with him. He eventually sent parts out to be studied to various researchers in the 1980s and 1990s. ...
... pathologist, who performed the autopsy. Harvey cut the brain into 240 pieces, which he kept in jars at his house. Harvey moved around the country but he always brought the brain with him. He eventually sent parts out to be studied to various researchers in the 1980s and 1990s. ...
Assignment 1 Key
... 3. Descartes was among the first to suggest that the brain drove body function through mechanical means. What form of energy did he suggest was the basis for movement? a. thermal energy produced by heat from the brain b. electrical energy produced by individual cells in the brain c. hydraulic energy ...
... 3. Descartes was among the first to suggest that the brain drove body function through mechanical means. What form of energy did he suggest was the basis for movement? a. thermal energy produced by heat from the brain b. electrical energy produced by individual cells in the brain c. hydraulic energy ...
BRAiNBAsED LEARNiNG - Slone Chiropractic
... a BrainBased Learning Program and has been trained to evaluate and treat many neurologic conditions such as Dyslexia, Autism, ADD/ADHD and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Treatment is designed to treat an area of the patient that is often overlooked… THE BRAIN. ...
... a BrainBased Learning Program and has been trained to evaluate and treat many neurologic conditions such as Dyslexia, Autism, ADD/ADHD and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Treatment is designed to treat an area of the patient that is often overlooked… THE BRAIN. ...
Nervous System
... homeostasis & processes information Accepts sensory signals & channels them to cerebrum for interpretation (e.g. thalmus may have a consciousness of pain but does not know the location of the pain – the cerebrum interprets the signal and we know where it hurts) ...
... homeostasis & processes information Accepts sensory signals & channels them to cerebrum for interpretation (e.g. thalmus may have a consciousness of pain but does not know the location of the pain – the cerebrum interprets the signal and we know where it hurts) ...
Laminar and Columnar organization of the cerebral cortex
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
100 - Bloomfield Central School
... sometimes severed to treat patients with seizures and epilepsy, is called… ...
... sometimes severed to treat patients with seizures and epilepsy, is called… ...
BRAIN What is the corpus callosum? The band of axons connecting
... Visual information is associated with this lobe. Occipital. Audio information is associated with this lobe. Temporal. ...
... Visual information is associated with this lobe. Occipital. Audio information is associated with this lobe. Temporal. ...
Lecture 6C
... Macaque monkeys were trained to stare at a pattern (left panel) while injected with radioactive glucose. The radioactive glucose was absorbed and metabolized by active neurons to a much greater extent than by other neurons. After the experiment, the animals were sacrificed and the cortical radioacti ...
... Macaque monkeys were trained to stare at a pattern (left panel) while injected with radioactive glucose. The radioactive glucose was absorbed and metabolized by active neurons to a much greater extent than by other neurons. After the experiment, the animals were sacrificed and the cortical radioacti ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
Brain PowerPoints - Raleigh Charter High School
... Includes Broca’s area (needed for forming words; located in left hemisphere only) Association areas in this region – judgment, ...
... Includes Broca’s area (needed for forming words; located in left hemisphere only) Association areas in this region – judgment, ...
Re-examining the debate about the functional role of motor cortex
... emerge artifactually, and in predictable patterns, from the biomechanical properties of the periphery. Peter Strick has colorfully referred to this controversy as a "muscles vs. movements" debate. Through a series of experimental and theoretical studies, my colleagues and I re-examine this debate in ...
... emerge artifactually, and in predictable patterns, from the biomechanical properties of the periphery. Peter Strick has colorfully referred to this controversy as a "muscles vs. movements" debate. Through a series of experimental and theoretical studies, my colleagues and I re-examine this debate in ...
AP Psychology
... 7. What are the two examples of poison that affect Ach transmission and what does each do? 8. What are the opiate receptors that we naturally produce and what is their purpose? 9. Give two examples of how drugs and other chemicals alter neurotransmission. 10. What are agonists and antagonists? 11. W ...
... 7. What are the two examples of poison that affect Ach transmission and what does each do? 8. What are the opiate receptors that we naturally produce and what is their purpose? 9. Give two examples of how drugs and other chemicals alter neurotransmission. 10. What are agonists and antagonists? 11. W ...
Document
... • carries messages from sensory nerves to the brain and motor nerve messages from the brain to organs, muscles and glands. • it contains two types of tissue: • grey matter - non-myelinated interneurons • white matter - myelinated neurons (motor and sensory) • the interneurons are arranged in tracts ...
... • carries messages from sensory nerves to the brain and motor nerve messages from the brain to organs, muscles and glands. • it contains two types of tissue: • grey matter - non-myelinated interneurons • white matter - myelinated neurons (motor and sensory) • the interneurons are arranged in tracts ...
CNS
... • carries messages from sensory nerves to the brain and motor nerve messages from the brain to organs, muscles and glands. • it contains two types of tissue: • grey matter - non-myelinated interneurons • white matter - myelinated neurons (motor and sensory) • the interneurons are arranged in tracts ...
... • carries messages from sensory nerves to the brain and motor nerve messages from the brain to organs, muscles and glands. • it contains two types of tissue: • grey matter - non-myelinated interneurons • white matter - myelinated neurons (motor and sensory) • the interneurons are arranged in tracts ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.