Neurons - Honors Biology 10 - 2222-03
... The messages carried by the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses. Nervous system impulses are transmitted by cells called neurons. ...
... The messages carried by the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses. Nervous system impulses are transmitted by cells called neurons. ...
Vertical Organization of r=Aminobutyric Acid
... least in part, for the additional functional properties that distinguish superficial and deep cortical cells from those lying at the heart of the thalamic terminal layers (e.g., Gilbert and Wiesel, 1979). Horizontal connections, in contrast, would form the basis for interactions between functional c ...
... least in part, for the additional functional properties that distinguish superficial and deep cortical cells from those lying at the heart of the thalamic terminal layers (e.g., Gilbert and Wiesel, 1979). Horizontal connections, in contrast, would form the basis for interactions between functional c ...
Central Nervous System
... • Located in the precentral gyrus of each cerebral hemisphere. • Contains large neurons (pyramidal cells) which project to SC neurons which eventually synapse on skeletal muscles – Allowing for voluntary motor control. – These pathways are known as the corticospinal tracts or pyramidal tracts. ...
... • Located in the precentral gyrus of each cerebral hemisphere. • Contains large neurons (pyramidal cells) which project to SC neurons which eventually synapse on skeletal muscles – Allowing for voluntary motor control. – These pathways are known as the corticospinal tracts or pyramidal tracts. ...
Unit – M Neuron, Impulse Generation, and Reflex Arc Structures and
... When the axon or dendrite is stimulated, sodium gates open which allows some Na+ to enter the axoplasm (interior). Now, the inside becomes more positive than the outside by 40 mv. This is called the Upswing Phase of the action potential. The charge changes from –60 mv to +40 mv. The change is calle ...
... When the axon or dendrite is stimulated, sodium gates open which allows some Na+ to enter the axoplasm (interior). Now, the inside becomes more positive than the outside by 40 mv. This is called the Upswing Phase of the action potential. The charge changes from –60 mv to +40 mv. The change is calle ...
Motor Cortex
... Located in the precentral gyrus of each cerebral hemisphere. Contains large neurons (pyramidal cells) which project to SC neurons which eventually synapse on skeletal muscles ...
... Located in the precentral gyrus of each cerebral hemisphere. Contains large neurons (pyramidal cells) which project to SC neurons which eventually synapse on skeletal muscles ...
Synaptic Democracy and Vesicular Transport in Axons
... the postsynaptic sites of a dendrite). Since vesicles are injected from the soma (anterograde transport), one might expect that synapses proximal to the soma would be preferentially supplied with resources. This problem persists even when the stochastic nature of motor transport and delivery of carg ...
... the postsynaptic sites of a dendrite). Since vesicles are injected from the soma (anterograde transport), one might expect that synapses proximal to the soma would be preferentially supplied with resources. This problem persists even when the stochastic nature of motor transport and delivery of carg ...
Funkcje ruchowe
... Premotor areas - functions Each premotor area contributes to different aspects of motor planning. Studies of the premotor areas have identified several basic features of the neural organization of motor preparation. First, movements that are initiated internally by the subject—such as the sequencin ...
... Premotor areas - functions Each premotor area contributes to different aspects of motor planning. Studies of the premotor areas have identified several basic features of the neural organization of motor preparation. First, movements that are initiated internally by the subject—such as the sequencin ...
Reflections on agranular architecture: predictive coding in the motor
... equations describing the neuronal dynamics implied by generalised predictive coding (e.g., Equation 3 in [30]). Note the hierarchical structure: predictive coding involves recursive interactions among an arbitrary number of hierarchical levels, of which just one, level (i), is shown in full here. Th ...
... equations describing the neuronal dynamics implied by generalised predictive coding (e.g., Equation 3 in [30]). Note the hierarchical structure: predictive coding involves recursive interactions among an arbitrary number of hierarchical levels, of which just one, level (i), is shown in full here. Th ...
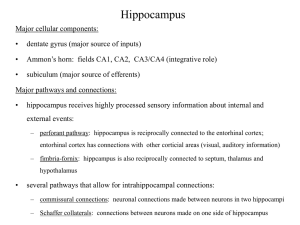
theta oscillation in the hippocampus
... synaptic potentials that entrain the discharge of neuronal populations within the D100–200 ms range. The cellular-synaptic generation of theta activity in the hippocampus was investigated by intracellular recordings from the somata and dendrites of CA1 pyramidal cells in urethaneanesthetized rats. T ...
... synaptic potentials that entrain the discharge of neuronal populations within the D100–200 ms range. The cellular-synaptic generation of theta activity in the hippocampus was investigated by intracellular recordings from the somata and dendrites of CA1 pyramidal cells in urethaneanesthetized rats. T ...
Accurate reconstruction of neuronal morphology
... 6.3.1.2. Injection of biocytin When sharp intracellular electrodes are used, the pipette solution should contain 2-4% biocytin (Sigma) by weight in 1M potassium acetate. This is about the limit in the amount of biocytin that can be dissolved in 1M potassium acetate, and slight warming may be require ...
... 6.3.1.2. Injection of biocytin When sharp intracellular electrodes are used, the pipette solution should contain 2-4% biocytin (Sigma) by weight in 1M potassium acetate. This is about the limit in the amount of biocytin that can be dissolved in 1M potassium acetate, and slight warming may be require ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... e. The main nutritional and metabolic region of the neuron. f. The transmitting or conductive region of the neuron. 7. (Page 6.) What are outgoing signals on neurons called? 8. (Page 6.) On what part of the neuron are action potentials conducted? In which direction do they go? 9. (Page 6.) How are a ...
... e. The main nutritional and metabolic region of the neuron. f. The transmitting or conductive region of the neuron. 7. (Page 6.) What are outgoing signals on neurons called? 8. (Page 6.) On what part of the neuron are action potentials conducted? In which direction do they go? 9. (Page 6.) How are a ...
Anatomy Review - Interactive Physiology
... • At their terminal ends, axons can branch profusely, forming thousands of endings called axon ...
... • At their terminal ends, axons can branch profusely, forming thousands of endings called axon ...
Cerebellum - DENTISTRY 2012
... 1. Molecular Layer- most superficial, consisting of axons of granule cells (parallel fibers) and dendrites of PCs 2. Purkinje Cell Layer- middle layer consisting of a single layer of large neuronal cell bodies (Purkinje cells) 3. Granule Cell Layer- deepest layer (next to white matter) consisting of ...
... 1. Molecular Layer- most superficial, consisting of axons of granule cells (parallel fibers) and dendrites of PCs 2. Purkinje Cell Layer- middle layer consisting of a single layer of large neuronal cell bodies (Purkinje cells) 3. Granule Cell Layer- deepest layer (next to white matter) consisting of ...
PDF
... been set to 0.1 and the mean input firing rate to 85 Hz. The alternation between up states and down states has also been found in several experimental studies using intracellular recordings (right panel). (B) Histogram of the distribution of the membrane potential recorded under the conditions as sh ...
... been set to 0.1 and the mean input firing rate to 85 Hz. The alternation between up states and down states has also been found in several experimental studies using intracellular recordings (right panel). (B) Histogram of the distribution of the membrane potential recorded under the conditions as sh ...
PDF
... distributed primarily in the granule cell areas surrounding the VCN (Fig. IB). The thin (<0.5 pm) labeled fibers entered the cochlear nucleus from its medial aspect by way of the dorsal and intermediate acoustic striae. These thin fibers branched repeatedly and distributed numerous en passant and te ...
... distributed primarily in the granule cell areas surrounding the VCN (Fig. IB). The thin (<0.5 pm) labeled fibers entered the cochlear nucleus from its medial aspect by way of the dorsal and intermediate acoustic striae. These thin fibers branched repeatedly and distributed numerous en passant and te ...
Self-referential forces are sufficient to explain different dendritic
... soma-tropic forces. Bottom row: Dendrites with distinct levels of ...
... soma-tropic forces. Bottom row: Dendrites with distinct levels of ...
Critical Periods:
... – an increase in neural activity will lead to an increase in neuronal connections – this strengthening process involves increasing synaptic input and the dendritic complexity of neurons: 1) more synapses, 2) more dendritic spines, 3) increase in length and branching of dendrites ...
... – an increase in neural activity will lead to an increase in neuronal connections – this strengthening process involves increasing synaptic input and the dendritic complexity of neurons: 1) more synapses, 2) more dendritic spines, 3) increase in length and branching of dendrites ...
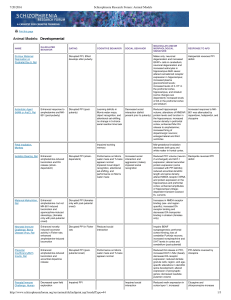
2. Parkinsons diseas and Movement Disorders. 1998
... Different areas of the cerebral cortex (neocortex) may be distinguished from one another by their histological features and neuroanatomical connections. Brodmann’s numbering scheme for cortical areas has been used for many years and will be introduced in this section. Projection areas. By following ...
... Different areas of the cerebral cortex (neocortex) may be distinguished from one another by their histological features and neuroanatomical connections. Brodmann’s numbering scheme for cortical areas has been used for many years and will be introduced in this section. Projection areas. By following ...
... Diverging neural pathways • Diverging neural pathways have one neuron branching out and feeding impulses to many neurons. • This allows for signals from a single source to be sent to several destinations and allows us to co-ordinate control (e.g. when threading a needle. This is fine motor control ...
Cell Surface Molecules Containing IV
... in layer 4 of the primary visual cortex of the cat, where it is associated exclusively with GABAergic local circuit neurons. We have studied this neuronal subset with intracellular electrophysiological recording and dye marking to identify the particular cell types expressing surface GalNac. Five di ...
... in layer 4 of the primary visual cortex of the cat, where it is associated exclusively with GABAergic local circuit neurons. We have studied this neuronal subset with intracellular electrophysiological recording and dye marking to identify the particular cell types expressing surface GalNac. Five di ...
The combinatorics and dynamics of a discrete k winners take all
... neuroscience research on hippocampus. In this model, those k neurons fire whose weighted inputs are maximal. The model tries to mimic the dynamics of the neural activity in the hippocampus, where only a few percentages of the neurons fire at the same time, however, all the neurons eventually fire in ...
... neuroscience research on hippocampus. In this model, those k neurons fire whose weighted inputs are maximal. The model tries to mimic the dynamics of the neural activity in the hippocampus, where only a few percentages of the neurons fire at the same time, however, all the neurons eventually fire in ...
Forea Wang
... system offers to fulfill the promise of controlled, multi-site stimulation in patterns that have not only a temporal component, but also a spatial one, and the integration of inputs from multiple cells in tandem can be investigated. Part of the UROP will involve dynamic discussions on how to design ...
... system offers to fulfill the promise of controlled, multi-site stimulation in patterns that have not only a temporal component, but also a spatial one, and the integration of inputs from multiple cells in tandem can be investigated. Part of the UROP will involve dynamic discussions on how to design ...
Neurons & the Nervous System
... • Afferent (sensory) neurons: send messages from sensory receptors to the spinal cord & brain • Efferent (motor) neurons: relay messages from brain & spinal cord to muscles & glands • Interneurons: transmits neural stimulus between sensory & motor neurons ...
... • Afferent (sensory) neurons: send messages from sensory receptors to the spinal cord & brain • Efferent (motor) neurons: relay messages from brain & spinal cord to muscles & glands • Interneurons: transmits neural stimulus between sensory & motor neurons ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Cellular Neurobiology, 38106 Braunschweig, Germany, and 3AG NIND, HZI, D-38124 Braunschweig, Germany ...
... Cellular Neurobiology, 38106 Braunschweig, Germany, and 3AG NIND, HZI, D-38124 Braunschweig, Germany ...