Nutrient Recycling Worksheet
... There is a _______________________________________ on earth e.g. you are probably aware of the water cycle – where water is _____________________________________ in nature. There are similar cycles for all nutrients. When plants and animals die, their ________________________________________________ ...
... There is a _______________________________________ on earth e.g. you are probably aware of the water cycle – where water is _____________________________________ in nature. There are similar cycles for all nutrients. When plants and animals die, their ________________________________________________ ...
Biogeochemical Cycles
... 3. Release – Denitrifying bacteria convert N03- back to N2 (denitrification); detrivorous bacteria convert organic compounds back to NH4+ (ammonification); animals excrete NH4+ (or NH3) urea, or uric acid. ...
... 3. Release – Denitrifying bacteria convert N03- back to N2 (denitrification); detrivorous bacteria convert organic compounds back to NH4+ (ammonification); animals excrete NH4+ (or NH3) urea, or uric acid. ...
Vocabulary for Plants
... Vocabulary for Plants 1. Plants – are multicellular eukaryotes, most of which make their own food through photosynthesis and have adapted to live on land. 2. cuticle – is a waxy, waterproof layer that helps hold in moisture in plants. 3. stomata – tiny holes in the cuticle. Special cells allow stoma ...
... Vocabulary for Plants 1. Plants – are multicellular eukaryotes, most of which make their own food through photosynthesis and have adapted to live on land. 2. cuticle – is a waxy, waterproof layer that helps hold in moisture in plants. 3. stomata – tiny holes in the cuticle. Special cells allow stoma ...
6-2.4 notes Plants - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... Absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Store extra food for the plants. The more root space that is available, the more water and nutrients it can absorb. There are two types of root systems: fibrous roots and taproots. 1. Fibrous roots consist of several main roots that branch off to form a mass ...
... Absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Store extra food for the plants. The more root space that is available, the more water and nutrients it can absorb. There are two types of root systems: fibrous roots and taproots. 1. Fibrous roots consist of several main roots that branch off to form a mass ...
Introduction to Plants
... Auxins – responsible for growth at the end of stems – cut them off, and plant will send out shoots from the sides of stems. Pruning uses this info to make bushier plants. Others include cytokinins for root growth, Giberellins for seed growth, ethylene for fruit ripening, and abscisic acid for fruit ...
... Auxins – responsible for growth at the end of stems – cut them off, and plant will send out shoots from the sides of stems. Pruning uses this info to make bushier plants. Others include cytokinins for root growth, Giberellins for seed growth, ethylene for fruit ripening, and abscisic acid for fruit ...
The Canadian Light Source is the only light source in the world
... Drought Tolerance in Wheat Nutrients in plant tissues and soils can be mapped on the micro and nano scale. In this image, the nutrients in a droughtsensitive and high-yield wheat variety known as Superb is compared to the lower-yield but drought resistant Stettler variety. ...
... Drought Tolerance in Wheat Nutrients in plant tissues and soils can be mapped on the micro and nano scale. In this image, the nutrients in a droughtsensitive and high-yield wheat variety known as Superb is compared to the lower-yield but drought resistant Stettler variety. ...
Plant Nutrition
... both normal growth and reproduction and for a specific structure or metabolic function. • There are 17 essential nutrients for most vascular plants. ...
... both normal growth and reproduction and for a specific structure or metabolic function. • There are 17 essential nutrients for most vascular plants. ...
Plant Function
... both normal growth and reproduction and for a specific structure or metabolic function. • There are 17 essential nutrients for most vascular plants. ...
... both normal growth and reproduction and for a specific structure or metabolic function. • There are 17 essential nutrients for most vascular plants. ...
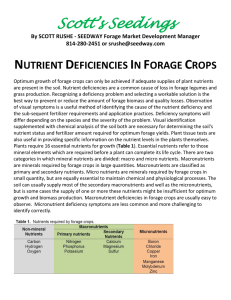
Forage Nutrients
... or purplish color. In some phosphorus deficient grasses, leaf blade margins tend to curl upward resulting in blade rolling and often purplish in color on the undersides. Roots are light brown and restricted in growth. Thin stands with coarse plants also characterize phosphorus deficiency. Since spar ...
... or purplish color. In some phosphorus deficient grasses, leaf blade margins tend to curl upward resulting in blade rolling and often purplish in color on the undersides. Roots are light brown and restricted in growth. Thin stands with coarse plants also characterize phosphorus deficiency. Since spar ...
Systems in Plants
... Distinguishing Features of a Plant • Typically green in colour – Why? – Chlorophyll – green pigmented molecules found in chloroplasts • Function: absorbs light and aids in photosynthesis by converting it into energy ...
... Distinguishing Features of a Plant • Typically green in colour – Why? – Chlorophyll – green pigmented molecules found in chloroplasts • Function: absorbs light and aids in photosynthesis by converting it into energy ...
Z Z Plant
... Use low to moderate light. Avoid any direct sunlight as this may burn or cause damage to the leaves. Water: Water the soil only when it dries out. Never over water, and ensure that there is good drainage. Usually every two weeks is sufficient, but it may be able to go longer in between watering. Rep ...
... Use low to moderate light. Avoid any direct sunlight as this may burn or cause damage to the leaves. Water: Water the soil only when it dries out. Never over water, and ensure that there is good drainage. Usually every two weeks is sufficient, but it may be able to go longer in between watering. Rep ...
objectives
... soil is not susceptible to the same nutrient deficiencies. For example, coarse-textured soils low in organic matter are susceptible to sulfur deficiencies whereas sulfur is usually in adequate supply in clayey soils or soils high in organic matter. Table 3 lists the soil conditions that lead to defi ...
... soil is not susceptible to the same nutrient deficiencies. For example, coarse-textured soils low in organic matter are susceptible to sulfur deficiencies whereas sulfur is usually in adequate supply in clayey soils or soils high in organic matter. Table 3 lists the soil conditions that lead to defi ...
Document
... Which three elements are essential for healthy plant growth? 1. Nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur. 2. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. 3. Nitrogen, sulphur and potassium. 4. Sulphur, potassium and phosphorus. ...
... Which three elements are essential for healthy plant growth? 1. Nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur. 2. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. 3. Nitrogen, sulphur and potassium. 4. Sulphur, potassium and phosphorus. ...
2003 North Dakota State FFA
... 38. A biological agent or virus that can cause a disease is known as a(n): A. BSE C. Pathogen B. Bactericide D. Prion 39. Cuttings of plants that are difficult to root are often _______ to increase the surface area for rooting and applying rooting hormone. A. de-barked C. pruned B. pinched D. wounde ...
... 38. A biological agent or virus that can cause a disease is known as a(n): A. BSE C. Pathogen B. Bactericide D. Prion 39. Cuttings of plants that are difficult to root are often _______ to increase the surface area for rooting and applying rooting hormone. A. de-barked C. pruned B. pinched D. wounde ...
Figure 18.1
... 2) Better soil structure and improved water holding capacity Better soil structure may enhance root development and exploration (see above). Good soil structure and plentiful humus content contributes to higher amounts of plantavailable water following rains or irrigation. This results in better pla ...
... 2) Better soil structure and improved water holding capacity Better soil structure may enhance root development and exploration (see above). Good soil structure and plentiful humus content contributes to higher amounts of plantavailable water following rains or irrigation. This results in better pla ...
Exploration and New Netherland Review Packet
... Flowers/fruits are important because they produce and protect seeds. ...
... Flowers/fruits are important because they produce and protect seeds. ...
Name - Fairfield Public Schools
... What are the differences between monocots and dicots in terms of venation, cotyledons, petal number, and leaf vein pattern. Be able to give examples of each. Ch. 29 Plant Structures: ...
... What are the differences between monocots and dicots in terms of venation, cotyledons, petal number, and leaf vein pattern. Be able to give examples of each. Ch. 29 Plant Structures: ...
Nitrogen and Phosphorous Cycles
... Completes N cycle by returning N2 to atmosphere (prevents N added as fertilizer from being “locked” in roots and soil) Requires energy; Reduction of nitrate/nitrite NO2 or NO3 + energy→N2 + O2 ...
... Completes N cycle by returning N2 to atmosphere (prevents N added as fertilizer from being “locked” in roots and soil) Requires energy; Reduction of nitrate/nitrite NO2 or NO3 + energy→N2 + O2 ...
No Slide Title - MrNoviasA-maze
... What are the 3 factors that a plant needs to perform photosynthesis ...
... What are the 3 factors that a plant needs to perform photosynthesis ...
Plant Growth
... Q5. Complete the given passage by given words. Plants make their own ____. They use a gas in the air called carbon dioxide, water and nutrients from the ____. They take these up through their _____. These nutrients travel up the ____ of the plant and reach out to the leaves. The stem of the _____ i ...
... Q5. Complete the given passage by given words. Plants make their own ____. They use a gas in the air called carbon dioxide, water and nutrients from the ____. They take these up through their _____. These nutrients travel up the ____ of the plant and reach out to the leaves. The stem of the _____ i ...
File
... 16. The processes called ____________________ creates carbohydrates and puts oxygen into the atmosphere. 17. __________________ is the process that bacteria use to cause the decay of dead organisms. 18. Humans have caused an imbalance in the carbon cycle through ______________. 19. _____________ con ...
... 16. The processes called ____________________ creates carbohydrates and puts oxygen into the atmosphere. 17. __________________ is the process that bacteria use to cause the decay of dead organisms. 18. Humans have caused an imbalance in the carbon cycle through ______________. 19. _____________ con ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.