Perennial Plant List
... Clusters of indigo-blue, pealike flowers are followed by interesting blueblack pods. Foliage is blue-green. Can be used as a small shrub. Takes a few years to become established but is very long-lived. Abundance of bright orange flowers in June lasting for many weeks. Host plant for the monarch butt ...
... Clusters of indigo-blue, pealike flowers are followed by interesting blueblack pods. Foliage is blue-green. Can be used as a small shrub. Takes a few years to become established but is very long-lived. Abundance of bright orange flowers in June lasting for many weeks. Host plant for the monarch butt ...
PPT as PDF
... Indo-Pakistani subcontinent since ancient times and is available in the market year round. ...
... Indo-Pakistani subcontinent since ancient times and is available in the market year round. ...
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
... 16 The table shows the deficiency symptoms that result from a lack of some substances in the human diet. Which symptom results from a deficiency in iron? deficiency symptom A ...
... 16 The table shows the deficiency symptoms that result from a lack of some substances in the human diet. Which symptom results from a deficiency in iron? deficiency symptom A ...
Aug2015 No Plumes on Pampas Grass
... *Pruning in late winter prior to the new growing season. Use hedge shears, lopping shears, or power pruners to cut it back. Some websites state to cut it down to roughly two feet, while others suggest cutting it down close to the ground. Regardless of how low it is cut, wise gardeners will be sure t ...
... *Pruning in late winter prior to the new growing season. Use hedge shears, lopping shears, or power pruners to cut it back. Some websites state to cut it down to roughly two feet, while others suggest cutting it down close to the ground. Regardless of how low it is cut, wise gardeners will be sure t ...
DALMATIAN TOADFLAX: Options for control
... flowering to fall. Dicamba (Banvel, Clarity, Van• Bio-agent Mecinus janthinus has been extremely quish) 2-4 qt/acre, pre-bloom to flowering stage. successful in Lincoln County. • Must use a surfactant due to the waxy leaf surCultural: face, for adequate herbicide penetration. • Healthy competitive v ...
... flowering to fall. Dicamba (Banvel, Clarity, Van• Bio-agent Mecinus janthinus has been extremely quish) 2-4 qt/acre, pre-bloom to flowering stage. successful in Lincoln County. • Must use a surfactant due to the waxy leaf surCultural: face, for adequate herbicide penetration. • Healthy competitive v ...
Characterization of AtAAP1 function in amino acid uptake by the root
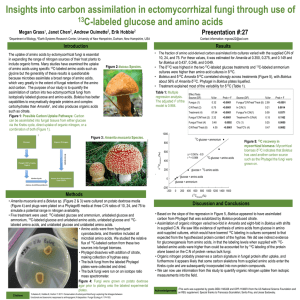
... for gluconeogenesis from amino acids, in that the labeling levels when supplied with 13Clabeled amino acids were higher than could be accounted for by 13C labeling of the protein alone based on the C:N of protein versus bulk fungi. • Organic nitrogen probably preserves a carbon signature in fungal p ...
... for gluconeogenesis from amino acids, in that the labeling levels when supplied with 13Clabeled amino acids were higher than could be accounted for by 13C labeling of the protein alone based on the C:N of protein versus bulk fungi. • Organic nitrogen probably preserves a carbon signature in fungal p ...
SANDEEP DALAL
... - The ovules are borne on megasporophylls which may be clustered to form the female cones. - Megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to form four megaspores. One of the megaspores enclosed within the Megasporangium (nucellus) develops into a multicellular female gametophyte that bears two or more a ...
... - The ovules are borne on megasporophylls which may be clustered to form the female cones. - Megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to form four megaspores. One of the megaspores enclosed within the Megasporangium (nucellus) develops into a multicellular female gametophyte that bears two or more a ...
Forest Soils vs. Agricultural Soils
... they tend to be more variable in their physical and chemical properties when compared to agricultural soils. The O horizon is usually more important in forest soil, as it is a primary source of nutrients. Agricultural soils associated with rangelands and grasslands often have horizons similar to for ...
... they tend to be more variable in their physical and chemical properties when compared to agricultural soils. The O horizon is usually more important in forest soil, as it is a primary source of nutrients. Agricultural soils associated with rangelands and grasslands often have horizons similar to for ...
SCIENCE FOCUS 9 UNIT 1
... A pollen tube then ______________________________________________________________ and sperm ____________________________________________________________________ As a result ________________________________________________________________ (120) 20. The process of _____________________________________ ...
... A pollen tube then ______________________________________________________________ and sperm ____________________________________________________________________ As a result ________________________________________________________________ (120) 20. The process of _____________________________________ ...
Field Crop Descriptions PDF | 441.93KB 10/12/2015 2:27:24 PM
... means one bouse) refers to those plants with two distinct types of flowers (male and female) found on the same plant. Male flowers (the tassel) are located at the top of the plant. The female flowers are found in the ears. The stem of com may vary from 2 to 20 feet tall in different typeS. The root ...
... means one bouse) refers to those plants with two distinct types of flowers (male and female) found on the same plant. Male flowers (the tassel) are located at the top of the plant. The female flowers are found in the ears. The stem of com may vary from 2 to 20 feet tall in different typeS. The root ...
plant anatomy lab
... 2. Explain how the guard cells regulate the opening and closing of the stomata? 3. Why was the nail polish applied to the under side of the leaf? 4. In what tissue layer of leaves are guard cells most prominent? Station 2: 5. Describe the difference in stem structure between a monocot and a dicot. ...
... 2. Explain how the guard cells regulate the opening and closing of the stomata? 3. Why was the nail polish applied to the under side of the leaf? 4. In what tissue layer of leaves are guard cells most prominent? Station 2: 5. Describe the difference in stem structure between a monocot and a dicot. ...
Oh Say Can You Seed - Alabama Ag In The Classroom
... Seed, by Bonnie Worth has been selected. The text is written in the fashion of Dr. Seuss and features The Cat in the Hat, Thing One, and Thing Two. The lessons included in this manual go along with Oh Say Can You Seed. The lessons can be taught effectively without the use of the text. A copy of the ...
... Seed, by Bonnie Worth has been selected. The text is written in the fashion of Dr. Seuss and features The Cat in the Hat, Thing One, and Thing Two. The lessons included in this manual go along with Oh Say Can You Seed. The lessons can be taught effectively without the use of the text. A copy of the ...
Dia 1 - Spate Irrigation
... Sorghum is grown in warm or hot regions that have summer rain-fall, even if rainfall is as low as 400-600 mm. The most favorable mean temperature is about 37oC. The minimum temperature for growth is 15oC. The sorghum plants seems to withstand extreme heat better than other crops. Sorghum is practica ...
... Sorghum is grown in warm or hot regions that have summer rain-fall, even if rainfall is as low as 400-600 mm. The most favorable mean temperature is about 37oC. The minimum temperature for growth is 15oC. The sorghum plants seems to withstand extreme heat better than other crops. Sorghum is practica ...
Growing Cucumbers in Greenhouses Types HGA-00434
... The optimum germination temperature for seedless varieties is 80° to 82°F while seeded varieties germinate well at 70° to 75°F. The soil temperature should not drop below 60°F during germination. Cover the seeded flats with glass or plastic to reduce heat loss and to prevent drying. Remove the cover ...
... The optimum germination temperature for seedless varieties is 80° to 82°F while seeded varieties germinate well at 70° to 75°F. The soil temperature should not drop below 60°F during germination. Cover the seeded flats with glass or plastic to reduce heat loss and to prevent drying. Remove the cover ...
garden curriculum
... Read the following story: Once there was a beautiful lake in China. In its waters grew the sacred lotus plant. Each year, seeds from the lotus flower fell into the water and sank to the muddy bottom. Over many years, the lake dried up. The lotus seeds, which were very hard and covered with a tough o ...
... Read the following story: Once there was a beautiful lake in China. In its waters grew the sacred lotus plant. Each year, seeds from the lotus flower fell into the water and sank to the muddy bottom. Over many years, the lake dried up. The lotus seeds, which were very hard and covered with a tough o ...
Northeast Natives - River Street Flowerland
... This underused iris happily grows and blooms in partial shade. Its blue-violet flowers cover the grassy clumps of foliage in late spring and make an attractive accent to rock cress (Arabis) and creeping phlox (Phlox subulata). Several varieties are available and form fast-spreading (but non-aggressi ...
... This underused iris happily grows and blooms in partial shade. Its blue-violet flowers cover the grassy clumps of foliage in late spring and make an attractive accent to rock cress (Arabis) and creeping phlox (Phlox subulata). Several varieties are available and form fast-spreading (but non-aggressi ...
Plants: A First Look - Discovery Education
... ferns, conifers, and flowering plants. The program shows how plants exist in very different environments. The video shows how all plants share characteristics with other living things. It first focuses on the needs of the students themselves. In order to survive, the students need water to drink. Th ...
... ferns, conifers, and flowering plants. The program shows how plants exist in very different environments. The video shows how all plants share characteristics with other living things. It first focuses on the needs of the students themselves. In order to survive, the students need water to drink. Th ...
Flowering Annuals
... Wilt and root rot diseases are difficult to control. Care should be taken to avoid planting unhealthy infected plants. If these disease problems have been observed in previous years, a new planting site should be selected. Chemical control is possible but impractical for most homeowners. Rotating pl ...
... Wilt and root rot diseases are difficult to control. Care should be taken to avoid planting unhealthy infected plants. If these disease problems have been observed in previous years, a new planting site should be selected. Chemical control is possible but impractical for most homeowners. Rotating pl ...
Crambe cordifolia - Woodinville Water District
... Crambe cordifolia is a large perennial that requires a lot of space. It has a foliage mound of huge, cabbage-like, green leaves which are usually deeply lobed. In early summer, small, white flowers appear in a large, baby's breath-like cloud of sweetly fragrant bloom. Flowers bloom spectacularly for ...
... Crambe cordifolia is a large perennial that requires a lot of space. It has a foliage mound of huge, cabbage-like, green leaves which are usually deeply lobed. In early summer, small, white flowers appear in a large, baby's breath-like cloud of sweetly fragrant bloom. Flowers bloom spectacularly for ...
ACANT H- ACEAE
... Flowers often sub tended by p romi nen t bracts Coroll a five-lobed, various ly bila biate, or un il abiate Stamens fou r or two, if two often w it h two staminod es, anthers often hav e offset or mi ssing thec ae. Fruit often exp losively dehiscent; Seeds with an enlarged and speciali zed funiculu ...
... Flowers often sub tended by p romi nen t bracts Coroll a five-lobed, various ly bila biate, or un il abiate Stamens fou r or two, if two often w it h two staminod es, anthers often hav e offset or mi ssing thec ae. Fruit often exp losively dehiscent; Seeds with an enlarged and speciali zed funiculu ...
Read the complete press article
... Nitrogen-fixing legume species can help increase productivity at low cost if the Rhizobia, beneficial microbes living in symbiosis with the plants’ roots, can fix nitrogen efficiently. For each legume species there is a specific and effective strain of Rhizobium which is needed to fix nitrogen succe ...
... Nitrogen-fixing legume species can help increase productivity at low cost if the Rhizobia, beneficial microbes living in symbiosis with the plants’ roots, can fix nitrogen efficiently. For each legume species there is a specific and effective strain of Rhizobium which is needed to fix nitrogen succe ...
Chapter 2. - Maryland Nursery Landscape and Greenhouse
... dry out quickly. It must be weed and disease free. Most nurseries use commercially prepared media, such as Jiffy Mix or ProMix. These all contain peat, vermiculite and a low concentration of fertilizer to nourish the seedling after germination. Once the seedlings have developed their first set of tr ...
... dry out quickly. It must be weed and disease free. Most nurseries use commercially prepared media, such as Jiffy Mix or ProMix. These all contain peat, vermiculite and a low concentration of fertilizer to nourish the seedling after germination. Once the seedlings have developed their first set of tr ...
AG-PSB-02.441-08.6p Reproducing Plants
... • IMPERFECT FLOWERS - Flowers that lack either the stamen or pistil. • Exception: Monoecious plants may have both male and female imperfect flowers on them. Corn is an example. ...
... • IMPERFECT FLOWERS - Flowers that lack either the stamen or pistil. • Exception: Monoecious plants may have both male and female imperfect flowers on them. Corn is an example. ...
reproducing plants
... PERFECT FLOWERS - Contain the stamen and pistil in the same flower. IMPERFECT FLOWERS - Flowers that lack either the stamen or pistil. Exception: Monoecious plants may have both male and female imperfect flowers on them. Corn is an example. ...
... PERFECT FLOWERS - Contain the stamen and pistil in the same flower. IMPERFECT FLOWERS - Flowers that lack either the stamen or pistil. Exception: Monoecious plants may have both male and female imperfect flowers on them. Corn is an example. ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.