Common Herbs and their Medicinal Uses
... worldwide continue to rely heavily on the use of traditional medicines as their primary source of healthcare, and medicinal plants are now being given serious attention by mainstream medical science. The pages that follow detail some commonly used medicinal plants (herbs) that can easily be planted ...
... worldwide continue to rely heavily on the use of traditional medicines as their primary source of healthcare, and medicinal plants are now being given serious attention by mainstream medical science. The pages that follow detail some commonly used medicinal plants (herbs) that can easily be planted ...
- Sustainable Learning
... Pupils share their written instructions with a partner. They discuss how the writing could be improved, and make changes based on these discussions. ...
... Pupils share their written instructions with a partner. They discuss how the writing could be improved, and make changes based on these discussions. ...
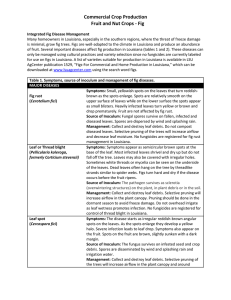
Commercial Crop Production Fruit and Nut Crops - Fig
... low yield and poor fruit quality. Infected roots are characterized by small galls or swellings on the roots. Source of inoculum: Root-knot nematode survives from season to season as eggs in the soil. After the eggs hatch, the second-stage juveniles infest the roots. Management: Nematodes are difficu ...
... low yield and poor fruit quality. Infected roots are characterized by small galls or swellings on the roots. Source of inoculum: Root-knot nematode survives from season to season as eggs in the soil. After the eggs hatch, the second-stage juveniles infest the roots. Management: Nematodes are difficu ...
The Invasive Species Handbook: A guide to invasive plants in the
... methods that have been used successfully elsewhere; the most suitable one for your situation will depend on the invasive plant, the size of the invasion, surrounding environmental conditions, and the management objectives for the area in question. We have divided the control options into three categ ...
... methods that have been used successfully elsewhere; the most suitable one for your situation will depend on the invasive plant, the size of the invasion, surrounding environmental conditions, and the management objectives for the area in question. We have divided the control options into three categ ...
mulches in the landscape
... house where termites are or could be a problem. Be sure to use aged wood chips as the green wood can potentially rob the plants of nutrients as it breaks down and additional fertilizer will be needed. Do not incorporate this mulch into the soil as its high carbon content will cause a nitrogen defici ...
... house where termites are or could be a problem. Be sure to use aged wood chips as the green wood can potentially rob the plants of nutrients as it breaks down and additional fertilizer will be needed. Do not incorporate this mulch into the soil as its high carbon content will cause a nitrogen defici ...
FACTORS OF SOIL FORMATION There are five soil forming factors
... give a good indication of organic matter contents, drainage conditions and mineralogical compositions. Black soil may indicate the presence of organic matter, red indicates the presence of oxidized iron while gray or bluish gray color indicates water saturation. Soil color is described by three attr ...
... give a good indication of organic matter contents, drainage conditions and mineralogical compositions. Black soil may indicate the presence of organic matter, red indicates the presence of oxidized iron while gray or bluish gray color indicates water saturation. Soil color is described by three attr ...
Water-Wise Gardening Guide
... fescue need more water. All are good choices for our area. Most nurseries carry a “blend” of grasses which thrive in Modesto’s climate. Hard fescue is an alternative lawn and grows 4-6” tall. It does not need to be mowed but does not tolerate hot summers and may die back. However, hard fescue grows ...
... fescue need more water. All are good choices for our area. Most nurseries carry a “blend” of grasses which thrive in Modesto’s climate. Hard fescue is an alternative lawn and grows 4-6” tall. It does not need to be mowed but does not tolerate hot summers and may die back. However, hard fescue grows ...
Lecture1
... give a good indication of organic matter contents, drainage conditions and mineralogical compositions. Black soil may indicate the presence of organic matter, red indicates the presence of oxidized iron while gray or bluish gray color indicates water saturation. Soil color is described by three attr ...
... give a good indication of organic matter contents, drainage conditions and mineralogical compositions. Black soil may indicate the presence of organic matter, red indicates the presence of oxidized iron while gray or bluish gray color indicates water saturation. Soil color is described by three attr ...
An Guide to PlAnninG Your own GArden CurriCulum
... water, ice, and waves break down rocks and minerals into a finer material that serves as the core substance of our soil. Added to this rocky material is organic matter, which originates from the decomposition of animals and plants. Organisms living in the soil, such as earthworms, fungus, and bacter ...
... water, ice, and waves break down rocks and minerals into a finer material that serves as the core substance of our soil. Added to this rocky material is organic matter, which originates from the decomposition of animals and plants. Organisms living in the soil, such as earthworms, fungus, and bacter ...
Accumulation of heavy metals in fibre crops flax, cotton and hemp
... Phytoremediation is an eco-friendly and low-cost biotechnology using plants to extract, contain, degrade, or immobilize pollutants from the contaminated environment. Selection of the ideal plant species and suitable enhancing measures to obtain high remediation ... Сродни статии Всички 3 версии Позо ...
... Phytoremediation is an eco-friendly and low-cost biotechnology using plants to extract, contain, degrade, or immobilize pollutants from the contaminated environment. Selection of the ideal plant species and suitable enhancing measures to obtain high remediation ... Сродни статии Всички 3 версии Позо ...
Stems
... • A shoot is not the same as a stem! Shoots are any new plant growth, not just new stems. • Stems are usually located above the surface, but there are some plants with underground stems. ...
... • A shoot is not the same as a stem! Shoots are any new plant growth, not just new stems. • Stems are usually located above the surface, but there are some plants with underground stems. ...
Woody Landscape Plant Breeding in Minnesota
... necrosis, foliage death, and shoot dieback) will be monitored up to one year after treatment. Because C. corni may infect without apparent symptom development, isolations will be made from the plants to test for presence of the fungus regardless of outward symptoms. The influence of environmental st ...
... necrosis, foliage death, and shoot dieback) will be monitored up to one year after treatment. Because C. corni may infect without apparent symptom development, isolations will be made from the plants to test for presence of the fungus regardless of outward symptoms. The influence of environmental st ...
2017 Spring Plant Sale
... container plant and will bloom late spring through early fall or it can be grown in the ground with good winter protection but may be slow to recover and will be back to blooming by midsummer. Grows 3-6’ tall & 5-7’ wide. Likes part sun to part shade. Thunbergia, Mercer Blue (Thunbergia battiscombei ...
... container plant and will bloom late spring through early fall or it can be grown in the ground with good winter protection but may be slow to recover and will be back to blooming by midsummer. Grows 3-6’ tall & 5-7’ wide. Likes part sun to part shade. Thunbergia, Mercer Blue (Thunbergia battiscombei ...
Living Things - Somerset Area School District
... The amount of darkness a plant receives determines the time of flowering in many plants. A plant’s response to these seasonal changes is called photoperiodism. Some plants are day-neutral. Their flowering cycle is not sensitive to periods of light and dark. ...
... The amount of darkness a plant receives determines the time of flowering in many plants. A plant’s response to these seasonal changes is called photoperiodism. Some plants are day-neutral. Their flowering cycle is not sensitive to periods of light and dark. ...
science-SOCIAL-ON-27-3-17
... A – HORIZON TOP SOIL WITH HUMUS AND MINERALS E – HORIZON INTERSECTION LAYER B – HORZON SUB SOIL C – HORIZON PARENT ROCK WITH GROUND WATER ...
... A – HORIZON TOP SOIL WITH HUMUS AND MINERALS E – HORIZON INTERSECTION LAYER B – HORZON SUB SOIL C – HORIZON PARENT ROCK WITH GROUND WATER ...
Camellias in Florida - UF/IFAS Extension Polk County
... growth at night. The application of a bait in late afternoon will provide control. Thrips are very small, slender insects that feed on camellia flowers. Close examination is necessary to find them. Their injury is revealed as distorted flowers. Specific insecticide recommendations can be obtained fr ...
... growth at night. The application of a bait in late afternoon will provide control. Thrips are very small, slender insects that feed on camellia flowers. Close examination is necessary to find them. Their injury is revealed as distorted flowers. Specific insecticide recommendations can be obtained fr ...
Plant Science Lessons
... comprised of sets of two questions. Once this question is answered, it leads to another set of questions. Therefore a dichotomous key is a device for identifying organisms based on the answers to a series of questions, with each question involving alternate choices. ...
... comprised of sets of two questions. Once this question is answered, it leads to another set of questions. Therefore a dichotomous key is a device for identifying organisms based on the answers to a series of questions, with each question involving alternate choices. ...
Nature`s Classroom - Langley Environmental Partners Society
... like food, light, water, heat as well as monitoring and attention to make sure they are getting all of these requirements. Mention some more unique requirements such as seeds that require a period of darkness to germinate and some that require heat from a forest fire. Part 1: Planting Tomato Seeds a ...
... like food, light, water, heat as well as monitoring and attention to make sure they are getting all of these requirements. Mention some more unique requirements such as seeds that require a period of darkness to germinate and some that require heat from a forest fire. Part 1: Planting Tomato Seeds a ...
Western Clematis: Clever, Clingy Native
... numerous insects. However, clematis is not known to be a major food source for wildlife species and is generally avoided by livestock. As with other members of the Ranunculaceae Family, clematis is considered poisonous by some sources. Members of this family contain alkaloids that can cause gastro ...
... numerous insects. However, clematis is not known to be a major food source for wildlife species and is generally avoided by livestock. As with other members of the Ranunculaceae Family, clematis is considered poisonous by some sources. Members of this family contain alkaloids that can cause gastro ...
Dietary nitrogen – definitions, digestion, excretion
... ruminants, and this can be exacerbated by application of N fertilisers to boost pasture growth. Excess dietary nitrogen (N) has negative implications for environmental sustainability and animal production, but producers and rural professionals are sometimes unaware of these issues and especially the ...
... ruminants, and this can be exacerbated by application of N fertilisers to boost pasture growth. Excess dietary nitrogen (N) has negative implications for environmental sustainability and animal production, but producers and rural professionals are sometimes unaware of these issues and especially the ...
Modes of Reproduction
... capable of giving rise to new offspring’s. These structures are called vegetative propagules. In all these plants, no involvement of union of gametes takes place. So the progeny looks like the parents without any variation and formed progeny are called clones. So, vegetative reproduction is also an ...
... capable of giving rise to new offspring’s. These structures are called vegetative propagules. In all these plants, no involvement of union of gametes takes place. So the progeny looks like the parents without any variation and formed progeny are called clones. So, vegetative reproduction is also an ...
O A RIGINAL RTICLES
... decreased and reached to 3.2% compared with plants irrigated with fresh water. The reduction in stem length might be due to that salinity decreased the cell division and elongation and meristemic activity (Rug et al (1963) and Bolus et al (1972). Data in Tables (3 and 4) indicated that the highest v ...
... decreased and reached to 3.2% compared with plants irrigated with fresh water. The reduction in stem length might be due to that salinity decreased the cell division and elongation and meristemic activity (Rug et al (1963) and Bolus et al (1972). Data in Tables (3 and 4) indicated that the highest v ...
Maianthemum racemosum
... Some of the seeds are produced without fertilization but are genetically identical to the parent plant. Birds (Class Aves) and small Mammals (Class Mammalia) eat these berries and help spread the seeds. Roots: Its root system consists of stout, thick, cylindrical, creeping, fleshy, light brown, knot ...
... Some of the seeds are produced without fertilization but are genetically identical to the parent plant. Birds (Class Aves) and small Mammals (Class Mammalia) eat these berries and help spread the seeds. Roots: Its root system consists of stout, thick, cylindrical, creeping, fleshy, light brown, knot ...
The Bacterial Stringent Response, Conserved in
... performs a wide variety of metabolic processes for host cells, which include photosynthesis as well as amino acid and fatty acid biosynthesis. The organelle conserves many bacterial systems in its functions, implicating its origin from symbiosis of a photosynthetic bacterium. In bacterial cells, the ...
... performs a wide variety of metabolic processes for host cells, which include photosynthesis as well as amino acid and fatty acid biosynthesis. The organelle conserves many bacterial systems in its functions, implicating its origin from symbiosis of a photosynthetic bacterium. In bacterial cells, the ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.