Botany Presentation - St. Lucie County Extension Office
... sucrose + O2 Carbon dioxide + water + light energy http://wps.prenhall.com/esm_freeman_biosci_1/0,6452,498648-,00.html ...
... sucrose + O2 Carbon dioxide + water + light energy http://wps.prenhall.com/esm_freeman_biosci_1/0,6452,498648-,00.html ...
The Plant Kingdom
... 1. ______________ _______________: This is a single layer of cells containing few or no ____________________. The cells are quite transparent and permit most of the light that strikes them to pass through to the underlying cells. The upper surface is covered with a waxy, waterproof _________________ ...
... 1. ______________ _______________: This is a single layer of cells containing few or no ____________________. The cells are quite transparent and permit most of the light that strikes them to pass through to the underlying cells. The upper surface is covered with a waxy, waterproof _________________ ...
AKUBOH OLIVIA 13/SCI03/001 BCH 413 How Humans Affect
... The nitrogen (N) cycle is a natural cycle that moves nitrogen through different compounds in the ecosystem. The nitrogen cycle is important because all organisms require nitrogen in order to live. Virtually everywhere prehistoric people lived they modified the environment for their benefit by the us ...
... The nitrogen (N) cycle is a natural cycle that moves nitrogen through different compounds in the ecosystem. The nitrogen cycle is important because all organisms require nitrogen in order to live. Virtually everywhere prehistoric people lived they modified the environment for their benefit by the us ...
131, Plant Structures - Colorado State University Extension
... Plant cells are grouped into tissues based on similar characteristics, then into five distinct structures (organs). Cells – Individual building blocks for life processes and growth. Common cells contain genetic matter (deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA) and metabolic organelles but they are mostly water ...
... Plant cells are grouped into tissues based on similar characteristics, then into five distinct structures (organs). Cells – Individual building blocks for life processes and growth. Common cells contain genetic matter (deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA) and metabolic organelles but they are mostly water ...
File
... sunlight and carbon dioxide to produce their own food. That’s why they are called producers. When an animal eats a plant, energy that the plant got from the sun is transferred to the animal. An animal that eats plants is called an herbivore. Since it is the first animal in the food chain, it is also ...
... sunlight and carbon dioxide to produce their own food. That’s why they are called producers. When an animal eats a plant, energy that the plant got from the sun is transferred to the animal. An animal that eats plants is called an herbivore. Since it is the first animal in the food chain, it is also ...
Plants - TeacherWeb
... • Chlorophyll is found in the plant cells of leaves • Leaves contain two parts: • Blade: thin, flat part of a leaf that is ...
... • Chlorophyll is found in the plant cells of leaves • Leaves contain two parts: • Blade: thin, flat part of a leaf that is ...
Chicago Hardy Fig Tree FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FIRST
... Water the plants thoroughly letting the excess water drain through the bottom of the pot. PLANT PREPARATION Cut away any yellow or brown leaves or broken stems that may have occurred. This grooming is completely normal and will take place as the plant grows. Branching out will rapidly follow any pru ...
... Water the plants thoroughly letting the excess water drain through the bottom of the pot. PLANT PREPARATION Cut away any yellow or brown leaves or broken stems that may have occurred. This grooming is completely normal and will take place as the plant grows. Branching out will rapidly follow any pru ...
Araceae Family - Missouri State University
... o specialized type of miniature inflorescence called a cyathium occurs in about 1,500 of the species in the genera Euphorbia and Chamaesyce o consists of a single female flower with a 3-lobed ovary surrounded by a number of male flowers consisting of a single stamen each o male cyathia may have colo ...
... o specialized type of miniature inflorescence called a cyathium occurs in about 1,500 of the species in the genera Euphorbia and Chamaesyce o consists of a single female flower with a 3-lobed ovary surrounded by a number of male flowers consisting of a single stamen each o male cyathia may have colo ...
Nonvascular Seedless Plants
... plants – Lycophyta Club mosses – Psilophyta Whiskferns – Spenophyta Horsetails – Pterophyta Ferns ...
... plants – Lycophyta Club mosses – Psilophyta Whiskferns – Spenophyta Horsetails – Pterophyta Ferns ...
Slide 1
... Arabidopsis thaliana is an ideal plant organism to be used for studying and experimenting because it behaves extremely similar to many crop plants found throughout the United States and Canada. It is also useful to study because it grows fast and matures quickly. In our experiment, we are testing th ...
... Arabidopsis thaliana is an ideal plant organism to be used for studying and experimenting because it behaves extremely similar to many crop plants found throughout the United States and Canada. It is also useful to study because it grows fast and matures quickly. In our experiment, we are testing th ...
Introduction and Menus To begin in English, Press 1 We at Cochlear
... It is interesting to note that carnivorous plants attract insects for two distinct purposes: pollination and nutrition. In both cases scents may be used, as well as ultraviolet pattern techniques that "bull’s eye" key flower or trap parts. This is not surprising since flowers and traps are both modi ...
... It is interesting to note that carnivorous plants attract insects for two distinct purposes: pollination and nutrition. In both cases scents may be used, as well as ultraviolet pattern techniques that "bull’s eye" key flower or trap parts. This is not surprising since flowers and traps are both modi ...
Ecology Unit Study Guide
... 12. Calculate the amount of calories for each trophic level (up to tertiary) if the producers of an ecosystem provide 50,000 calories. 13. Identify the nutrient cycle connected with the greenhouse effect. 14. Draw and identify the components of the water cycle. 15. What is the greenhouse effect and ...
... 12. Calculate the amount of calories for each trophic level (up to tertiary) if the producers of an ecosystem provide 50,000 calories. 13. Identify the nutrient cycle connected with the greenhouse effect. 14. Draw and identify the components of the water cycle. 15. What is the greenhouse effect and ...
PDF version
... produces seeds (yes or no), and if free water is required for fertilization (yes or no). plant ...
... produces seeds (yes or no), and if free water is required for fertilization (yes or no). plant ...
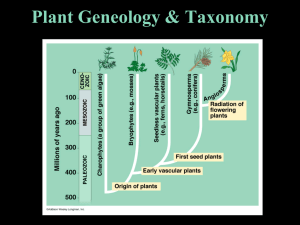
Plant Geneology & Taxonomy
... – Leaves are needle-like or scaly – Do not produce flowers – Many produce cones to protect seeds - conifers – Seeds not enclosed in fruit – Stems are woody • Example: ...
... – Leaves are needle-like or scaly – Do not produce flowers – Many produce cones to protect seeds - conifers – Seeds not enclosed in fruit – Stems are woody • Example: ...
World of Plants
... absorption • Water moves from cell to cell until it reaches the xylem vessels • Xylem carries water and dissolved minerals to the leaves for photosynthesis • The sugars made in photosynthesis are carried from the leaves in phloem tubes ...
... absorption • Water moves from cell to cell until it reaches the xylem vessels • Xylem carries water and dissolved minerals to the leaves for photosynthesis • The sugars made in photosynthesis are carried from the leaves in phloem tubes ...
NO Vascular tissues - Effingham County Schools
... inside seeds and fruits so the young of seed plants tend to survive better. The spores of ferns and mosses must land in a wet habitat. If they do not, they will die. ...
... inside seeds and fruits so the young of seed plants tend to survive better. The spores of ferns and mosses must land in a wet habitat. If they do not, they will die. ...
Temperate deciduous forest
... • Human populations are quite high in this zone (which includes many of world's largest cities), fairly pleasant climatically and very productive of harvestable plant and animal life. Because the soil is excellent for agriculture, much of it has been cleared for a very long time all over the world f ...
... • Human populations are quite high in this zone (which includes many of world's largest cities), fairly pleasant climatically and very productive of harvestable plant and animal life. Because the soil is excellent for agriculture, much of it has been cleared for a very long time all over the world f ...
Plant Structures & Processes
... 0 Each stomata is surrounded by two guard cells 0 Guard cells open during the day allowing water to transpire 0 Guard cells close at night and during dry conditions to prevent water loss ...
... 0 Each stomata is surrounded by two guard cells 0 Guard cells open during the day allowing water to transpire 0 Guard cells close at night and during dry conditions to prevent water loss ...
Week 1 Topic: Plant anatomy Reading: Chapter 24, sections 1
... • Leaves: made up of a blade and a petiole. On the underside, stomata, allow air into and out of the spongy ground tissue, the mesophyl, where photosynthesis takes place. Vascular bundles bring water into a leave, and carry sugars away. • Stems: supports the leaves and raised them up into the sunlig ...
... • Leaves: made up of a blade and a petiole. On the underside, stomata, allow air into and out of the spongy ground tissue, the mesophyl, where photosynthesis takes place. Vascular bundles bring water into a leave, and carry sugars away. • Stems: supports the leaves and raised them up into the sunlig ...
Plant Adaptation to Habitats Tour
... 3. Succulent stems store water for the plant, which helps it survive drought. 4. Many cacti are able to grow new roots (sometimes called rain roots) very quickly when it rains—to absorb the rainwater from the upper few inches of the soil. These ...
... 3. Succulent stems store water for the plant, which helps it survive drought. 4. Many cacti are able to grow new roots (sometimes called rain roots) very quickly when it rains—to absorb the rainwater from the upper few inches of the soil. These ...
Chapter 42a
... • Leaves: made up of a blade and a petiole. On the underside, stomata, allow air into and out of the spongy ground tissue, the mesophyl, where photosynthesis takes place. Vascular bundles bring water into a leave, and carry sugars away. • Stems: supports the leaves and raised them up into the sunlig ...
... • Leaves: made up of a blade and a petiole. On the underside, stomata, allow air into and out of the spongy ground tissue, the mesophyl, where photosynthesis takes place. Vascular bundles bring water into a leave, and carry sugars away. • Stems: supports the leaves and raised them up into the sunlig ...
Controlled release nutrition for strawberries - Haifa
... 3.7.2 Phosphorus (P) Phosphorus is important in order for the plants to store energy, and plays a role in fruit development. It is often present in adequate amounts for good strawberry growth, but much of it is not readily available to the plants because it gets tied up in both the mineral and organ ...
... 3.7.2 Phosphorus (P) Phosphorus is important in order for the plants to store energy, and plays a role in fruit development. It is often present in adequate amounts for good strawberry growth, but much of it is not readily available to the plants because it gets tied up in both the mineral and organ ...
ovary
... 2. Plants have special tissues that move water and nutrients up from the soil, and others that distribute the products of photosynthesis (oxygen and glucose) throughout the plant ...
... 2. Plants have special tissues that move water and nutrients up from the soil, and others that distribute the products of photosynthesis (oxygen and glucose) throughout the plant ...
Mini-Lesson: Punnett Squares
... Each square represents a potential offspring. Discuss the results and ask students to explain why each offspring in this example will be tall. Ask students to hypothesize how a short plant could be produced. Can two tall plants produce a short plant? Complete the next example: Plant 1 = Mixed Hybrid ...
... Each square represents a potential offspring. Discuss the results and ask students to explain why each offspring in this example will be tall. Ask students to hypothesize how a short plant could be produced. Can two tall plants produce a short plant? Complete the next example: Plant 1 = Mixed Hybrid ...
Reading Your Orchid Plants
... or hang from. Plants grown this way get all their nutrients from the fertilizer in the water. Like to dry out between watering. ...
... or hang from. Plants grown this way get all their nutrients from the fertilizer in the water. Like to dry out between watering. ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.