7 Water - Minerals-Vitamins Fill in the Blanks - mrs
... • __________ of vitamins can block one or more specific ___________ reactions in a cell. This may ________ metabolic balance within a cell and entire body ...
... • __________ of vitamins can block one or more specific ___________ reactions in a cell. This may ________ metabolic balance within a cell and entire body ...
Plant Physiology, Fifth Edition
... ©2012 Sinauer Associates, Inc. This material cannot be copied, reproduced, manufactured or disseminated in any form without express written permission from the publisher. ...
... ©2012 Sinauer Associates, Inc. This material cannot be copied, reproduced, manufactured or disseminated in any form without express written permission from the publisher. ...
B0910A Meet the Plants Unit 1 - Member`s Guide
... chicken, ham, or bacon to eat. If you explore your refrigerator more closely, you may find eggs, milk, cream, butter, cheese, yogurt, and ice cream. All these foods came from animals that eat plants for food. Chickens, pigs, cows, and sheep eat grains and hay, which are dried seeds and stems from co ...
... chicken, ham, or bacon to eat. If you explore your refrigerator more closely, you may find eggs, milk, cream, butter, cheese, yogurt, and ice cream. All these foods came from animals that eat plants for food. Chickens, pigs, cows, and sheep eat grains and hay, which are dried seeds and stems from co ...
Superstar Spirea
... This is an exciting smaller, naturally dwarf spirea that requires minimal pruning; new leaves start out scarlet, becoming dark green, then change to a brilliant bronze in fall; pink blossoms cover the shrub all summer long; a sure winner in the landscape ...
... This is an exciting smaller, naturally dwarf spirea that requires minimal pruning; new leaves start out scarlet, becoming dark green, then change to a brilliant bronze in fall; pink blossoms cover the shrub all summer long; a sure winner in the landscape ...
CB098-008.41_Roots - Workforce Solutions
... This product is sponsored by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The information contained in this product was created by a grantee organization and does not necessarily ref ...
... This product is sponsored by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The information contained in this product was created by a grantee organization and does not necessarily ref ...
Review #3 Chapters 9 – 10
... a. The light reactions convert solar energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH b. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar c. Photosystem I contains P700 chlorophyll a molecules at the reaction center; photosystem II contains P680 molecules d. In chemiosmosis, electro ...
... a. The light reactions convert solar energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH b. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar c. Photosystem I contains P700 chlorophyll a molecules at the reaction center; photosystem II contains P680 molecules d. In chemiosmosis, electro ...
3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant 2.3.7 Functions of Meiosis
... The pollen tube grows towards chemicals released by the ovule – chemotropism The haploid generative nucleus divides by mitosis as it moves down the pollen tube to form two haploid sperm nuclei or male gametes When the pollen tube reaches the micropyle the male gametes go into the embryo sac ...
... The pollen tube grows towards chemicals released by the ovule – chemotropism The haploid generative nucleus divides by mitosis as it moves down the pollen tube to form two haploid sperm nuclei or male gametes When the pollen tube reaches the micropyle the male gametes go into the embryo sac ...
Lesson 1 How Does a Seed Become a Plant?
... Designate a wall or bulletin board where bags may be taped or pinned for easy observation. Discuss students’ predictions about what will occur. If they suggest seeds will sprout, ask whether or not all three kinds of seeds will sprout at the same time, and whether or not all the seeds of one kind (e ...
... Designate a wall or bulletin board where bags may be taped or pinned for easy observation. Discuss students’ predictions about what will occur. If they suggest seeds will sprout, ask whether or not all three kinds of seeds will sprout at the same time, and whether or not all the seeds of one kind (e ...
Isolation and Characterization of Nitrogen
... gate of the area. At each of the collection sites, spatula was used to remove the over laying earth and sample collected from about 3 cm depth. ...
... gate of the area. At each of the collection sites, spatula was used to remove the over laying earth and sample collected from about 3 cm depth. ...
Understanding Soil Texture and Structure
... Objective 3: Describe soil structure, its formation, and importance. • A. Soil structure is the arrangement of the soil particles into clusters or aggregates of various sizes and shapes. Aggregates that occur naturally in the soil are referred to as peds, while clumps of soil caused by tillage are ...
... Objective 3: Describe soil structure, its formation, and importance. • A. Soil structure is the arrangement of the soil particles into clusters or aggregates of various sizes and shapes. Aggregates that occur naturally in the soil are referred to as peds, while clumps of soil caused by tillage are ...
Propagation of Flowers and Ornamental Plants by Specialized
... vegetative plant organs like sucker, tuber, corm, runner, rhizome etc. B. Specialized Vegetative Structures B.1. Bulb A bulb is a modified orthotropic underground stem consisting of basal plate (bottom of bulb from which roots grow), a terminal bud and numerous scale leaves (swollen bases of foliage ...
... vegetative plant organs like sucker, tuber, corm, runner, rhizome etc. B. Specialized Vegetative Structures B.1. Bulb A bulb is a modified orthotropic underground stem consisting of basal plate (bottom of bulb from which roots grow), a terminal bud and numerous scale leaves (swollen bases of foliage ...
Science of Life Explorations: Plants as Living Things
... This includes plants. However, some plants can reproduce asexually (without two sources of genes) because they and produce small ‘daughter’ plants or plantlets through their roots or by creating runners. The common houseplant, the spider plant, is an easy-to -recognize example of this. This lesson f ...
... This includes plants. However, some plants can reproduce asexually (without two sources of genes) because they and produce small ‘daughter’ plants or plantlets through their roots or by creating runners. The common houseplant, the spider plant, is an easy-to -recognize example of this. This lesson f ...
Section 3 * Vascular Plants
... – Native to American Southwest – Turns brown and curls into a ball during a drought • Will uncurl after a few hours if moistened (Resurrection Plant) ...
... – Native to American Southwest – Turns brown and curls into a ball during a drought • Will uncurl after a few hours if moistened (Resurrection Plant) ...
Soil Formation
... layer of soil. Soil scientists estimate that in the very best soil forming conditions, soil forms at a rate of about 1mm/year. In poor conditions, it may take thousands of years! Weathering ...
... layer of soil. Soil scientists estimate that in the very best soil forming conditions, soil forms at a rate of about 1mm/year. In poor conditions, it may take thousands of years! Weathering ...
Scientific Name: Anthoxanthum nitens (Weber) Y. Schouten
... Storage: Store dry at room temperature (Smreciu et al. 2002). Longevity: Seed maintains viability up to three years (Smreciu et al. 2002). Propagation Natural Regeneration: Can produce by seed or rhizomes (vegetative). New plants are commonly produced vegetatively as many seeds are non-viable (Rook ...
... Storage: Store dry at room temperature (Smreciu et al. 2002). Longevity: Seed maintains viability up to three years (Smreciu et al. 2002). Propagation Natural Regeneration: Can produce by seed or rhizomes (vegetative). New plants are commonly produced vegetatively as many seeds are non-viable (Rook ...
IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT)
... The plant actually develops best in areas where the summers are cool. Hence, it is no surprise that the chiretta can thrive and flourish both in conditions where there is full sunlight as well as partial shade. The chiretta plants are able to withstand temperatures as low as -15° C and still continu ...
... The plant actually develops best in areas where the summers are cool. Hence, it is no surprise that the chiretta can thrive and flourish both in conditions where there is full sunlight as well as partial shade. The chiretta plants are able to withstand temperatures as low as -15° C and still continu ...
REVIEW Sauropus androgynus (L.) Merrill
... system, our body entirely depend upon dietary sources to meet the needs of this vitamin3. Apart from the well-known roles in vision, vitamin A is also important for several other physiological processes including, foetal development, cell growth and regulation of immune system45. According to the si ...
... system, our body entirely depend upon dietary sources to meet the needs of this vitamin3. Apart from the well-known roles in vision, vitamin A is also important for several other physiological processes including, foetal development, cell growth and regulation of immune system45. According to the si ...
answers - Parkway C-2
... 23. Inferring What is the function of the pollination drop (sticky substance) secreted by female pine cones? What would happen if it were not present? 24. Predicting Some plants form flowers that produce stamens but no carpels. Could fruit form on one of these flowers? Explain your answer. ...
... 23. Inferring What is the function of the pollination drop (sticky substance) secreted by female pine cones? What would happen if it were not present? 24. Predicting Some plants form flowers that produce stamens but no carpels. Could fruit form on one of these flowers? Explain your answer. ...
canopy - California Academy of Sciences
... This depends on which flower each student noticed being visited by a pollinator. Butterflies are attracted to bright colors and feed on nectar. The nectar guides, or patterns on a flower’s petals point out the path to the nectar. Butterfly-pollinated flowers often grow in clusters which allow butter ...
... This depends on which flower each student noticed being visited by a pollinator. Butterflies are attracted to bright colors and feed on nectar. The nectar guides, or patterns on a flower’s petals point out the path to the nectar. Butterfly-pollinated flowers often grow in clusters which allow butter ...
Propagating Tropical Fruit - Miami
... Once the mature seeds have been collected and cleaned, they are ready to be sown. Seeds with a very hard seed coat may benefit from soaking in clean water for 24 to 48 hours. It is important that a well-draining, aerated and sterile medium is used. Seeds may be sown directly on top of the media in a ...
... Once the mature seeds have been collected and cleaned, they are ready to be sown. Seeds with a very hard seed coat may benefit from soaking in clean water for 24 to 48 hours. It is important that a well-draining, aerated and sterile medium is used. Seeds may be sown directly on top of the media in a ...
Bougainvillea spp. - Environmental Horticulture
... and could be planted more Invasive potential: not known to be invasive Pest resistance: long-term health usually not affected by pests ...
... and could be planted more Invasive potential: not known to be invasive Pest resistance: long-term health usually not affected by pests ...
Rainbow Fetterbush
... Rainbow Fetterbush will grow to be about 5 feet tall at maturity, with a spread of 6 feet. It tends to fill out right to the ground and therefore doesn't necessarily require facer plants in front, and is suitable for planting under power lines. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions c ...
... Rainbow Fetterbush will grow to be about 5 feet tall at maturity, with a spread of 6 feet. It tends to fill out right to the ground and therefore doesn't necessarily require facer plants in front, and is suitable for planting under power lines. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions c ...
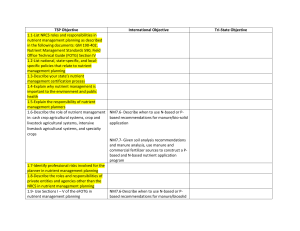
Specialty 4R Performance Objectives Comparison Version
... atmospheric deposition, erosion, runoff 2.2-Explain Liebig’s Law of the Minimum 2.3-Outline nutrient cycles for C, N, P, K, and S ...
... atmospheric deposition, erosion, runoff 2.2-Explain Liebig’s Law of the Minimum 2.3-Outline nutrient cycles for C, N, P, K, and S ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.