PPT
... Here are areas where neural activation was greater when listening to sentences using incorrect syntax vs correct syntax (blue) ...
... Here are areas where neural activation was greater when listening to sentences using incorrect syntax vs correct syntax (blue) ...
Lecture - Lawrence Moon
... 1. Ramic et al., 2006. Axonal plasticity is associated with motor recovery following amphetamine treatment combined with rehabilitation after brain injury in the adult rat. Brain Res. 1111:176186. 2. Platz et al,. 2007. Amphetamine fails to facilitate motor performance and to enhance motor recovery ...
... 1. Ramic et al., 2006. Axonal plasticity is associated with motor recovery following amphetamine treatment combined with rehabilitation after brain injury in the adult rat. Brain Res. 1111:176186. 2. Platz et al,. 2007. Amphetamine fails to facilitate motor performance and to enhance motor recovery ...
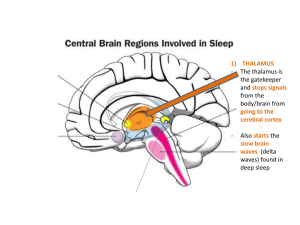
Sleep Brain Labelling
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
chapter32_part2
... make up the bulk of the cord’s white matter. Cell bodies, dendrites, and neuroglia make up gray matter. • The spinal cord also has a role in some simple reflexes, automatic responses that occur without conscious thought or learning. Signals from sensory neurons enter the cord through the dorsal root ...
... make up the bulk of the cord’s white matter. Cell bodies, dendrites, and neuroglia make up gray matter. • The spinal cord also has a role in some simple reflexes, automatic responses that occur without conscious thought or learning. Signals from sensory neurons enter the cord through the dorsal root ...
Syllabus - University of Pennsylvania
... of the decision process in the human brain, from identification of choice options, to the calculation of their utility, to selecting one for consumption, and learning from this experience. We are also beginning to understand how fundamental economic principles like risk, ambiguity, and volatility sh ...
... of the decision process in the human brain, from identification of choice options, to the calculation of their utility, to selecting one for consumption, and learning from this experience. We are also beginning to understand how fundamental economic principles like risk, ambiguity, and volatility sh ...
Exam 3 Review KEY
... 6) The smaller / bigger the size of the nerve fiber, the slower / faster the speed of nerve impulse. And the less / more myelin, which means larger diameter of the nerve fiber, the greater the speed. 7) Bundles of afferent and efferent neurons outside the CNS but inside the PNS are referred to as ne ...
... 6) The smaller / bigger the size of the nerve fiber, the slower / faster the speed of nerve impulse. And the less / more myelin, which means larger diameter of the nerve fiber, the greater the speed. 7) Bundles of afferent and efferent neurons outside the CNS but inside the PNS are referred to as ne ...
Document
... The nervous system receives signals: called stimulus. (this can be from inside or outside your body) When our nervous system reacts to this stimulus it is called a: response. ...
... The nervous system receives signals: called stimulus. (this can be from inside or outside your body) When our nervous system reacts to this stimulus it is called a: response. ...
AP Practice unit 3 and 4
... 62. The reticular formation is located in the A) brainstem. B) limbic system. C) sensory cortex. D) motor cortex. E) cerebellum. ...
... 62. The reticular formation is located in the A) brainstem. B) limbic system. C) sensory cortex. D) motor cortex. E) cerebellum. ...
Unit 1 2016/17 VCE Study Design – student trail
... inside us and in our environment. It makes sure that all of our body systems work together. The nervous system allows us to think and make decisions, carry out different actions and store memories. ...
... inside us and in our environment. It makes sure that all of our body systems work together. The nervous system allows us to think and make decisions, carry out different actions and store memories. ...
CH. 2 (BIOLOGY)
... Wernicke in 1874) it is involved with your ability to understand what someone else says (receptive language). Damage to Wernicke’s area might leave a person able to hear words but unable to comprehend the meaning of sentences created with the ...
... Wernicke in 1874) it is involved with your ability to understand what someone else says (receptive language). Damage to Wernicke’s area might leave a person able to hear words but unable to comprehend the meaning of sentences created with the ...
The Structure of the Brain
... What is it? It is a machine used to record the electrical activity of large portions of the brain. Wires are connected to various areas of your scalp, allowing the rhythms, or brain waves caused by the neurons to be read. ...
... What is it? It is a machine used to record the electrical activity of large portions of the brain. Wires are connected to various areas of your scalp, allowing the rhythms, or brain waves caused by the neurons to be read. ...
Chronic Stress and The Body
... o Adrenaline increases the heart rate, elevates BP and boosts the supply of energy o Cortisol increases glucose in the blood stream, increases the use of glucose by the brain and increases our body’s ability to repair tissues “Fight-or-Flight” response is normally self-limiting, however if there is ...
... o Adrenaline increases the heart rate, elevates BP and boosts the supply of energy o Cortisol increases glucose in the blood stream, increases the use of glucose by the brain and increases our body’s ability to repair tissues “Fight-or-Flight” response is normally self-limiting, however if there is ...
Chapter 2: Brain and Behavior
... acts like the brain’s alarm clock Activates and arouses cerebral cortex ...
... acts like the brain’s alarm clock Activates and arouses cerebral cortex ...
The Nervous System
... The cerebral cortex processes information from the sense organs and controls body movements Folds and grooves on the outer surface of the cerebral cortex greatly increase its surface area ...
... The cerebral cortex processes information from the sense organs and controls body movements Folds and grooves on the outer surface of the cerebral cortex greatly increase its surface area ...
Nervous System Test Review After you accidentally touch a hot pan
... a. A change or signals in the environment that can make an organism react. 16. Define response. a. A reaction to a stimulus 17. What part of a neuron carries nerve impulses away from the cell body? a. Axon 18. Where does a motor neuron send an impulse to? a. Muscles 19. What is a synapse? a. The spa ...
... a. A change or signals in the environment that can make an organism react. 16. Define response. a. A reaction to a stimulus 17. What part of a neuron carries nerve impulses away from the cell body? a. Axon 18. Where does a motor neuron send an impulse to? a. Muscles 19. What is a synapse? a. The spa ...
SinirBilimin Kısa Tarihi
... Extreme localism and holism have both been replaced by "connectionism." This view contends that lower level or primary sensory/motor functions are strongly localized but higher-level functions, like object recognition, memory, and language are the result of interconnections between brain areas. In a ...
... Extreme localism and holism have both been replaced by "connectionism." This view contends that lower level or primary sensory/motor functions are strongly localized but higher-level functions, like object recognition, memory, and language are the result of interconnections between brain areas. In a ...
UNIT 3A: Biological Bases of Behavior – Neural Processing and the
... Curare, a poison certain So. American Indians have applied to hunting-dart tips, occupies and blocks ACh receptor sites, leaving the neurotransmitter unable to affect the muscles. The animal is paralyzed. ...
... Curare, a poison certain So. American Indians have applied to hunting-dart tips, occupies and blocks ACh receptor sites, leaving the neurotransmitter unable to affect the muscles. The animal is paralyzed. ...
Brain Lecture - Scott County Schools
... • a. Natural pain killers in the brain • b. Morphine is a synthetic endorphin • c. Substance P is a neuro-cheimical that is still not fully understood but researchers suspect that it is involved in triggering the pain response ...
... • a. Natural pain killers in the brain • b. Morphine is a synthetic endorphin • c. Substance P is a neuro-cheimical that is still not fully understood but researchers suspect that it is involved in triggering the pain response ...
Flyer
... neuroimaging technologies with the purpose of exploring the fundamental roles, interactions as well as practical impacts of Brain Informatics. BIH’16 addresses the computational, cognitive, physiological, biological, physical, ecological and social perspectives of brain informatics, as well as topic ...
... neuroimaging technologies with the purpose of exploring the fundamental roles, interactions as well as practical impacts of Brain Informatics. BIH’16 addresses the computational, cognitive, physiological, biological, physical, ecological and social perspectives of brain informatics, as well as topic ...
brain - Austin Community College
... Neural change responsible for retention and storage of knowledge is known as the memory trace Consolidation - Process of transferring and fixing short-term memory traces into long-term memory stores Working memory - Temporarily holds and interrelates various pieces of information relevant to a curre ...
... Neural change responsible for retention and storage of knowledge is known as the memory trace Consolidation - Process of transferring and fixing short-term memory traces into long-term memory stores Working memory - Temporarily holds and interrelates various pieces of information relevant to a curre ...
The Brain
... see objects, but are unable to identify them by sight. However, objects may be identified by touch, sound, and/or smell. For example, affected individuals may not be able to identify a set of keys by sight, but can identify them upon holding them in their hands. Primary visual agnosia results from d ...
... see objects, but are unable to identify them by sight. However, objects may be identified by touch, sound, and/or smell. For example, affected individuals may not be able to identify a set of keys by sight, but can identify them upon holding them in their hands. Primary visual agnosia results from d ...
Nervous System
... Sensory information comes into spinal cord via sensory neurons that are packed with other neurons in nerves Sensory neurons from synapses with interneurons and motor neurons Motor neurons transmit action potentials generating reflex response At same time, interneurons transmit sensory information to ...
... Sensory information comes into spinal cord via sensory neurons that are packed with other neurons in nerves Sensory neurons from synapses with interneurons and motor neurons Motor neurons transmit action potentials generating reflex response At same time, interneurons transmit sensory information to ...
Page 1 - Rochester Community Schools
... B) range of traits that contribute to reproductive success. C) set of genetic material in an organism's chromosomes. D) set of interactions between genes and environments. E) collection of genetic and hormonal influences on behavior. 29. Compared with identical twins, fraternal twins are A) less lik ...
... B) range of traits that contribute to reproductive success. C) set of genetic material in an organism's chromosomes. D) set of interactions between genes and environments. E) collection of genetic and hormonal influences on behavior. 29. Compared with identical twins, fraternal twins are A) less lik ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.