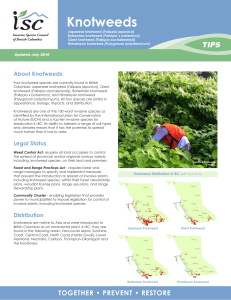
Knotweeds - Invasive Species Council of BC
... Treated knotweed canes can be left on site to compost. Elevate cut or mowed stems until they are completely desiccated and no longer viable, and not permitted to touch soil or water during the desiccation process. Once completely brown and dry, they may be safely composted, as long as seeds are not ...
... Treated knotweed canes can be left on site to compost. Elevate cut or mowed stems until they are completely desiccated and no longer viable, and not permitted to touch soil or water during the desiccation process. Once completely brown and dry, they may be safely composted, as long as seeds are not ...
Beware of Ragweed "Relatives"
... About 22 million people in the United States who have seasonal allergies are affected by ragweed. This plant produces light, airy pollens that can travel up to 400 miles. The ragweed season in this country is usually from August to November, peaking in mid-September. If you know you are allergic to ...
... About 22 million people in the United States who have seasonal allergies are affected by ragweed. This plant produces light, airy pollens that can travel up to 400 miles. The ragweed season in this country is usually from August to November, peaking in mid-September. If you know you are allergic to ...
Genetic Disorders Leading to Hypoglycaemia
... Introduction An overview of glucose physiology Glucose is the principal substrate for energy metabolism and disorders that affect its availability or use can result in hypoglycaemia. A normal blood glucose level is maintained by the interplay of glucose production and glucose utilisation. The key so ...
... Introduction An overview of glucose physiology Glucose is the principal substrate for energy metabolism and disorders that affect its availability or use can result in hypoglycaemia. A normal blood glucose level is maintained by the interplay of glucose production and glucose utilisation. The key so ...
mechanism of photosynthesis
... It has been observed that light affects respiration and the rate of respiration in light may be three to five times higher than the respiration in darkness. Such type of respiration is called photorespiration.In photorespiration, temperature plays a very vital role, its rate being very high in betwe ...
... It has been observed that light affects respiration and the rate of respiration in light may be three to five times higher than the respiration in darkness. Such type of respiration is called photorespiration.In photorespiration, temperature plays a very vital role, its rate being very high in betwe ...
a sustainable waste management solution and effective soil
... position in the global cacao supply chain, supplying beans to Mondelēz International. As Mondelēz demands an increasingly better quality of crop and higher yields, cacao growing techniques have evolved accordingly, in order to meet demand and maximise return. As part of this process, growers are enc ...
... position in the global cacao supply chain, supplying beans to Mondelēz International. As Mondelēz demands an increasingly better quality of crop and higher yields, cacao growing techniques have evolved accordingly, in order to meet demand and maximise return. As part of this process, growers are enc ...
Impact Assessment of Soil Contamination with Antibiotics (for
... complexes with fungicidal preparation. The restoration of population density of bacteria was observed after 60 and 120 days of the experiment. It was virtually complete upon application of antibiotics in minimum concentration, 75-85% of the control in the case of maximum concentrations of antibiotic ...
... complexes with fungicidal preparation. The restoration of population density of bacteria was observed after 60 and 120 days of the experiment. It was virtually complete upon application of antibiotics in minimum concentration, 75-85% of the control in the case of maximum concentrations of antibiotic ...
[W][OA] - Plant Physiology
... and Zhang, 2010). The exine is then formed by sequential polymerization of sporopollenin, which consists of phenols and fatty acid derivatives (Morant et al., 2007; Ariizumi and Toriyama, 2011; Li and Zhang, 2010). During the tetrad stage, sporopollenin is deposited onto the primexine. Once that firs ...
... and Zhang, 2010). The exine is then formed by sequential polymerization of sporopollenin, which consists of phenols and fatty acid derivatives (Morant et al., 2007; Ariizumi and Toriyama, 2011; Li and Zhang, 2010). During the tetrad stage, sporopollenin is deposited onto the primexine. Once that firs ...
Wild About Wildflowers! — A Classroom Activity Guide
... For this guide, wildflowers are defined as flowers that grow in the wild or on their own, without cultivation. The Florida Wildflower Foundation informs us that wildflowers have adapted to Florida’s conditions and pests; typically require less water, fertilizer and pesticides than other flowers; and ...
... For this guide, wildflowers are defined as flowers that grow in the wild or on their own, without cultivation. The Florida Wildflower Foundation informs us that wildflowers have adapted to Florida’s conditions and pests; typically require less water, fertilizer and pesticides than other flowers; and ...
Alcohol Dehydrogenase and Ethanol in the
... cambium of all species. The ethanol concentrations in the cambium of trees at Cranberry Lake were: A. saccharum, 123.4 ± 7.6 nmol g-' fresh weight; P. grandidentata, 56.5 ± 6.4 nmol g-' fresh weight; and P. tremuloides, 34.7 ± 10.0 nmol g-' fresh weight. There was no significant relationship between ...
... cambium of all species. The ethanol concentrations in the cambium of trees at Cranberry Lake were: A. saccharum, 123.4 ± 7.6 nmol g-' fresh weight; P. grandidentata, 56.5 ± 6.4 nmol g-' fresh weight; and P. tremuloides, 34.7 ± 10.0 nmol g-' fresh weight. There was no significant relationship between ...
FINAL 8/28/2015 1 PFC Committee Report/Minutes AAFCO Annual
... for Growth and Reproduction recommends the minimum crude protein concentration of dry matter to be 22.5%. Therefore, the expected apparent digestibility for crude protein in a diet formulated to meet the AAFCO Dog Food Nutrient Profile for Growth and Reproduction is at least 80% [(18 x (1.00)/22.5) ...
... for Growth and Reproduction recommends the minimum crude protein concentration of dry matter to be 22.5%. Therefore, the expected apparent digestibility for crude protein in a diet formulated to meet the AAFCO Dog Food Nutrient Profile for Growth and Reproduction is at least 80% [(18 x (1.00)/22.5) ...
Fusarium wilt Resistance in Eight Identified Multiple Disease Resistant
... causing pathogen in Cucumis melo, has been established which causes yellowing, necrosis and finally wilting under conditions of artificial inoculation. Fusarium wilt of melons occurs worldwide (3,7), and Risser, et al. in 1976 (4) proposed four races of the pathogen (Races 0, 1, 2, and 1-2). However ...
... causing pathogen in Cucumis melo, has been established which causes yellowing, necrosis and finally wilting under conditions of artificial inoculation. Fusarium wilt of melons occurs worldwide (3,7), and Risser, et al. in 1976 (4) proposed four races of the pathogen (Races 0, 1, 2, and 1-2). However ...
Plant Physiology
... Study of function How things work e.g. what controls growth e.g. what controls flowering and fruiting ...
... Study of function How things work e.g. what controls growth e.g. what controls flowering and fruiting ...
Introduction Milk is the exclusive nutrient source for the neonate. ... practices and availability of highly selected sows have allowed for...
... practices and availability of highly selected sows have allowed for increased litter sizes. The ability of the sow to produce adequate milk for large litters is limiting to neonate growth and total pig production (Boyd & Kensinger, 1998). Many studies have focused on improving nutrition for the high ...
... practices and availability of highly selected sows have allowed for increased litter sizes. The ability of the sow to produce adequate milk for large litters is limiting to neonate growth and total pig production (Boyd & Kensinger, 1998). Many studies have focused on improving nutrition for the high ...
Cannas for the Florida Landscape1
... already. Remove this shoot also when its blooms are withered. Another flowering shoot will soon develop on the node below the second shoot. If the first and second shoots are not removed, all the nutrition will be used for the developing seed pods, and the flower cluster on the third node usually wi ...
... already. Remove this shoot also when its blooms are withered. Another flowering shoot will soon develop on the node below the second shoot. If the first and second shoots are not removed, all the nutrition will be used for the developing seed pods, and the flower cluster on the third node usually wi ...
Succulent of the Month - San Gabriel Cactus and Succulent Society
... and keeping the young seedlings alive is often a challenge. Crassulas to Crave Crassula alstonii a wonderful miniature species with tight hemispherical leaves piling on one another. A specimen from the Huntington Library conservatory is shown below. ...
... and keeping the young seedlings alive is often a challenge. Crassulas to Crave Crassula alstonii a wonderful miniature species with tight hemispherical leaves piling on one another. A specimen from the Huntington Library conservatory is shown below. ...
DATA SHEET FOR IAS
... Flowering occurs mainly in the third year of growth but under unfavourable conditions such as grazing, cutting or nutrient deficiency, flowering is postponed until sufficient reserves have been accumulated. In pastures, flowering may be delayed by up to 7 years, and anecdotes of 12 years have been r ...
... Flowering occurs mainly in the third year of growth but under unfavourable conditions such as grazing, cutting or nutrient deficiency, flowering is postponed until sufficient reserves have been accumulated. In pastures, flowering may be delayed by up to 7 years, and anecdotes of 12 years have been r ...
Longitudinal Study of Nutrient Intakes in Infants Aged 12
... was 605 µg/d. Preformed vitamin A intake exceeded the UL (600 µg/d) in 20% of 12-month-olds. Toddlers 18 Months of Age. The usual energy and nutrient intake distributions of 18-month-olds are displayed in Table 3. The mean energy intake was 1089 kcal/d for boys and girls combined. Those values were ...
... was 605 µg/d. Preformed vitamin A intake exceeded the UL (600 µg/d) in 20% of 12-month-olds. Toddlers 18 Months of Age. The usual energy and nutrient intake distributions of 18-month-olds are displayed in Table 3. The mean energy intake was 1089 kcal/d for boys and girls combined. Those values were ...
Amino acid composition of the aerial part of G. pratense L., G
... Materials obtained from plants growing in Leningrad region at the stage of fruit development in july-august of 2011. The aerial part of G. pratense and G. palustre was harvested in Pudost’ of Gatchinskiy district. The raw material of G. sylvaticum was collected beside Lembolovo of Vsevolozhskiy dist ...
... Materials obtained from plants growing in Leningrad region at the stage of fruit development in july-august of 2011. The aerial part of G. pratense and G. palustre was harvested in Pudost’ of Gatchinskiy district. The raw material of G. sylvaticum was collected beside Lembolovo of Vsevolozhskiy dist ...
Diversity And Classification of Flowering Plants:
... (L. armoracia, "horseradish" + pertaining to the country) Part used: ROOT (more as a flavoring than a vegetable) ...
... (L. armoracia, "horseradish" + pertaining to the country) Part used: ROOT (more as a flavoring than a vegetable) ...
Print this article - University of Toronto Journal of Undergraduate Life
... plants. The presence of algae in freshwater creates competition for CO2 during the day, but CO2 is more available through respiration during the night. Thus, practicing nocturnal carbon fixation, CAM usage may be advantageous for freshwater plants [1]. Water availability imposes an immediate stress ...
... plants. The presence of algae in freshwater creates competition for CO2 during the day, but CO2 is more available through respiration during the night. Thus, practicing nocturnal carbon fixation, CAM usage may be advantageous for freshwater plants [1]. Water availability imposes an immediate stress ...
The sucrose-cleaving enzymes of plants are crucial for development
... in potato tubers by antisense technology leads to a marked reduction in their starch content and, thereby, to a marked reduction in tuber yield26. During tomato fruit development, sucrose synthase, but not acid invertase, is positively correlated with fruit relative growth rate and with starch conte ...
... in potato tubers by antisense technology leads to a marked reduction in their starch content and, thereby, to a marked reduction in tuber yield26. During tomato fruit development, sucrose synthase, but not acid invertase, is positively correlated with fruit relative growth rate and with starch conte ...
Abstract - Trees for Life Journal
... mineral which may be the mechanism by which the hemopoeitic tissue becomes flavored with more available iron. A significant association of serum retinol with hematocrit, serum iron and serum ferritin has been reported by Bloem et al (1989) in a cross sectional study of children in north east Thailan ...
... mineral which may be the mechanism by which the hemopoeitic tissue becomes flavored with more available iron. A significant association of serum retinol with hematocrit, serum iron and serum ferritin has been reported by Bloem et al (1989) in a cross sectional study of children in north east Thailan ...
Profile of Invasive Plant Species within the Peace River Regional
... Germination happens all season because it is triggered by temperature. It has a short maturation period and produces viable seeds a few days after pollination. The first line of control should be preventing the spread of these plants to noninfested areas. Prevention measures include cleaning clothin ...
... Germination happens all season because it is triggered by temperature. It has a short maturation period and produces viable seeds a few days after pollination. The first line of control should be preventing the spread of these plants to noninfested areas. Prevention measures include cleaning clothin ...
wild flowers of india
... can be about a metre tall. The dark green, ovate leaves are irregularly lobed and toothed. The trumpet-shaped flowers are white and tinged with violet on the outer side. The flowers are very noticeable on account of their large size. The datura flowers from the beginning of the winter and through ti ...
... can be about a metre tall. The dark green, ovate leaves are irregularly lobed and toothed. The trumpet-shaped flowers are white and tinged with violet on the outer side. The flowers are very noticeable on account of their large size. The datura flowers from the beginning of the winter and through ti ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.





![[W][OA] - Plant Physiology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015058058_1-9cefc7621f9eb60812ee98259ea6bb4d-300x300.png)

















