neurobiological-basis-of-behavior
... 5. Terminal bulbs (end bulbs) – tiny bulbs located at the end of the axon’s branches; contains neurotransmitters 6. Synapse – infinitely small space between an end bulb and a muscle, body organ, or cell body - When end bulbs are stimulated, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse ...
... 5. Terminal bulbs (end bulbs) – tiny bulbs located at the end of the axon’s branches; contains neurotransmitters 6. Synapse – infinitely small space between an end bulb and a muscle, body organ, or cell body - When end bulbs are stimulated, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse ...
SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
... • receptors nourished by blood vessels in: • blood vessels on vitreous humor side nourish ganglion cells • used to assess health of small blood vessels ...
... • receptors nourished by blood vessels in: • blood vessels on vitreous humor side nourish ganglion cells • used to assess health of small blood vessels ...
Basic Pattern of the Central Nervous System
... _____________________________ (controls the opposite side of the body) • Hemispheres are not equal in function • No functional area acts alone; conscious behavior involves the entire cortex ...
... _____________________________ (controls the opposite side of the body) • Hemispheres are not equal in function • No functional area acts alone; conscious behavior involves the entire cortex ...
addiction
... colleagues recruited cocaine addicts who had been using for an average of seven to eight years and had used on 16 of the past 30 days. After making sure none had a heart problem or any other condition that would put them at risk, Breiter and colleagues gave each a "party" dose of cocaine, up to abou ...
... colleagues recruited cocaine addicts who had been using for an average of seven to eight years and had used on 16 of the past 30 days. After making sure none had a heart problem or any other condition that would put them at risk, Breiter and colleagues gave each a "party" dose of cocaine, up to abou ...
Psy101 Brain.lst
... Differentiate between how information is transmitted within neurons and between neurons. ...
... Differentiate between how information is transmitted within neurons and between neurons. ...
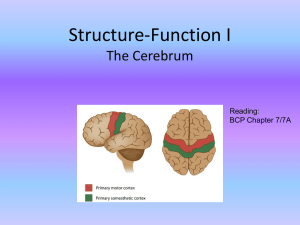
Structure-Function I
... widely known and frequently cited map of human cortex. Brodmann postulated that these areas with different structures performed different functions. ...
... widely known and frequently cited map of human cortex. Brodmann postulated that these areas with different structures performed different functions. ...
Meart: 1000 word catalogue essay:
... images to and receives impulses from an in-vitro culture of rat neurons via the internet. The neurons are housed in Dr. Steve Potter’s neuro-science engineering laboratory at Georgia Institute of Technology. The simplified process follows. Video images (generated at the exhibition site) are sent to ...
... images to and receives impulses from an in-vitro culture of rat neurons via the internet. The neurons are housed in Dr. Steve Potter’s neuro-science engineering laboratory at Georgia Institute of Technology. The simplified process follows. Video images (generated at the exhibition site) are sent to ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint Biological basis of behavior-
... Endocrine system, p. 62 Hormones, p. 62 Adrenal glands, p. 63 Pituitary gland, p. 63 ...
... Endocrine system, p. 62 Hormones, p. 62 Adrenal glands, p. 63 Pituitary gland, p. 63 ...
Exploring the Human Nervous System
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
Axon Outgrowth in the Developing Cerebral
... During the development of the mammalian cerebral cortex, neurons are required to migrate to their final destinations within the developed brain, connect with other neurons through their axons and dendrites, and integrate functionally to produce the mature nervous system. One essential aspect in this ...
... During the development of the mammalian cerebral cortex, neurons are required to migrate to their final destinations within the developed brain, connect with other neurons through their axons and dendrites, and integrate functionally to produce the mature nervous system. One essential aspect in this ...
9.1-9.4 Notes
... • Sensory-sensory receptors are at the end of peripheral neurons – Gather information about changes in and out of the body • Example: temperature, light, sound, oxygen levels ...
... • Sensory-sensory receptors are at the end of peripheral neurons – Gather information about changes in and out of the body • Example: temperature, light, sound, oxygen levels ...
Physiology Unit Objectives and Assignments
... Using the table below, put an X in the box for the each objective. If you really understand the concept and think you could explain it to someone, mark the Green Light Box. If you kind of get it but still have some questions or need to a study a little more to memorize it, put an X in the Orange Lig ...
... Using the table below, put an X in the box for the each objective. If you really understand the concept and think you could explain it to someone, mark the Green Light Box. If you kind of get it but still have some questions or need to a study a little more to memorize it, put an X in the Orange Lig ...
Vocabulary Terms
... All of the words below are ones that students will encounter while playing Episode Four: Mystery of Morpheus. Their definitions are contained within the adventure in either the InfoArchives or the Glossary. Teachers should alert the students to the ability to click on the hot-linked words in the gam ...
... All of the words below are ones that students will encounter while playing Episode Four: Mystery of Morpheus. Their definitions are contained within the adventure in either the InfoArchives or the Glossary. Teachers should alert the students to the ability to click on the hot-linked words in the gam ...
The Brain
... Chapter Three Teaching the Chapter Some students will find material on the biological basis of behavior to be intimidating, whereas others will be awestruck by the fact that our experience of the world happens “up there.” Consider using neurological case studies (e.g. Oliver Sacks’ work) to illustr ...
... Chapter Three Teaching the Chapter Some students will find material on the biological basis of behavior to be intimidating, whereas others will be awestruck by the fact that our experience of the world happens “up there.” Consider using neurological case studies (e.g. Oliver Sacks’ work) to illustr ...
Chapter 12: The Central Nervous System
... parietal lobes 3. Parieto-occipital sulcus a. Separates the parietal and occipital lobes 4. Lateral sulcus a. Separates the parietal and temporal lobes 5. Precentral and postcentral gyri border the central sulcus C. Cerebral Cortex 1. Cortex a. Superficial gray matter b. Accounts for 40% of the mass ...
... parietal lobes 3. Parieto-occipital sulcus a. Separates the parietal and occipital lobes 4. Lateral sulcus a. Separates the parietal and temporal lobes 5. Precentral and postcentral gyri border the central sulcus C. Cerebral Cortex 1. Cortex a. Superficial gray matter b. Accounts for 40% of the mass ...
Brain Research Methods - RevisionforPsy3
... cortex that’s the source of the epileptic seizures as a last resort for patients. When stimulated area of the cortex Penfield ask patients to report their experiences ...
... cortex that’s the source of the epileptic seizures as a last resort for patients. When stimulated area of the cortex Penfield ask patients to report their experiences ...
Brain Compatible Learning Strategies
... Brain Fact: Visual –vs- auditory Brain Activation • The brain processes information differently depending on how it’s communicated. • When listening to a sentence, a different cortical activation pathway was forged than when subjects read the words silently. • Total amount of activation was signifi ...
... Brain Fact: Visual –vs- auditory Brain Activation • The brain processes information differently depending on how it’s communicated. • When listening to a sentence, a different cortical activation pathway was forged than when subjects read the words silently. • Total amount of activation was signifi ...
Annual Review of Neuroscience
... attention here.” “hold one thing in mind”) The Miller Lab has taken monkey training to a higher level than any other lab. We have taught monkeys to juggle multiple things in memory, anticipate and imagine forthcoming events, make cognitive decisions, to recognize abstract categories and concepts (“c ...
... attention here.” “hold one thing in mind”) The Miller Lab has taken monkey training to a higher level than any other lab. We have taught monkeys to juggle multiple things in memory, anticipate and imagine forthcoming events, make cognitive decisions, to recognize abstract categories and concepts (“c ...
PSYC550 Emotions and Memory
... • central nucleus (CE) – The region of the amygdala that receives information from the basal, lateral, and accessory basal nuclei and sends projections to a wide variety of regions in the brain; involved in emotional responses. ...
... • central nucleus (CE) – The region of the amygdala that receives information from the basal, lateral, and accessory basal nuclei and sends projections to a wide variety of regions in the brain; involved in emotional responses. ...
Wellness 10 Day #3
... called TRIGGERS, actually cause a surge of dopamine in the brain. This dopamine release causes the user to experience very strong CRAVINGS for the drug. NOTE: This is why it is so hard for cigarette smokers to stop when they are around other ...
... called TRIGGERS, actually cause a surge of dopamine in the brain. This dopamine release causes the user to experience very strong CRAVINGS for the drug. NOTE: This is why it is so hard for cigarette smokers to stop when they are around other ...
Perinatal Neuorscience and Skin to Skin Contact
... and walking around 12 months) develop first. The maturation process is much slower in the prefrontal cortex of the brain, which is responsible for executive functions. During childhood, axons and dendrites proliferate for the purpose of developing synaptic connections, which is why it is much easie ...
... and walking around 12 months) develop first. The maturation process is much slower in the prefrontal cortex of the brain, which is responsible for executive functions. During childhood, axons and dendrites proliferate for the purpose of developing synaptic connections, which is why it is much easie ...
The Nervous System
... • General interpretative and speech centers (Wernicke’s area – receives info from all sensory association areas, integrates sensory to visual and auditory memories) • Language-based skills (speech center = Broca’s area) • Representational Hemisphere (usually right) • Spatial relationships • Logical ...
... • General interpretative and speech centers (Wernicke’s area – receives info from all sensory association areas, integrates sensory to visual and auditory memories) • Language-based skills (speech center = Broca’s area) • Representational Hemisphere (usually right) • Spatial relationships • Logical ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.