Nervous System - Calgary Christian School
... parts of the body that are relatively leaky to a variety of molecules, the blood-brain barrier keeps many substances, including toxins, away from the neurons and glia. Most drugs do not get into the brain. Only drugs that are fat soluble can penetrate the blood-brain barrier. These include drugs of ...
... parts of the body that are relatively leaky to a variety of molecules, the blood-brain barrier keeps many substances, including toxins, away from the neurons and glia. Most drugs do not get into the brain. Only drugs that are fat soluble can penetrate the blood-brain barrier. These include drugs of ...
presentation source
... MOTOR CORTEX CORTICAL EFFERENT ZONES: VERTICAL COLUMNS OF CELLS EACH ZONE CONTROLS ONE MUSCLE SIX DIFFERENT LAYERS OF CELLS OUTPUT LAYER IS LAYER V EXCITE BOTH ALPHA AND GAMMA MOTOR NEURONS ...
... MOTOR CORTEX CORTICAL EFFERENT ZONES: VERTICAL COLUMNS OF CELLS EACH ZONE CONTROLS ONE MUSCLE SIX DIFFERENT LAYERS OF CELLS OUTPUT LAYER IS LAYER V EXCITE BOTH ALPHA AND GAMMA MOTOR NEURONS ...
Pain
... the fingers are stimulated; (b) when the hand is stimulated; and (c) when the arm is stimulated. (d) Stimulation of two nearby points on the finger causes separated activation on the finger area of the cortex, but stimulation of two nearby points on the arm causes overlapping activation in the arm a ...
... the fingers are stimulated; (b) when the hand is stimulated; and (c) when the arm is stimulated. (d) Stimulation of two nearby points on the finger causes separated activation on the finger area of the cortex, but stimulation of two nearby points on the arm causes overlapping activation in the arm a ...
View Full PDF - Biochemical Society Transactions
... Laval, Faculte de medecine, Univenite Laval, Quebec, Canada G I K 7P4 ...
... Laval, Faculte de medecine, Univenite Laval, Quebec, Canada G I K 7P4 ...
Antipsychotic Medications and the Brain
... clear what they indicate. Whether they are related to the efficacy of the drug or a marker for side effects remains to be determined. If the latter, developing a tool to identify such changes in living individuals could provide an early marker for tardive dyskinesia and thus indicate which individua ...
... clear what they indicate. Whether they are related to the efficacy of the drug or a marker for side effects remains to be determined. If the latter, developing a tool to identify such changes in living individuals could provide an early marker for tardive dyskinesia and thus indicate which individua ...
Peripheral nervous system
... Nervous system & its function Classification of nervous system Brain Parts of the brain & the function of each part Spinal cord & spinal nerves Meninges & cerebrospinal fluid Peripheral nervous system Components of PNS Functional classification of PNS Neurons Structure of neurons Clas ...
... Nervous system & its function Classification of nervous system Brain Parts of the brain & the function of each part Spinal cord & spinal nerves Meninges & cerebrospinal fluid Peripheral nervous system Components of PNS Functional classification of PNS Neurons Structure of neurons Clas ...
100 Fascinating Facts You Never Knew About the
... what they actually are. The unconscious mind strives to make connections with concepts you will understand, so dreams are largely symbolic representations. 72. Adenosine. Caffeine works to block naturally occurring adenosine in the body, creating alertness. Scientists have recently discovered this c ...
... what they actually are. The unconscious mind strives to make connections with concepts you will understand, so dreams are largely symbolic representations. 72. Adenosine. Caffeine works to block naturally occurring adenosine in the body, creating alertness. Scientists have recently discovered this c ...
Chapter 7 Appendix
... more detailed look at the structures of the forebrain. The i n t c m a l c a p s t r l ei s t h e l a r g e c o l l e c t i o no f a x o n s c o n n e c t i n g t h e c o r t i c a lr v h i l e n r a n er w i t h t h e t h a l a m u s , a n d t h e c o r l ) u s c a l l < l s r u ni s t h e e n o r ...
... more detailed look at the structures of the forebrain. The i n t c m a l c a p s t r l ei s t h e l a r g e c o l l e c t i o no f a x o n s c o n n e c t i n g t h e c o r t i c a lr v h i l e n r a n er w i t h t h e t h a l a m u s , a n d t h e c o r l ) u s c a l l < l s r u ni s t h e e n o r ...
CVI
... abnormalities. The ultrasound could not provide a clear picture and we were instructed to schedule a MRI to review his brain in further detail after he was three months of age. Thankfully, Richard was nursing well and he was able to come home to his family. The next few months were filled with tests ...
... abnormalities. The ultrasound could not provide a clear picture and we were instructed to schedule a MRI to review his brain in further detail after he was three months of age. Thankfully, Richard was nursing well and he was able to come home to his family. The next few months were filled with tests ...
∂ u /∂ t = u(x,t) +∫ w(x,y)f(u(y,t)) + I(x) + L(x)
... A honeybee may forage on 1,000s of flowers for nectar and pollen in its lifetime. Scent is one of the primary means that it uses for identifying rewarding flowers. How honeybees and other animals learn to associate complex and variable scents with important events is still not ...
... A honeybee may forage on 1,000s of flowers for nectar and pollen in its lifetime. Scent is one of the primary means that it uses for identifying rewarding flowers. How honeybees and other animals learn to associate complex and variable scents with important events is still not ...
Ch. 35 Nervous System edit
... Drug abuse = can be defined as using any drug in a way that most doctors would not approve ...
... Drug abuse = can be defined as using any drug in a way that most doctors would not approve ...
brain movement and disorder
... with areflexia and atonia (spinal shock). Later spasticity (hyperreflexia and rigidity), stiff extended leg & poor use of fingers. Often comes with sudden aphasia (inability to speak), dysphasia (difficulty saying words) or talking non-sense; new onset unilateral poor vision. Most often associated w ...
... with areflexia and atonia (spinal shock). Later spasticity (hyperreflexia and rigidity), stiff extended leg & poor use of fingers. Often comes with sudden aphasia (inability to speak), dysphasia (difficulty saying words) or talking non-sense; new onset unilateral poor vision. Most often associated w ...
cerebral cortex - krigolson teaching
... particular, the speech function has been found to be localized in one of the hemispheres that is commonly called dominant. The left hemisphere is dominant in about 96% of right-handed persons and in about 70% of left-handed persons. Note that the cerebrospinal tract goes on its way from one side of ...
... particular, the speech function has been found to be localized in one of the hemispheres that is commonly called dominant. The left hemisphere is dominant in about 96% of right-handed persons and in about 70% of left-handed persons. Note that the cerebrospinal tract goes on its way from one side of ...
Module 24 Powerpoint
... Karl Lashley (18901958) showed that rats who had learned a maze retained parts of that memory, even when various small parts of their brain were removed. ...
... Karl Lashley (18901958) showed that rats who had learned a maze retained parts of that memory, even when various small parts of their brain were removed. ...
The Nervous System
... grooves and covered with an outer layer of gray matter called the cerebral cortex. • Divided into 4 lobes ...
... grooves and covered with an outer layer of gray matter called the cerebral cortex. • Divided into 4 lobes ...
Laboratory Exercise 11: Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain
... to their size. More cortical area is devoted to muscles involved in skill, complex, delicate movements, as in the movement of the fingers than of the muscles of the back. Postcentral (Sensory) Gyrus of the parietal lobe - in the postcentral gyrus there is a point to point representation of location ...
... to their size. More cortical area is devoted to muscles involved in skill, complex, delicate movements, as in the movement of the fingers than of the muscles of the back. Postcentral (Sensory) Gyrus of the parietal lobe - in the postcentral gyrus there is a point to point representation of location ...
As Powerpoint Slide
... 1 Department of Neurosurgery, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and ; 2 Center for Brain Injury and Repair, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA ; ...
... 1 Department of Neurosurgery, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and ; 2 Center for Brain Injury and Repair, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA ; ...
The Nervous System - Ione Community Charter School
... grooves and covered with an outer layer of gray matter called the cerebral cortex. • Divided into 4 lobes ...
... grooves and covered with an outer layer of gray matter called the cerebral cortex. • Divided into 4 lobes ...
The Nervous System
... grooves and covered with an outer layer of gray matter called the cerebral cortex. • Divided into 4 lobes ...
... grooves and covered with an outer layer of gray matter called the cerebral cortex. • Divided into 4 lobes ...
Section: Nervous system
... 13. Neurons that gather information about what is happening and send that information to the brain are ___________ neurons. 14. Neurons that send impulses from the brain to other systems are called ______________ neurons. 15. A nerve is a collection of ____________ bundled together with _________ __ ...
... 13. Neurons that gather information about what is happening and send that information to the brain are ___________ neurons. 14. Neurons that send impulses from the brain to other systems are called ______________ neurons. 15. A nerve is a collection of ____________ bundled together with _________ __ ...
Nervous system summary
... dopamine flood, or “high”—an effect known as “tolerance.” Long-Term Effects Drug use can eventually lead to dramatic changes in neurons and brain circuits. These changes can still be present even after the person has stopped taking drugs. This is more likely to happen when a drug is taken over and o ...
... dopamine flood, or “high”—an effect known as “tolerance.” Long-Term Effects Drug use can eventually lead to dramatic changes in neurons and brain circuits. These changes can still be present even after the person has stopped taking drugs. This is more likely to happen when a drug is taken over and o ...
The Nervous System and the Brain
... receptors and muscles. Neurons in the somatic nervous system transmit messages about sights, sounds, smell, temperature, and body position to the CNS. It also transmits information from the brain to produce purposeful motor movements. The autonomic nervous system is “automatic”. It controls and regu ...
... receptors and muscles. Neurons in the somatic nervous system transmit messages about sights, sounds, smell, temperature, and body position to the CNS. It also transmits information from the brain to produce purposeful motor movements. The autonomic nervous system is “automatic”. It controls and regu ...
Effects of experience on brain development
... for a few years after birth. • By the age of 2 years old, the brain is about 80% of the adult size. • End product at adulthood is approximately 1400 g (3 lb). ...
... for a few years after birth. • By the age of 2 years old, the brain is about 80% of the adult size. • End product at adulthood is approximately 1400 g (3 lb). ...
L7-Brainstem Student..
... • (3) It has centers for Brainstem Reflexes , such as cough reflex , gag reflex , swallowing , and vomiting ; + visual & auditory orientation reflexes (required for head movements. through Superior & Inferior Colliculi ) • (4) Contributes to maintenance of body balance through the vestibular nucle ...
... • (3) It has centers for Brainstem Reflexes , such as cough reflex , gag reflex , swallowing , and vomiting ; + visual & auditory orientation reflexes (required for head movements. through Superior & Inferior Colliculi ) • (4) Contributes to maintenance of body balance through the vestibular nucle ...
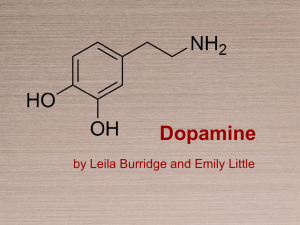
Dopamine 2013
... ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Dopamine.aspx ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/Dopamine-Functions.aspx ● http://www.livestrong.com/article/195851-what-are-the-causes-of-lowdopamine-levels/ ● http://www.livestrong.com/article/73358-side-effects-lack-dopamine/ ● http://www.livestrong. ...
... ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Dopamine.aspx ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/Dopamine-Functions.aspx ● http://www.livestrong.com/article/195851-what-are-the-causes-of-lowdopamine-levels/ ● http://www.livestrong.com/article/73358-side-effects-lack-dopamine/ ● http://www.livestrong. ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.