Introduction to Psychology
... study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior ...
... study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior ...
TWINS AND GENETICS
... same genes might be totally different. In one family, a rare gene C (Family 3) might have a large impact on genetic predisposition to a disease. However, because of its rarity in the general population, the overall population effect of this gene would be small. Some genes that predispose individuals ...
... same genes might be totally different. In one family, a rare gene C (Family 3) might have a large impact on genetic predisposition to a disease. However, because of its rarity in the general population, the overall population effect of this gene would be small. Some genes that predispose individuals ...
novel uses to study complex traits and genetic diseases
... applications, both to simulated and real datasets. For example, the computation of genetic factor scores based on multivariate data could, in certain circumstances, dramatically increase the power to detect quantitative trait loci (QTLs)25. Multivariate methods have been extended recently to maximiz ...
... applications, both to simulated and real datasets. For example, the computation of genetic factor scores based on multivariate data could, in certain circumstances, dramatically increase the power to detect quantitative trait loci (QTLs)25. Multivariate methods have been extended recently to maximiz ...
Genetics Lesson 5 ALL vocabulary
... 5. allele- different forms of the genes that code for different variations of a trait 6. dominant allele- will always show its effect even when only one dominate allele is present in an organisms genotype. 7. genotype- the actual genes (alleles) the organism has. 8. heterozygous- when the two al ...
... 5. allele- different forms of the genes that code for different variations of a trait 6. dominant allele- will always show its effect even when only one dominate allele is present in an organisms genotype. 7. genotype- the actual genes (alleles) the organism has. 8. heterozygous- when the two al ...
Boulder 2014 Friday 9am NGM - Institute for Behavioral Genetics
... The value of DZ twins for within-pair association tests for ruling out population stratification Within-family regression results of the polygenic scores on College and EduYears in the QIMR and Swedish Twin Registry cohorts using SNPs selected from the meta-analysis excluding the QIMR and STR cohor ...
... The value of DZ twins for within-pair association tests for ruling out population stratification Within-family regression results of the polygenic scores on College and EduYears in the QIMR and Swedish Twin Registry cohorts using SNPs selected from the meta-analysis excluding the QIMR and STR cohor ...
Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
... more resemblance to each other than two biological siblings (in terms of personality) ...
... more resemblance to each other than two biological siblings (in terms of personality) ...
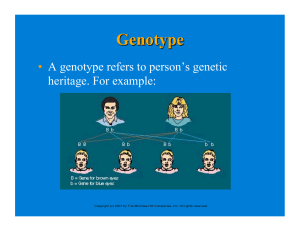
• A genotype refers to person`s genetic heritage. For example:
... carriers- but will not have disease – normal X chromosome protects ...
... carriers- but will not have disease – normal X chromosome protects ...
GenesEnv
... (come from the same parent plant) from Yarrow plant clones grew differently at three different altitudes Cuttings from one plant grew tall at the lowest and the highest elevation But a third cutting remained short at midelevation Even though these plants were genetically identical, their pheno ...
... (come from the same parent plant) from Yarrow plant clones grew differently at three different altitudes Cuttings from one plant grew tall at the lowest and the highest elevation But a third cutting remained short at midelevation Even though these plants were genetically identical, their pheno ...
evolution and genetics in psychology
... B. The contribution of heredity to various psychological attributes is often expressed in terms of a heritability coefficient, a number on a scale from 0 to 1 that expresses the proportion of the variation among individuals that is alleged to be due to heredity. It is important to remember that the ...
... B. The contribution of heredity to various psychological attributes is often expressed in terms of a heritability coefficient, a number on a scale from 0 to 1 that expresses the proportion of the variation among individuals that is alleged to be due to heredity. It is important to remember that the ...
No Slide Title
... We can take a specific family member (proband) and compare their behaviours with people of differing genetic relatedness. If a characteristic is more common in closely related individuals then we may conclude that it has a genetic component. However, family members are typically raised in simi ...
... We can take a specific family member (proband) and compare their behaviours with people of differing genetic relatedness. If a characteristic is more common in closely related individuals then we may conclude that it has a genetic component. However, family members are typically raised in simi ...
BG Studies of Psychopathology
... • Several twin studies suggest a genetic influence: Plomin estimates a MZ concordance rate of 60% (i.e. 1000 times the population rate), while DZ concordances are lower • Initially, autism was thought to be environmentally determined (cold, rejecting parents) but is now considered one of the most he ...
... • Several twin studies suggest a genetic influence: Plomin estimates a MZ concordance rate of 60% (i.e. 1000 times the population rate), while DZ concordances are lower • Initially, autism was thought to be environmentally determined (cold, rejecting parents) but is now considered one of the most he ...
Document
... • Important to know whether genes contribute to phenotypic variation of quantitative character • Heritability is a population trait, not property of individual • Not same as familial trait shared by members of a family • Characters are heritable only if similarity arises from shared genotypes – esti ...
... • Important to know whether genes contribute to phenotypic variation of quantitative character • Heritability is a population trait, not property of individual • Not same as familial trait shared by members of a family • Characters are heritable only if similarity arises from shared genotypes – esti ...
Genetics
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
Genetics - Dave Brodbeck
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
Active GE relation
... • Genes never cause behavior directly • The behavioral consequences of genetic instructions depends on environment ...
... • Genes never cause behavior directly • The behavioral consequences of genetic instructions depends on environment ...
Behavior Genetics and Evolutionary Psychology
... Critics of separated twin studies note that such similarities can be found between strangers. However, researchers point out that differences between fraternal twins are greater than identical twins. ...
... Critics of separated twin studies note that such similarities can be found between strangers. However, researchers point out that differences between fraternal twins are greater than identical twins. ...
Biological theories
... Mesomorph Some research finds criminals are more mesomorphic, slightly shorter and lighter--why? ...
... Mesomorph Some research finds criminals are more mesomorphic, slightly shorter and lighter--why? ...
natural selection
... With roughly similar environment, and educational and intellectual levels as that of the birth mothers. ...
... With roughly similar environment, and educational and intellectual levels as that of the birth mothers. ...
Chapter 1 - FacultyWeb Support Center
... Phenotypes include ◦ physical characteristics (such as height, weight, and hair color) ◦ psychological characteristics (such as personality and intelligence) ...
... Phenotypes include ◦ physical characteristics (such as height, weight, and hair color) ◦ psychological characteristics (such as personality and intelligence) ...
B1 You and Your Genes
... Doctors can test embryos, foetuses and adults for certain alleles by genetic tests What happens during embryo selection (pre-implantation genetic diagnosis) The implications of the use of genetic testing by others (e.g. by employers and insurance companies) and comparisons of technical feasibi ...
... Doctors can test embryos, foetuses and adults for certain alleles by genetic tests What happens during embryo selection (pre-implantation genetic diagnosis) The implications of the use of genetic testing by others (e.g. by employers and insurance companies) and comparisons of technical feasibi ...
RAFT: Genetics - Catawba County Schools
... to new generations Utilize appropriate information systems to build an understanding of heredity and genetics Objectives: The students will KNOW Vocabulary: gene, DNA, RNA, recessive trait, dominant trait, bacteria, virus, mutation, zygote. The students will UNDERSTAND THAT Genes are units of ...
... to new generations Utilize appropriate information systems to build an understanding of heredity and genetics Objectives: The students will KNOW Vocabulary: gene, DNA, RNA, recessive trait, dominant trait, bacteria, virus, mutation, zygote. The students will UNDERSTAND THAT Genes are units of ...
Twin study

Twin studies reveal the absolute and relative importance of environmental and genetic influences on individuals in a sample. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in content fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the methods used in behavior genetics, which includes all data that are genetically informative – siblings, adoptees, pedigree data etc.Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of varying family environments (across pairs) and widely differing genetic makeup: ""identical"" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share nearly 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) is due to experiences that one twin has but not the other twin. ""Fraternal"" or dizygotic (DZ) twins share only about 50% of their genes. Thus powerful tests of the effects of genes can be made. Twins share many aspects of their environment (e.g., uterine environment, parenting style, education, wealth, culture, community) by virtue of being born in the same time and place. The presence of a given genetic trait in only one member of a pair of identical twins (called discordance) provides a powerful window into environmental effects.The classical twin design compares the similarity of monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins. If identical twins are considerably more similar than fraternal twins (which is found for most traits), this implicates that genes play an important role in these traits. By comparing many hundreds of families of twins, researchers can then understand more about the roles of genetic effects, shared environment, and unique environment in shaping behavior.Modern twin studies have shown that almost all traits are in part influenced by genetic differences, with some characteristics showing a strong influence (e.g. height), others an intermediate level (e.g. personality traits) and some more complex heritabilities, with evidence for different genes affecting different aspects of the trait — as in the case of autism.