Lecture_12
... differing regulatory properties. Three distinct aspartate kinases control the synthesis of threonine, methionine, and lysine in E. coli. 3. Cumulative feedback inhibition: A common step for several pathways is partly inhibited independently by each of the various end products. This type of regulatio ...
... differing regulatory properties. Three distinct aspartate kinases control the synthesis of threonine, methionine, and lysine in E. coli. 3. Cumulative feedback inhibition: A common step for several pathways is partly inhibited independently by each of the various end products. This type of regulatio ...
Trace Minerals - lbccnutrition
... • Overload and toxicity – UL: 45 mg/day – Accidental overdose in children http://www.chop.edu/service/poison-controlcenter/tox-talk/iron-poisoning.html – Hemochromatosis ...
... • Overload and toxicity – UL: 45 mg/day – Accidental overdose in children http://www.chop.edu/service/poison-controlcenter/tox-talk/iron-poisoning.html – Hemochromatosis ...
Water and Minerals: The Ocean Within
... Cofactors for _____________ Components of _________________ Participate in many chemical reaction Essential for: – ______________________ – Immune System ...
... Cofactors for _____________ Components of _________________ Participate in many chemical reaction Essential for: – ______________________ – Immune System ...
Five Little Seeds - Clay Hill Memorial Forest
... i. Water, air, sunlight, and nutrients Seed Activities ...
... i. Water, air, sunlight, and nutrients Seed Activities ...
24-28 - aensi
... medicine. Today, medicinal plants with antimicrobial effects of specific and important place in traditional medicine around the world for clinical and enjoy. The results of the study showed that the flora of the study area contains 99 species, 42 species of which 42 percent are based on available re ...
... medicine. Today, medicinal plants with antimicrobial effects of specific and important place in traditional medicine around the world for clinical and enjoy. The results of the study showed that the flora of the study area contains 99 species, 42 species of which 42 percent are based on available re ...
Fluid Fertilizers - UKnowledge
... Fluid fertilizers are available in a wide range of products to Kentucky farmers. Although the term "liquid fertilizer" is commonly used to describe all fluid fertilizers, in reality the two terms do not imply the exact same meaning. Technically, all fertilizers of fluid consistency which can be tran ...
... Fluid fertilizers are available in a wide range of products to Kentucky farmers. Although the term "liquid fertilizer" is commonly used to describe all fluid fertilizers, in reality the two terms do not imply the exact same meaning. Technically, all fertilizers of fluid consistency which can be tran ...
5.3 reading
... a single valence electron and are extremely reactive. Because they are so reactive, alkali metals are found in nature only in compounds. The most familiar of these compounds is table salt—a compound of sodium and chlorine (sodium chloride). Sodium chloride can be obtained through the evaporation of ...
... a single valence electron and are extremely reactive. Because they are so reactive, alkali metals are found in nature only in compounds. The most familiar of these compounds is table salt—a compound of sodium and chlorine (sodium chloride). Sodium chloride can be obtained through the evaporation of ...
Soil Contamination #11 - Compost Education Centre
... into roots and up into plants? Binding: to become attached chemically, or immobile/not likely to dissolve in water or uptaken by plants pH - a measure of acidity (low pH) or alkalinity/basicity (high pH). This number indicates, on a scale of 0 to 14, the acidity/alkalinity of a solution like soil. I ...
... into roots and up into plants? Binding: to become attached chemically, or immobile/not likely to dissolve in water or uptaken by plants pH - a measure of acidity (low pH) or alkalinity/basicity (high pH). This number indicates, on a scale of 0 to 14, the acidity/alkalinity of a solution like soil. I ...
Does homeostasis or disturbance of homeostasis in minimum leaf
... season. Stomata react to prevent embolism at different levels of Ψleaf, and so the mechanisms controlling stomatal closure also involve differences in hydraulic architecture in the leaves: the onset of leaf vein cavitation makes Ψleaf drop sharply to maintain the same transpiration rate and thus act ...
... season. Stomata react to prevent embolism at different levels of Ψleaf, and so the mechanisms controlling stomatal closure also involve differences in hydraulic architecture in the leaves: the onset of leaf vein cavitation makes Ψleaf drop sharply to maintain the same transpiration rate and thus act ...
Kehidupan Sehari hari
... If this palm is cut just before flowering, the starch-rich pith in the trunk can be harvested for sago. If left to form a flowerstalk, a sweet juice (or toddy) can be tapped by repeatedly slicing off the end of the stalk. The juice is fermented to produce palm wine. In Kalimantan, fishing line was m ...
... If this palm is cut just before flowering, the starch-rich pith in the trunk can be harvested for sago. If left to form a flowerstalk, a sweet juice (or toddy) can be tapped by repeatedly slicing off the end of the stalk. The juice is fermented to produce palm wine. In Kalimantan, fishing line was m ...
Ch 13 Soil Analysis notes
... The presence of soil __________________________ can show that a suspect or victim must have been in that area. __________________________________ taken from shoes or the wheels of vehicles can show a suspect was present at a series of locations. Explain how each of the following is useful in the exa ...
... The presence of soil __________________________ can show that a suspect or victim must have been in that area. __________________________________ taken from shoes or the wheels of vehicles can show a suspect was present at a series of locations. Explain how each of the following is useful in the exa ...
Nutritive Value of Fresh Vegetables
... Contraction of muscles and normal functioning of heart and nervous system ...
... Contraction of muscles and normal functioning of heart and nervous system ...
RuBisCO and C4 plants
... There is a problem. When ribulose-1,5-biphopshate (RuBP) is carboxylated, it reacts with carbon dioxide and water to give two glycerate-3-phosphate (GP) molecules, which can be utilised in the ‘C3’ Calvin cycle. But this reaction is very slow at low carbon dioxide concentrations. Rubisco also cataly ...
... There is a problem. When ribulose-1,5-biphopshate (RuBP) is carboxylated, it reacts with carbon dioxide and water to give two glycerate-3-phosphate (GP) molecules, which can be utilised in the ‘C3’ Calvin cycle. But this reaction is very slow at low carbon dioxide concentrations. Rubisco also cataly ...
Inborn Errors of Amino Acid Metabolism
... Tyr will not be converted to catecholamine (neurotransmitter), which requires BH4 Trp will not be converted to serotonin (a neurotransmitter) as it requires BH4 Elevated phenylalanine in tissues, plasma, urine. Phe is degraded to phenyllactate, phenylacetate, and phenylpyruvate, which gi ...
... Tyr will not be converted to catecholamine (neurotransmitter), which requires BH4 Trp will not be converted to serotonin (a neurotransmitter) as it requires BH4 Elevated phenylalanine in tissues, plasma, urine. Phe is degraded to phenyllactate, phenylacetate, and phenylpyruvate, which gi ...
Forest Floor Ltd Bamboo Catalogue
... Of the Bambusas, the hardiest is multiplex which can take as low as -10.5. Bambusa oldhamii has been reported to survive -9 but is not usually recommended below -7 Celcius unless protected from wind. These temperatures are the minimum that an established plant can take for a short duration,and still ...
... Of the Bambusas, the hardiest is multiplex which can take as low as -10.5. Bambusa oldhamii has been reported to survive -9 but is not usually recommended below -7 Celcius unless protected from wind. These temperatures are the minimum that an established plant can take for a short duration,and still ...
Ethnobotanical Survey of Medicinal Plants Used
... documented. Prominent among them are Rauvolfia vomitoria, Aframomum meleguata, Momordica charantia, Xylopia aethiopica, Senna spp. and Vernonia amygdalina. These species were found to be very important and useful in the treatment of diabetes based on their frequency of occurrence in the recipes obta ...
... documented. Prominent among them are Rauvolfia vomitoria, Aframomum meleguata, Momordica charantia, Xylopia aethiopica, Senna spp. and Vernonia amygdalina. These species were found to be very important and useful in the treatment of diabetes based on their frequency of occurrence in the recipes obta ...
Document
... A. Composition - essential macro- and micro-nutrients; A nutrient is considered essential if: a. it is required for the plant to complete its life cycle and/or b. it is part of a molecule that is an essential plant constituent or metabolite, a cofactor, osmolyte, etc. ...
... A. Composition - essential macro- and micro-nutrients; A nutrient is considered essential if: a. it is required for the plant to complete its life cycle and/or b. it is part of a molecule that is an essential plant constituent or metabolite, a cofactor, osmolyte, etc. ...
PDF
... The leaflets are approximately 7 mm (0.3 in) long and 1 mm (0.04 in) wide. The inflorescence is a loose raceme with up to 20 creamy white, purple tinged flowers reaching approximately 1 cm (0.4 in) in length. The fruit is an inflated, narrowly elliptic, yellow-green pod with reddish mottling, approx ...
... The leaflets are approximately 7 mm (0.3 in) long and 1 mm (0.04 in) wide. The inflorescence is a loose raceme with up to 20 creamy white, purple tinged flowers reaching approximately 1 cm (0.4 in) in length. The fruit is an inflated, narrowly elliptic, yellow-green pod with reddish mottling, approx ...
Greenhouse Management of Western Flower Thrips and Tomato
... G, Pupa. H, Adult female. [From: Jones, R.KX and J.R. Baker. 1989. Tomato spotted wilt virus. N. C. Flower Growers Bulletin 34(l):12-15.] One characteristic of this disease is that infected plants tend to show the most obvious symptoms when plant growth has been slow or checked, for example by cool ...
... G, Pupa. H, Adult female. [From: Jones, R.KX and J.R. Baker. 1989. Tomato spotted wilt virus. N. C. Flower Growers Bulletin 34(l):12-15.] One characteristic of this disease is that infected plants tend to show the most obvious symptoms when plant growth has been slow or checked, for example by cool ...
Noogoora Burr - Narrabri Shire Council
... Potential: Plants compete with pasture production for space and nutrients. Plants also enter natural systems competing against endemic native species. ...
... Potential: Plants compete with pasture production for space and nutrients. Plants also enter natural systems competing against endemic native species. ...
Thiosulfate - International Plant Nutrition Institute
... Thiosulfate can slow the rate of urea hydrolysis…the conversion of urea to ammonium (NH4+)…and reduce loss of ammonia (NH3) as a gas when ATS is mixed with UAN. This inhibiting effect is likely due to the formation and presence of the intermediate tetrathionate, rather than the thiosulfate itself. ...
... Thiosulfate can slow the rate of urea hydrolysis…the conversion of urea to ammonium (NH4+)…and reduce loss of ammonia (NH3) as a gas when ATS is mixed with UAN. This inhibiting effect is likely due to the formation and presence of the intermediate tetrathionate, rather than the thiosulfate itself. ...
Hino Crimson Azalea - TLC Garden Centers
... Hino Crimson Azalea will grow to be about 4 feet tall at maturity, with a spread of 4 feet. It tends to be a little leggy, with a typical clearance of 1 feet from the ground. It grows at a slow rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for 40 years or more. This shrub does best in ful ...
... Hino Crimson Azalea will grow to be about 4 feet tall at maturity, with a spread of 4 feet. It tends to be a little leggy, with a typical clearance of 1 feet from the ground. It grows at a slow rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for 40 years or more. This shrub does best in ful ...
Kobold Blazing Star
... above the foliage from mid summer to early fall, which are most effective when planted in groupings. The flowers are excellent for cutting. It's grassy leaves remain green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. ...
... above the foliage from mid summer to early fall, which are most effective when planted in groupings. The flowers are excellent for cutting. It's grassy leaves remain green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. ...
Practice Exam I Key - Iowa State University
... 4. Calculate the percent of k-calories coming from fat in a large hamburger with cheese, which has the following nutrient profile: Carbohydrates – 53g, Protein – 36g, Fat – 50g. ...
... 4. Calculate the percent of k-calories coming from fat in a large hamburger with cheese, which has the following nutrient profile: Carbohydrates – 53g, Protein – 36g, Fat – 50g. ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
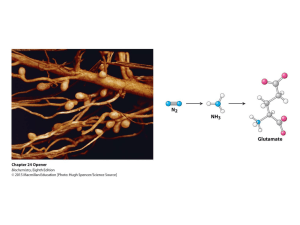
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.