Lec. 2 - DNA replication 1
... prefers substrates that are doublestranded, with only one strand needing ligation, and lacking gaps. ...
... prefers substrates that are doublestranded, with only one strand needing ligation, and lacking gaps. ...
Worked solutions to textbook questions 1 Chapter 13 DNA Q1. Copy
... Just one missing nucleotide in the DNA sequence that codes for haemoglobin production causes a defective molecule in red blood cells, so that they change shape where oxygen concentration is low. The red blood cells have a shorter lifespan and this causes anaemia. ...
... Just one missing nucleotide in the DNA sequence that codes for haemoglobin production causes a defective molecule in red blood cells, so that they change shape where oxygen concentration is low. The red blood cells have a shorter lifespan and this causes anaemia. ...
DNA Replication, Repair, and Recombination
... Problem: no priming at 5’ of lagging strand possible without shortening of the chromosome upon every replication Telomer sequence: unusual, G-rich, 3’ overhang (20-200bp) Specialized enzyme: telomerase adds G-rich repeats without teplate, is ribonucleoprotein, RNA acts as template ...
... Problem: no priming at 5’ of lagging strand possible without shortening of the chromosome upon every replication Telomer sequence: unusual, G-rich, 3’ overhang (20-200bp) Specialized enzyme: telomerase adds G-rich repeats without teplate, is ribonucleoprotein, RNA acts as template ...
Total genomic DNA of non-treated and DHPA
... Figure S1 - MSAP analysis of DNA samples isolated from tobacco seedlings treated with 0 μM (DHPA 0), 10 μM (DHPA 10) and 100 μM (DHPA 100) 9-(S)-(2,3dihydroxypropyl)-adenine (DHPA; [1]). DHPA preferentially induces hypomethylation of CHG sequences and also some CG sequences at elevated concentra ...
... Figure S1 - MSAP analysis of DNA samples isolated from tobacco seedlings treated with 0 μM (DHPA 0), 10 μM (DHPA 10) and 100 μM (DHPA 100) 9-(S)-(2,3dihydroxypropyl)-adenine (DHPA; [1]). DHPA preferentially induces hypomethylation of CHG sequences and also some CG sequences at elevated concentra ...
Exam 1 Practice Answers
... Two 21bp dsDNA molecules are shown below. Which molecule will have the higher Tm if they were each placed in separate solutions with the same salt concentration. Briefly explain your answer. (10 points) DNA molecule A: 5’ ATAGCGTAGCTGTCGTATCGC 3’ ...
... Two 21bp dsDNA molecules are shown below. Which molecule will have the higher Tm if they were each placed in separate solutions with the same salt concentration. Briefly explain your answer. (10 points) DNA molecule A: 5’ ATAGCGTAGCTGTCGTATCGC 3’ ...
Lecture
... Case 1: Screening for the sickle-cell gene Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder in which both genes in the patient encode the amino acid valine (Val) in the sixth position of the beta chain (betaS) of the hemoglobin molecule. "Normal" beta chains (betaA) have glutamic acid at this position. The ...
... Case 1: Screening for the sickle-cell gene Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder in which both genes in the patient encode the amino acid valine (Val) in the sixth position of the beta chain (betaS) of the hemoglobin molecule. "Normal" beta chains (betaA) have glutamic acid at this position. The ...
Recombination and Repair
... • General Excision Repair System (“Cut and Patch” Repair) 1. The most widely distributed sysytem for DNA repair. 2. Recognize the bulge of DNA strand. e.g., UV (TT dimer) ...
... • General Excision Repair System (“Cut and Patch” Repair) 1. The most widely distributed sysytem for DNA repair. 2. Recognize the bulge of DNA strand. e.g., UV (TT dimer) ...
the DNA Binding Lab Lesson Plan Powerpoint
... How many different bases are in this DNA fragment? ...
... How many different bases are in this DNA fragment? ...
General Biology Program for Secondary
... explanations and technological designs may change with new information over time (e.g., the understanding of DNA, the design of computers). ...
... explanations and technological designs may change with new information over time (e.g., the understanding of DNA, the design of computers). ...
Forensic DNA Analysis
... billion chance of error. This means there may be one other person on the planet that would be too similar to tell the difference. If all other satellite regions are also considered, the chances of error go way, way down… 1 in 53,581,500,000,000,000,000 ...
... billion chance of error. This means there may be one other person on the planet that would be too similar to tell the difference. If all other satellite regions are also considered, the chances of error go way, way down… 1 in 53,581,500,000,000,000,000 ...
Document
... Some Phraseology Review • Recall from general biology the heirarchy of structure of DNA: • Humans carry 2 copies of the DNA in their cells (diploid). The exception is sperm and eggs which contain one copy (haploid) • The DNA is organized into chromosomes – long strands of DNA • On the chromosomes, ...
... Some Phraseology Review • Recall from general biology the heirarchy of structure of DNA: • Humans carry 2 copies of the DNA in their cells (diploid). The exception is sperm and eggs which contain one copy (haploid) • The DNA is organized into chromosomes – long strands of DNA • On the chromosomes, ...
Teacher`s Notes - University of California, Irvine
... fields. Human DNA can be analyzed to provide evidence in criminal cases, to diagnose ...
... fields. Human DNA can be analyzed to provide evidence in criminal cases, to diagnose ...
Part 3
... Genetics found strong evidence that tobacco use can chemically modify and affect the activity of genes through hypomethylations which are known to increase the risk of developing cancer. This was the first study to establish a close link between epigenetic modifications on a cancer gene and the risk ...
... Genetics found strong evidence that tobacco use can chemically modify and affect the activity of genes through hypomethylations which are known to increase the risk of developing cancer. This was the first study to establish a close link between epigenetic modifications on a cancer gene and the risk ...
Chapter 7: DNA and Gel Electrophoresis Extended Objective Checklist
... At the conclusion of this unit, the student should be able to do: DNA Background _____1. Write the full name of the DNA molecule _____ 2. Describe the structure of a DNA molecule as proposed by Watson Crick in 1953. _____3. List four nitrogen bases found in a DNA molecule. _____ 4. Explain complemen ...
... At the conclusion of this unit, the student should be able to do: DNA Background _____1. Write the full name of the DNA molecule _____ 2. Describe the structure of a DNA molecule as proposed by Watson Crick in 1953. _____3. List four nitrogen bases found in a DNA molecule. _____ 4. Explain complemen ...
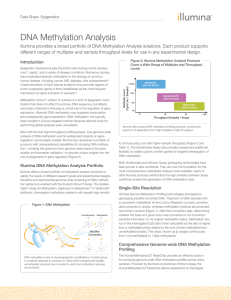
DNA Methylation Analysis
... Illumina offers a broad portfolio of methylation analysis products to satisfy the needs of different research goals and experimental designs. Sensitive and reproducible genome-wide screening of DNA methylation patterns is enabled with the trusted Infinium® Assay. The GoldenGate® Assay for Methylatio ...
... Illumina offers a broad portfolio of methylation analysis products to satisfy the needs of different research goals and experimental designs. Sensitive and reproducible genome-wide screening of DNA methylation patterns is enabled with the trusted Infinium® Assay. The GoldenGate® Assay for Methylatio ...
9.1 Manipulating DNA
... PCR uses polymerases (enzymes) to copy DNA segments. • PCR makes many copies of a specific DNA sequence in a few hours. • PCR amplifies DNA samples. • PCR is similar to DNA replication. Compare and Contrast: How are replication and PCR similar? Different? Explain. ...
... PCR uses polymerases (enzymes) to copy DNA segments. • PCR makes many copies of a specific DNA sequence in a few hours. • PCR amplifies DNA samples. • PCR is similar to DNA replication. Compare and Contrast: How are replication and PCR similar? Different? Explain. ...
Epigenetic Regulation of the Glucocorticoid receptor in human brain
... cellular phenotype caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA nucleotide sequence. DNA methylation and histone deacetylation are two processes which can cause these heritable changes. ...
... cellular phenotype caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA nucleotide sequence. DNA methylation and histone deacetylation are two processes which can cause these heritable changes. ...
... dvances in diagnostic and treatment technologies have resulted in excellent long term survival for Gastric cancer but it is still the second most cause of cancer death in the world.1 About 95% of stomach cancers are of adenocarcinoma type which starts from one of the common cell types found in the l ...
to 3
... and migrate to the positive pole D. A buffer must cover the gel to allow a current to pass through the system E. Restriction enzymes cut DNA in only certain sites on the strand ...
... and migrate to the positive pole D. A buffer must cover the gel to allow a current to pass through the system E. Restriction enzymes cut DNA in only certain sites on the strand ...
Lab 8
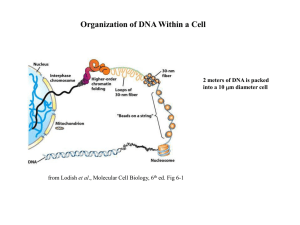
... In our cells, DNA is found inside the nucleus, wrapped around basic protein molecules called histones (kind of like thread wrapped around a spool). This combination of DNA and protein is called a nucleosome. The DNA does not leave the nucleus, so when new proteins or other structures need to be made ...
... In our cells, DNA is found inside the nucleus, wrapped around basic protein molecules called histones (kind of like thread wrapped around a spool). This combination of DNA and protein is called a nucleosome. The DNA does not leave the nucleus, so when new proteins or other structures need to be made ...
File - Alexis Kezirian
... localization and intensity for LacZ expression when the transgene is not inverted. When the transgene is inverted, LacZ expression for the paternallyinherited transgene is highly upregulated and expressed throughout most of the embryo interior, whereas almost a complete absence of LacZ expression is ...
... localization and intensity for LacZ expression when the transgene is not inverted. When the transgene is inverted, LacZ expression for the paternallyinherited transgene is highly upregulated and expressed throughout most of the embryo interior, whereas almost a complete absence of LacZ expression is ...
Document
... and view the 2D animation and 3D Cartoon Video to see Restriction enzymes in action ...
... and view the 2D animation and 3D Cartoon Video to see Restriction enzymes in action ...
Ch06 Answers to Concept Check Questions
... Answer: Erasure allows eggs to transmit unmethylated copies of the gene to the offspring. FIGURE 6.11. Concept check: What process prevents the binding of CTC-binding factor to the ICR? Answer: Methylation prevents CTC-binding factor from binding to the ICR. FIGURE 6.12. Concept check: What is the ...
... Answer: Erasure allows eggs to transmit unmethylated copies of the gene to the offspring. FIGURE 6.11. Concept check: What process prevents the binding of CTC-binding factor to the ICR? Answer: Methylation prevents CTC-binding factor from binding to the ICR. FIGURE 6.12. Concept check: What is the ...
DNA methylation

DNA methylation is a process by which methyl groups are added to DNA. Methylation modifies the function of the DNA, typically acting to suppress gene transcription. DNA methylation is essential for normal development and is associated with a number of key processes including genomic imprinting, X-chromosome inactivation, suppression of repetitive elements, and carcinogenesis.Two of DNA's four nucleotides, cytosine and adenine, can be methylated. Adenine methylation is restricted to prokaryotes.The rate of cytosine DNA methylation differs strongly between species: 14% of cytosines are methylated in Arabidopsis thaliana, 4% in Mus musculus, 2.3% in Escherichia coli, 0.03% in Drosophila, and virtually none (< 0.0002%) in yeast species.DNA methylation can stably alter the expression of genes in cells as cells divide and differentiate from embryonic stem cells into specific tissues. The resulting change is normally permanent and unidirectional, preventing a cell from reverting to a stem cell or converting into a different cell type. However, DNA methylation can be removed either passively, by dilution as cells divide, or by a faster, active, process. The latter process occurs via hydroxylation of the methyl groups that are to be removed, rather than by complete removal of methyl groups. DNA methylation is typically removed during zygote formation and re-established through successive cell divisions during development. Methylation modifications that regulate gene expression are usually heritable through mitotic cell division; some methylation is also heritable through the specialized meiotic cell division that creates egg and sperm cells, resulting in genomic imprinting. DNA methylation suppresses the expression of endogenous retroviral genes and other harmful stretches of DNA that have been incorporated into the host genome over time. DNA methylation also forms the basis of chromatin structure, which enables a single cell to grow into multiple organs or perform multiple functions. DNA methylation also plays a crucial role in the development of nearly all types of cancer.DNA methylation at the 5 position of cytosine has the specific effect of reducing gene expression and has been found in every vertebrate examined. In adult somatic cells (cells in the body, not used for reproduction), DNA methylation typically occurs in a CpG dinucleotide context; non-CpG methylation is prevalent in embryonic stem cells, and has also been indicated in neural development.