The Nervous System
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
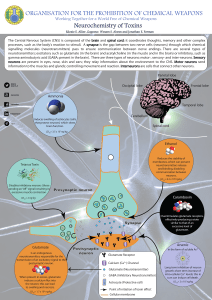
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
Nervous System - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... Part X: The Nervous System – The nervous system receives and then sends out information about your body. It also monitors and responds to changes in your environment. ◊ Name a few important body functions that your nervous system controls on its own without you having to think about it much? ...
... Part X: The Nervous System – The nervous system receives and then sends out information about your body. It also monitors and responds to changes in your environment. ◊ Name a few important body functions that your nervous system controls on its own without you having to think about it much? ...
The Nervous System
... Nerve impulses are electrical and/or chemical signals sent through our bodies. Nerve impulses travels within the neuron as an electrical signal-an impulse travels within a neuron from the dendrites through to the axon terminals Nerve impulses travel between neurons as chemical signals-Neurons are no ...
... Nerve impulses are electrical and/or chemical signals sent through our bodies. Nerve impulses travels within the neuron as an electrical signal-an impulse travels within a neuron from the dendrites through to the axon terminals Nerve impulses travel between neurons as chemical signals-Neurons are no ...
brain development - EDUC111ChildGrowthDevelopment
... the bones and muscles do not grow to their optimal size. Serious malnutrition prevents the head from reaching maximum capacity, and may limit brain size. Malnutrition interferes with the process of myelination. Poor nutrition also reduces resistance to disease, creating a destructive downward spiral ...
... the bones and muscles do not grow to their optimal size. Serious malnutrition prevents the head from reaching maximum capacity, and may limit brain size. Malnutrition interferes with the process of myelination. Poor nutrition also reduces resistance to disease, creating a destructive downward spiral ...
Unit 2 - Monroe Community College
... Specialization of the Hemispheres in an Intact Brain ● perceptual asymmetries: left/right imbalances in the speed of visual or auditory processing - in normal people the input sent to one hemisphere is quickly shared with the other - but subtle differences can be detected by measuring how long it ta ...
... Specialization of the Hemispheres in an Intact Brain ● perceptual asymmetries: left/right imbalances in the speed of visual or auditory processing - in normal people the input sent to one hemisphere is quickly shared with the other - but subtle differences can be detected by measuring how long it ta ...
Human Biology - St Mary's College, Wallasey
... to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
... to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
Higher Mind - Source Naturals
... For the past decade, researchers have been investigating the role in brain health of a remarkable neuroceutical, phosphatidyl serine (PS). This key structural molecule is integral to the matrix of fats and proteins that compose cell membranes. Although PS is found in all the cells of the body, its h ...
... For the past decade, researchers have been investigating the role in brain health of a remarkable neuroceutical, phosphatidyl serine (PS). This key structural molecule is integral to the matrix of fats and proteins that compose cell membranes. Although PS is found in all the cells of the body, its h ...
Nervous System - Anderson School District One
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
The Biological Bases of Behaviour
... the basic unit of structure and function of the nervous system. 4.Direct electrical stimulation of the brain provides another way to test the functions of certain brain areas. ...
... the basic unit of structure and function of the nervous system. 4.Direct electrical stimulation of the brain provides another way to test the functions of certain brain areas. ...
Gene Mutation Story
... Gene Mutation Story -Alzheimer’s It was just a typical day in the brain, no different than it always was, all cells seemed to be in order working in tip top shape, blood was being pumped through the brain, and the host William who was 60 years old was sound asleep. But there was a subtle disturbance ...
... Gene Mutation Story -Alzheimer’s It was just a typical day in the brain, no different than it always was, all cells seemed to be in order working in tip top shape, blood was being pumped through the brain, and the host William who was 60 years old was sound asleep. But there was a subtle disturbance ...
nervous system
... a transparent layer of cells called the cornea. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by muscles of the iris, which is the part of the eye that is colored. Behind the iris is the lens. The lens inverts the image and projects it onto the retina. The retina contains receptor cells called ...
... a transparent layer of cells called the cornea. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by muscles of the iris, which is the part of the eye that is colored. Behind the iris is the lens. The lens inverts the image and projects it onto the retina. The retina contains receptor cells called ...
Biological_Bases
... Blocks release of ACh at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis “Botox” is botulism toxin used to prevent ...
... Blocks release of ACh at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis “Botox” is botulism toxin used to prevent ...
The CNS Efficiency Model of the Chiropractic Subluxation
... i.e. general mechanisms of functional plasticity (e.g., learning) and of developmental plasticity It has been argued that there must also be a mechanism to assess and adjust the functional connectivity of the circuit in order to optimize its ...
... i.e. general mechanisms of functional plasticity (e.g., learning) and of developmental plasticity It has been argued that there must also be a mechanism to assess and adjust the functional connectivity of the circuit in order to optimize its ...
Nervous System - Seattle Central
... • Relay nuclei: – Reticular Formation: Share info between cerebrum & cerebellum ...
... • Relay nuclei: – Reticular Formation: Share info between cerebrum & cerebellum ...
A1985AUW1100002
... thought that, memory aside, the hippocampus offered several advantages. It has a cellular architecture that is remarkably conserved throughout mammals, and the main cetts, catted the pyramidal cells, are clustered in a discrete layer, an easy target for microelectrodes. These cells send their axons ...
... thought that, memory aside, the hippocampus offered several advantages. It has a cellular architecture that is remarkably conserved throughout mammals, and the main cetts, catted the pyramidal cells, are clustered in a discrete layer, an easy target for microelectrodes. These cells send their axons ...
Slide 1
... the stimulus causes channels to open and there must be enough of them opened to depolarize the membrane increasing a stimulus above threshold does not result in a larger response - this is all-or-nothing. If all stimuli above threshold cause a neuron to fire, how do we detect different intensities o ...
... the stimulus causes channels to open and there must be enough of them opened to depolarize the membrane increasing a stimulus above threshold does not result in a larger response - this is all-or-nothing. If all stimuli above threshold cause a neuron to fire, how do we detect different intensities o ...
Nervous System Notes
... the stimulus causes channels to open and there must be enough of them opened to depolarize the membrane increasing a stimulus above threshold does not result in a larger response - this is all-or-nothing. If all stimuli above threshold cause a neuron to fire, how do we detect different intensities o ...
... the stimulus causes channels to open and there must be enough of them opened to depolarize the membrane increasing a stimulus above threshold does not result in a larger response - this is all-or-nothing. If all stimuli above threshold cause a neuron to fire, how do we detect different intensities o ...
28.1_Responses
... Show high degree of cephalization and have highly developed nervous systems Interneurons in brain are connected with each other and with sensory neurons and motor neurons in the head and elsewhere in the body. ...
... Show high degree of cephalization and have highly developed nervous systems Interneurons in brain are connected with each other and with sensory neurons and motor neurons in the head and elsewhere in the body. ...
DOC
... generates desire. When dopamine is released, it helps motivate you to find the things you need. Once you achieve your goal, dopamine is released again to strengthen the memory of what caused the good feeling. POP-UP_ENDORPHINS Endorphins are brain chemicals released by the pituitary gland, the hypot ...
... generates desire. When dopamine is released, it helps motivate you to find the things you need. Once you achieve your goal, dopamine is released again to strengthen the memory of what caused the good feeling. POP-UP_ENDORPHINS Endorphins are brain chemicals released by the pituitary gland, the hypot ...
notes as
... be wrong (but we mustn’t forget that they are wrong!) – E.g. neurons that communicate real values rather than discrete spikes of activity. ...
... be wrong (but we mustn’t forget that they are wrong!) – E.g. neurons that communicate real values rather than discrete spikes of activity. ...
Unit 2-Week 1 Notes Sheets
... Name: ___________________________________________________________ Hr: ______________ ...
... Name: ___________________________________________________________ Hr: ______________ ...
Anatomy and Physiology brain
... temporal, parietal, and occipital. Each hemisphere has one of each of these lobes, which generally control function on the opposite side of the body. The different portions of each lobe and the four different lobes communicate and function together through very complex relationships, but each one al ...
... temporal, parietal, and occipital. Each hemisphere has one of each of these lobes, which generally control function on the opposite side of the body. The different portions of each lobe and the four different lobes communicate and function together through very complex relationships, but each one al ...
Cognitive Psychology
... & Wernicke’s areas) • Human-lesion studies - These days, we can take pictures of the brain while it’s still in the skull (CAT, MRI) an determine where the lesions are while someone is still alive. ...
... & Wernicke’s areas) • Human-lesion studies - These days, we can take pictures of the brain while it’s still in the skull (CAT, MRI) an determine where the lesions are while someone is still alive. ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.