two parts/categories roots shoots stem leaves flowers roots The
... soil situations, reducing soil oxygen levels, will kill roots and lead to a shallow root system. The structure and growth habits of roots have a pronounced effect on Size and vigor of the plants Adaptation to certain soils Response to cultural practices Because they are out of sight, roots are ...
... soil situations, reducing soil oxygen levels, will kill roots and lead to a shallow root system. The structure and growth habits of roots have a pronounced effect on Size and vigor of the plants Adaptation to certain soils Response to cultural practices Because they are out of sight, roots are ...
Growing Haskap / Blue honeysuckle in Canada
... If you get soil testing done, it is highly unlikely that any Windbreaks: Protection to the west and north of any prairie orchard is highly recommended. Winter damage testing company will know what to recommend is often a function of desiccation caused by direct specifically for haskap due to lack of ...
... If you get soil testing done, it is highly unlikely that any Windbreaks: Protection to the west and north of any prairie orchard is highly recommended. Winter damage testing company will know what to recommend is often a function of desiccation caused by direct specifically for haskap due to lack of ...
Nonflowering_Plants
... Peat moss often forms extensive sphagnum bogs that can reach an age of 10,000 years or more. Because of the chemical activity of peat moss, the water stored in the bog is acidic, an environment that does not favor the activity of decomposing bacteria and fungi. Dead Sphagnum and other plants, includ ...
... Peat moss often forms extensive sphagnum bogs that can reach an age of 10,000 years or more. Because of the chemical activity of peat moss, the water stored in the bog is acidic, an environment that does not favor the activity of decomposing bacteria and fungi. Dead Sphagnum and other plants, includ ...
Seed Plants - mrs
... Is a flower with 6 petals a monocot? To answer this question you need to determine if 6 is a multiple of 3. A number is a multiple of 3 if there is a nonzero whole number that, when multiplied by 3, gives you that number. In this case, 6 is a multiple of 3 because you can multiply 2 (a nonzero whole ...
... Is a flower with 6 petals a monocot? To answer this question you need to determine if 6 is a multiple of 3. A number is a multiple of 3 if there is a nonzero whole number that, when multiplied by 3, gives you that number. In this case, 6 is a multiple of 3 because you can multiply 2 (a nonzero whole ...
Gardens of Oceania
... tectonic plate moves under the Pacific plate. These pieces of land have been colonised since their formation by plant species that have come from elsewhere, carried by winds, ocean currents or birds. When humans first arrived on these islands they certainly found edible species there, but at the sam ...
... tectonic plate moves under the Pacific plate. These pieces of land have been colonised since their formation by plant species that have come from elsewhere, carried by winds, ocean currents or birds. When humans first arrived on these islands they certainly found edible species there, but at the sam ...
Stairway To Heaven Jacob`s Ladder
... cleaned up in early spring before it resumes active growth for the season. Deer don't particularly care for this plant and will usually leave it alone in favor of tastier treats. It has no significant negative characteristics. Stairway To Heaven Jacob's Ladder is recommended for the following landsc ...
... cleaned up in early spring before it resumes active growth for the season. Deer don't particularly care for this plant and will usually leave it alone in favor of tastier treats. It has no significant negative characteristics. Stairway To Heaven Jacob's Ladder is recommended for the following landsc ...
petal 22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants TEKS 6G, 10B
... 22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants TEKS 6G, 10B Flowers contain reproductive organs protected by specialized leaves. • Sepals and petals are modified leaves. – Sepals are outermost layer that protects developing flower ...
... 22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants TEKS 6G, 10B Flowers contain reproductive organs protected by specialized leaves. • Sepals and petals are modified leaves. – Sepals are outermost layer that protects developing flower ...
22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants TEKS 6G
... 22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants TEKS 6G, 10B The student is expected to: 6G recognize the significance of meiosis to sexual reproduction and 10B describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of transport, reproduction, and response in plants ...
... 22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants TEKS 6G, 10B The student is expected to: 6G recognize the significance of meiosis to sexual reproduction and 10B describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of transport, reproduction, and response in plants ...
Fact Sheet: Nodding Thistle
... either Metsulfuron-methyl or 2,4-D, is registered for use on nodding thistle. Always check product labels to ensure the herbicide is registered for use on the target plant in Canada by the Pest Management Regulatory Agency. Always read and follow label directions. Consult your local Agricultural Fie ...
... either Metsulfuron-methyl or 2,4-D, is registered for use on nodding thistle. Always check product labels to ensure the herbicide is registered for use on the target plant in Canada by the Pest Management Regulatory Agency. Always read and follow label directions. Consult your local Agricultural Fie ...
Chapter 22-Gymnosperms Key innovations in the evolution of land
... The ovule is composed of tissue of the megasporangium inside a protective coating called the integument. The integument has a small hole, Within the megasporangium, meiosis produces a megaspore which gives rise to the female gametophyte and ultimately the egg cell is produced in the archegonium. ...
... The ovule is composed of tissue of the megasporangium inside a protective coating called the integument. The integument has a small hole, Within the megasporangium, meiosis produces a megaspore which gives rise to the female gametophyte and ultimately the egg cell is produced in the archegonium. ...
pub3368SweetOliveLeafScorchFINAL / 1.65MB
... Sweet olive’s dark, shiny green leaves and white fragrant flowers make it a popular choice of gardeners and landscape professionals. Sweet olive is susceptible to a bacterial disease called leaf scorch, which is caused by Xylella fastidiosa. Different strains of this bacterium are known to cause sev ...
... Sweet olive’s dark, shiny green leaves and white fragrant flowers make it a popular choice of gardeners and landscape professionals. Sweet olive is susceptible to a bacterial disease called leaf scorch, which is caused by Xylella fastidiosa. Different strains of this bacterium are known to cause sev ...
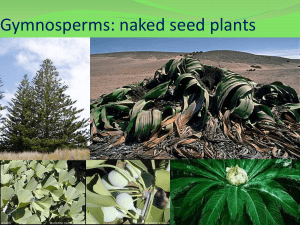
Gymnosperms
... A. Gymnosperms include: pines, firs, spruces, ginkgos, and cycads. B. Possession of a true seed. C. Contain secondary growth that forms woody stems D. No water necessary for sperm to reach egg. E. Leaves usually needle-like; exceptions exist. F. Sweden’s pines produce 75,000 tons of pollen each Spri ...
... A. Gymnosperms include: pines, firs, spruces, ginkgos, and cycads. B. Possession of a true seed. C. Contain secondary growth that forms woody stems D. No water necessary for sperm to reach egg. E. Leaves usually needle-like; exceptions exist. F. Sweden’s pines produce 75,000 tons of pollen each Spri ...
Flower and Fruit Drop - The University of Arizona Extension
... to the female part of flower in self-pollinating types of plants. Plants in this group include tomato, pepper, and snap bean. Pecan also are wind pollinated. In greenhouses bees are often introduced to facilitate pollination. Physiological Differences Vegetable and melon plants that require the tran ...
... to the female part of flower in self-pollinating types of plants. Plants in this group include tomato, pepper, and snap bean. Pecan also are wind pollinated. In greenhouses bees are often introduced to facilitate pollination. Physiological Differences Vegetable and melon plants that require the tran ...
The Good Earth - Iowa State University Extension and Outreach
... heavier soils. A small amount of well-rotted manure can be worked into the soil at the bottom of the trench before planting. Space the crowns 12 to 18 inches apart in rows that are 4 to 5 feet apart. Spread the roots out in the trench with the buds pointing upward. After planting, completely fill in ...
... heavier soils. A small amount of well-rotted manure can be worked into the soil at the bottom of the trench before planting. Space the crowns 12 to 18 inches apart in rows that are 4 to 5 feet apart. Spread the roots out in the trench with the buds pointing upward. After planting, completely fill in ...
Topic 5: Seedless Vascular Plants (Ch. 29)
... anchor vascular plants and enable them to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. allow the shoot system to grow taller. Leaves: organs that increase the surface area of vascular plants, capturing more solar energy for photosynthesis In terms of size and complexity, leaves can be classif ...
... anchor vascular plants and enable them to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. allow the shoot system to grow taller. Leaves: organs that increase the surface area of vascular plants, capturing more solar energy for photosynthesis In terms of size and complexity, leaves can be classif ...
topic5 BIOL1030NR
... anchor vascular plants and enable them to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. allow the shoot system to grow taller. Leaves: organs that increase the surface area of vascular plants, capturing more solar energy for photosynthesis In terms of size and complexity, leaves can be classif ...
... anchor vascular plants and enable them to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. allow the shoot system to grow taller. Leaves: organs that increase the surface area of vascular plants, capturing more solar energy for photosynthesis In terms of size and complexity, leaves can be classif ...
IDENTIFICATION OF MINNESOTA INVASIVE
... METHOD OF REPRODUCTION (biennial—1st year basal rosette; 2nd year bloom, set seed, die) Seeds—100+ seed produced by each plant, will remain viable in soil for up to 5 years VECTORS OF SPREAD Short-distance dispersal of seed by explosive release (6 feet) Long-distance dispersal of seed by human ...
... METHOD OF REPRODUCTION (biennial—1st year basal rosette; 2nd year bloom, set seed, die) Seeds—100+ seed produced by each plant, will remain viable in soil for up to 5 years VECTORS OF SPREAD Short-distance dispersal of seed by explosive release (6 feet) Long-distance dispersal of seed by human ...
01469-03.1 Identifying_Plant_Structures_and_Their_Function
... B. Roots have several functions. 1. Roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil. 2. Roots support the plant in an upright position. 3. Roots distribute food energy produced by the leaves downwards to the growing root tip. 4. Some plants utilize their roots for specialized food storage. C. The fir ...
... B. Roots have several functions. 1. Roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil. 2. Roots support the plant in an upright position. 3. Roots distribute food energy produced by the leaves downwards to the growing root tip. 4. Some plants utilize their roots for specialized food storage. C. The fir ...
AP Biology 2016 Free-Response Questions
... season for an annual plant 3. The graph above illustrates the percent dry weight of different parts of a particular annual plant (plants that live less than one year) from early May to late August. The percent dry weight can be used to estimate the amount of energy a plant uses to produce its leaves ...
... season for an annual plant 3. The graph above illustrates the percent dry weight of different parts of a particular annual plant (plants that live less than one year) from early May to late August. The percent dry weight can be used to estimate the amount of energy a plant uses to produce its leaves ...
Chapter 1 Parts of Plants A2 Lesson Preview LESSON 1 Carrots
... Like animals and all other living things, plants are made of cells (sehlz). A cell is the smallest and most basic unit of a living thing. Plant cells have stiff walls that support the plant and give it shape. Plants cannot move from place to place to find food and water like animals can. So how do p ...
... Like animals and all other living things, plants are made of cells (sehlz). A cell is the smallest and most basic unit of a living thing. Plant cells have stiff walls that support the plant and give it shape. Plants cannot move from place to place to find food and water like animals can. So how do p ...
Biology, 8th Edition
... In Chapter 27, you learned that some seedless vascular plants are heterosporous. However, all seed plants are heterosporous and produce two types of spores: microspores and megaspores. In fact, heterospory is a requirement of seed production. Following fertilization in seed plants, an ovule, which i ...
... In Chapter 27, you learned that some seedless vascular plants are heterosporous. However, all seed plants are heterosporous and produce two types of spores: microspores and megaspores. In fact, heterospory is a requirement of seed production. Following fertilization in seed plants, an ovule, which i ...
Cultural Requirements of Phalaenopsis By George Vasquez
... Commercial growers realize that bottom heat is the best source of heat for plants; it warms the pots so the plants grow faster. In the greenhouse, lay inexpensive propagating mats on the benches. These heat the pots and, therefore, warm the plants to a proper temperature, without wasting energy heat ...
... Commercial growers realize that bottom heat is the best source of heat for plants; it warms the pots so the plants grow faster. In the greenhouse, lay inexpensive propagating mats on the benches. These heat the pots and, therefore, warm the plants to a proper temperature, without wasting energy heat ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.