Quiz: The Brain and Addiction
... 4. A: The brain is wired to remember feelings of pleasure, including those produced by drugs unnaturally. The brain then strives to repeat those feelings, which the drug user experiences as a craving for the drug. 5. B: At first, drug use may cause floods of dopamine. But prolonged drug abuse causes ...
... 4. A: The brain is wired to remember feelings of pleasure, including those produced by drugs unnaturally. The brain then strives to repeat those feelings, which the drug user experiences as a craving for the drug. 5. B: At first, drug use may cause floods of dopamine. But prolonged drug abuse causes ...
36.1 The Nervous System Neurons: Basic units of
... The cerebrum controls conscious activities – language, intelligence, memory, movement, senses The cerebellum controls balance, posture, and coordination The medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities The sympathetic nervous system control functions in times of stress and the parasympathetic c ...
... The cerebrum controls conscious activities – language, intelligence, memory, movement, senses The cerebellum controls balance, posture, and coordination The medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities The sympathetic nervous system control functions in times of stress and the parasympathetic c ...
Quiz: The Brain and Addiction
... 4. A: The brain is wired to remember feelings of pleasure, including those produced by drugs unnaturally. The brain then strives to repeat those feelings, which the drug user experiences as a craving for the drug. 5. B: At first, drug use may cause floods of dopamine. But prolonged drug abuse causes ...
... 4. A: The brain is wired to remember feelings of pleasure, including those produced by drugs unnaturally. The brain then strives to repeat those feelings, which the drug user experiences as a craving for the drug. 5. B: At first, drug use may cause floods of dopamine. But prolonged drug abuse causes ...
Andrea Sookchan Jasmine Hodge Billy Chang
... This is where the message is transmitted from one cell to another. Neurotransmitters travel along the axon to the terminal buttons of the first neuron and are released in the synaptic gap. They are received by the second neuron on its receptor sites on the dendrites. ...
... This is where the message is transmitted from one cell to another. Neurotransmitters travel along the axon to the terminal buttons of the first neuron and are released in the synaptic gap. They are received by the second neuron on its receptor sites on the dendrites. ...
The_road_to_brain-scale_simulation
... NEST simulator [3] is tailored to this resolution. Neurons are represented as small systems of differential equations, which interact by δ-impulses [4,5] to form networks of natural size and complexity. The top-down approach starts from an abstract description of a particular brain function and inve ...
... NEST simulator [3] is tailored to this resolution. Neurons are represented as small systems of differential equations, which interact by δ-impulses [4,5] to form networks of natural size and complexity. The top-down approach starts from an abstract description of a particular brain function and inve ...
Primer
... proportion to the density of receptors. In addition to being distorted in ways that reflect the functional importance of different body regions, cortical maps are plastic and can adapt to experience, especially if it occurs early in life. For example, the area of cortex devoted to inputs from the fi ...
... proportion to the density of receptors. In addition to being distorted in ways that reflect the functional importance of different body regions, cortical maps are plastic and can adapt to experience, especially if it occurs early in life. For example, the area of cortex devoted to inputs from the fi ...
Lecture_31_2014_noquiz
... How Does Information Flow through the Nervous System? The brain integrates sensory information and sends signals to effector cells. Sensory neuron ...
... How Does Information Flow through the Nervous System? The brain integrates sensory information and sends signals to effector cells. Sensory neuron ...
Document
... – Cerebral Palsy: is a disorder that affects muscle tone, movement, and motor skills (the ability to move in a coordinated and purposeful way). CP is usually caused by brain damage that occurs before or during a child's birth, or during the first 3 to 5 years of a child's life. There is no cure for ...
... – Cerebral Palsy: is a disorder that affects muscle tone, movement, and motor skills (the ability to move in a coordinated and purposeful way). CP is usually caused by brain damage that occurs before or during a child's birth, or during the first 3 to 5 years of a child's life. There is no cure for ...
Brain, Cognition and Language
... neuronal excitation in the brain – the input is processed. After the stimulation, there always follows the activity of innumerable neurons in different areas of the brain. There are brain areas which are active one after the other and those which are active at the same time: the neurons cooperate in ...
... neuronal excitation in the brain – the input is processed. After the stimulation, there always follows the activity of innumerable neurons in different areas of the brain. There are brain areas which are active one after the other and those which are active at the same time: the neurons cooperate in ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
PNS and CNS Nervous System Organization Peripheral Nervous
... • 1rst (preganglionic) has cell body in CNS – synapses with 2nd in the ...
... • 1rst (preganglionic) has cell body in CNS – synapses with 2nd in the ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... Parietal Lobes • Perception of somatesthetic senses (touch, pressure, heat, cold, pain) – Somatosensory cortex - postcentral gyrus of the central fissue ...
... Parietal Lobes • Perception of somatesthetic senses (touch, pressure, heat, cold, pain) – Somatosensory cortex - postcentral gyrus of the central fissue ...
Nervous System 2
... c. Which is primarily involved in energy conservation and basic self-maintenance, and which in rapid mobilization of energy (fight or flight) d. Know major effects of each, including specific effects on specific organs. Note that these are easier to learn if you can think logically about which organ ...
... c. Which is primarily involved in energy conservation and basic self-maintenance, and which in rapid mobilization of energy (fight or flight) d. Know major effects of each, including specific effects on specific organs. Note that these are easier to learn if you can think logically about which organ ...
Wilkinson Handout 2014
... • A sustained experience, such as that provided by longer term counselling or psychotherapy, that is experience over time of a different kind of relating enables a different kind of attachment to be learned. • Outcomes: ‘a state of neural integration and more complex cortical development and capacit ...
... • A sustained experience, such as that provided by longer term counselling or psychotherapy, that is experience over time of a different kind of relating enables a different kind of attachment to be learned. • Outcomes: ‘a state of neural integration and more complex cortical development and capacit ...
1. The axons of certain neurons are covered by a layer of fatty tissue
... 2) Your central nervous systems’ hungry brain activates and guides the muscles of your arm and hand via your peripheral nervous system’s motor neurons. As you pick up the fork, your brain processes the information from your sensory nervous system, enabling it to continue to guide the fork to your mo ...
... 2) Your central nervous systems’ hungry brain activates and guides the muscles of your arm and hand via your peripheral nervous system’s motor neurons. As you pick up the fork, your brain processes the information from your sensory nervous system, enabling it to continue to guide the fork to your mo ...
Fill in the blanks on LB page 67-68.
... 1. Neurotransmitters must be removed from the synaptic cleft to discontinue stimulation. 2. There are three methods of removal: a. Some amount of transmitter simply diffuses out of the cleft. b. Enzymes, such as acetylcholinesterase, break down the transmitters. c. Membrane transport proteins active ...
... 1. Neurotransmitters must be removed from the synaptic cleft to discontinue stimulation. 2. There are three methods of removal: a. Some amount of transmitter simply diffuses out of the cleft. b. Enzymes, such as acetylcholinesterase, break down the transmitters. c. Membrane transport proteins active ...
Understanding Perceptual Motor Function Building Better Robots
... Program of Development 1) Subcomponents of nervous system are formed from cells whose destination and function are largely predetermined before they migrate from the wall of ventricles 2) Development is marked by an initial abundance of cells, branches, and connections, with important part of subseq ...
... Program of Development 1) Subcomponents of nervous system are formed from cells whose destination and function are largely predetermined before they migrate from the wall of ventricles 2) Development is marked by an initial abundance of cells, branches, and connections, with important part of subseq ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... • Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs, a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... • Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs, a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
What is the Nervous System?
... 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex Frontal: movement, executive functions ...
... 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex Frontal: movement, executive functions ...
Deanne Boules presentation pdf
... medicine, genetics and applied disciplines such as psychology ...
... medicine, genetics and applied disciplines such as psychology ...
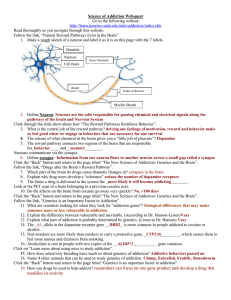
Science of Addiction WebquestKEY
... 8. Explain why drug users develop a “tolerance” reduce the number of dopamine receptors 9. The faster a drug is delivered to the system the _more likely it will become addicting________. Look at the PET scan of a brain belonging to a previous cocaine user. 10. Do the affects on the brain from cocain ...
... 8. Explain why drug users develop a “tolerance” reduce the number of dopamine receptors 9. The faster a drug is delivered to the system the _more likely it will become addicting________. Look at the PET scan of a brain belonging to a previous cocaine user. 10. Do the affects on the brain from cocain ...
No Slide Title
... What acts as a relay station for information going to the cerebrum (sensory information) is the __________. ...
... What acts as a relay station for information going to the cerebrum (sensory information) is the __________. ...
4/7
... Neurons are commonly connected to many other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron will do. ...
... Neurons are commonly connected to many other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron will do. ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.