Glossary of Botanical Terms
... With stamens in two whorls, outer opposite petals, inner opposite the sepals ...
... With stamens in two whorls, outer opposite petals, inner opposite the sepals ...
A comparative study of dry and fresh Hibiscus trioni herba tinctures
... Pharmacopoeia (Farmacopeea Română, 1993), determining the relative density with an Anton Paar digital densitometer - DSM35, quantitative determination of the residue obtained by evaporation, the determination of the concentration of alcohol by distillation and the determination of the relative densi ...
... Pharmacopoeia (Farmacopeea Română, 1993), determining the relative density with an Anton Paar digital densitometer - DSM35, quantitative determination of the residue obtained by evaporation, the determination of the concentration of alcohol by distillation and the determination of the relative densi ...
The Culture of The State Flower of Alabama
... directly related to the extent and vigor of the root system. Physical characteristics of the soil, such as air and water-holding capacity, determine, to a large extent, the growth and useful activity of plant roots. An ideal soil is actually composed of 50 percent soil particles and 50 percent pore ...
... directly related to the extent and vigor of the root system. Physical characteristics of the soil, such as air and water-holding capacity, determine, to a large extent, the growth and useful activity of plant roots. An ideal soil is actually composed of 50 percent soil particles and 50 percent pore ...
Comprehend Nutrition Principles 2
... health, and disease prevention. Information regarding healthy eating behaviors, lifestyle, and nutrition knowledge are essential components for long-term health and wellness. Good physical health includes having enough energy to meet the demands of your day, maintain a normal growth rate, and resist ...
... health, and disease prevention. Information regarding healthy eating behaviors, lifestyle, and nutrition knowledge are essential components for long-term health and wellness. Good physical health includes having enough energy to meet the demands of your day, maintain a normal growth rate, and resist ...
Grasses
... The stems of dharill have been used by Aboriginal people to weave baskets and bags, and the women sometimes made skirts to wear (Howell 1983). Twine was made from dharill. The stems can be used to make light spears which can be used to spear fish. The stems are also used to make fire (Williams & Sid ...
... The stems of dharill have been used by Aboriginal people to weave baskets and bags, and the women sometimes made skirts to wear (Howell 1983). Twine was made from dharill. The stems can be used to make light spears which can be used to spear fish. The stems are also used to make fire (Williams & Sid ...
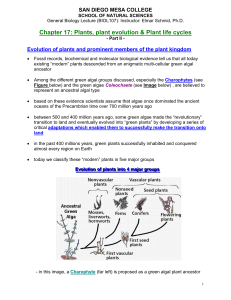
plant life cycles - San Diego Mesa College
... - cycad fossils date back more than 250 million years into the Mesozoic, a time where the dinosaurs roamed on planet Earth! - they reproduce with the help of cone-like structures, which produce the seeds; - today they are mostly found in warm, tropical zones on planet Earth - they show a very slow g ...
... - cycad fossils date back more than 250 million years into the Mesozoic, a time where the dinosaurs roamed on planet Earth! - they reproduce with the help of cone-like structures, which produce the seeds; - today they are mostly found in warm, tropical zones on planet Earth - they show a very slow g ...
Suggested Methodologies for Cottonwood Pole, Willow Whip
... where soils stay cold into midsummer (as root development can only begin when soils warm up). Since soils often do not warm up until August on high elevation sites, it may be more productive to plant potted plant material with developed roots on high elevation sites (and plant in August when soils a ...
... where soils stay cold into midsummer (as root development can only begin when soils warm up). Since soils often do not warm up until August on high elevation sites, it may be more productive to plant potted plant material with developed roots on high elevation sites (and plant in August when soils a ...
Pastures for Horses - University of Tennessee Extension
... a composite sample for testing. A shovel can be used to take samples, but most Extension offices have soil probes available for use. A soil sample submitted to the lab should represent no more than a 10-acre field. If a pasture is larger than 10 acres, or has changes in topography, soil type, fertil ...
... a composite sample for testing. A shovel can be used to take samples, but most Extension offices have soil probes available for use. A soil sample submitted to the lab should represent no more than a 10-acre field. If a pasture is larger than 10 acres, or has changes in topography, soil type, fertil ...
Soil salinity in Veneto plain. Introduction Soil
... 6) the corresponding MU mean is added to the residuals values to get EC1:2 at each node of the 1 km regular grid. The omnidirectional standardized variograms of the normalized residuals (lag 1500 m) were calculated and modelled for the two reference depth. For both depths a nested double spherical m ...
... 6) the corresponding MU mean is added to the residuals values to get EC1:2 at each node of the 1 km regular grid. The omnidirectional standardized variograms of the normalized residuals (lag 1500 m) were calculated and modelled for the two reference depth. For both depths a nested double spherical m ...
PROPAGATING PLANTS FROM SEED
... As soon as seedlings have developed at least one set of true leaves and are large enough to handle, they should be transplanted to individual pots or spaced out in flats. This is called “potting up”. Failure to transplant promptly results in crowded spindly seedlings that can’t develop properly. Gen ...
... As soon as seedlings have developed at least one set of true leaves and are large enough to handle, they should be transplanted to individual pots or spaced out in flats. This is called “potting up”. Failure to transplant promptly results in crowded spindly seedlings that can’t develop properly. Gen ...
The Succulent Plant Page: Glossary of Botanical Terms
... set fruit and prevent premature fruit drop. Synthetic auxins such as 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T stimulate uncontrolled DNA and protein synthesis and are effective herbicides. 2,4-D is still used as a herbicide but use of 2,4,5-T has been banned because it tends to be contaminated with carcinogenic dioxin. Br ...
... set fruit and prevent premature fruit drop. Synthetic auxins such as 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T stimulate uncontrolled DNA and protein synthesis and are effective herbicides. 2,4-D is still used as a herbicide but use of 2,4,5-T has been banned because it tends to be contaminated with carcinogenic dioxin. Br ...
Plant Lipoxygenases. Physiological and Molecular Features
... molecular oxygen to polyunsaturated fatty acids containing a (Z,Z)-1,4-pentadiene system to produce an unsaturated fatty acid hydroperoxide. LOX initiates the synthesis of a group of acyclic or cyclic compounds collectively called oxylipins, which are products of fatty acid oxidation, with diverse f ...
... molecular oxygen to polyunsaturated fatty acids containing a (Z,Z)-1,4-pentadiene system to produce an unsaturated fatty acid hydroperoxide. LOX initiates the synthesis of a group of acyclic or cyclic compounds collectively called oxylipins, which are products of fatty acid oxidation, with diverse f ...
lecture outline
... Male wasps of the species Campsoscolia ciliata transfer pollen to the Mediterranean orchid Ophrys speculum, although the orchid does not provide energy-rich nectar to the wasp. o The shape of the orchid’s largest petal and the frill of orange bristles around it vaguely resemble the female wasp. o Op ...
... Male wasps of the species Campsoscolia ciliata transfer pollen to the Mediterranean orchid Ophrys speculum, although the orchid does not provide energy-rich nectar to the wasp. o The shape of the orchid’s largest petal and the frill of orange bristles around it vaguely resemble the female wasp. o Op ...
2015 Sego Lily newsletter - Utah Native Plant Society
... petals and a ball-like head of numerous 1-seeded fruits. Leaves of Jupiter buttercup are deeply threelobed and resemble the foot of a bird (another common name for Ranunculus is crowfoot). The uppermost leaves sometimes form a whorl surrounding the relatively large flowers. But the Jupiter buttercup ...
... petals and a ball-like head of numerous 1-seeded fruits. Leaves of Jupiter buttercup are deeply threelobed and resemble the foot of a bird (another common name for Ranunculus is crowfoot). The uppermost leaves sometimes form a whorl surrounding the relatively large flowers. But the Jupiter buttercup ...
Chapter 5 Lecture PowerPoint Handout
... metamorphic rocks at the Earth’s surface due to a reduction in confining pressure • Salt crystal growth–expansion due to crystal growth (coastal and roads) • Biological activity – disintegration resulting from plants and animals ...
... metamorphic rocks at the Earth’s surface due to a reduction in confining pressure • Salt crystal growth–expansion due to crystal growth (coastal and roads) • Biological activity – disintegration resulting from plants and animals ...
Healthy Eating – Its Starts When Your Young
... vitamin D to the active form. This allows calcium to be absorbed and bones to be strong S Rickets causes severely bowed legs, pain in the bones and ...
... vitamin D to the active form. This allows calcium to be absorbed and bones to be strong S Rickets causes severely bowed legs, pain in the bones and ...
Grapes
... Temperature Light (photosynthesis) Stored carbohydrates Water Nutrients ~ primarily Zn and B ...
... Temperature Light (photosynthesis) Stored carbohydrates Water Nutrients ~ primarily Zn and B ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 4. Digestion breaks triglycerides down into fatty acids and glycerol. 5. Glycerol and fatty acids are transported in the lymph to the blood then to tissues. 6. Beta-oxidation is a series of reactions that converts some fatty acids to acetyl coenzyme A. 7. Fatty acid oxidases function to break down f ...
... 4. Digestion breaks triglycerides down into fatty acids and glycerol. 5. Glycerol and fatty acids are transported in the lymph to the blood then to tissues. 6. Beta-oxidation is a series of reactions that converts some fatty acids to acetyl coenzyme A. 7. Fatty acid oxidases function to break down f ...
Physcomitrella patens Taxonomy
... in both damp (including freshwater) and drier situations. Mosses possess erect or prostrate leafless stems, which give rise to leafless stalks bearing capsules. Spores formed in the capsules are released and grow to produce new plants. (Concise Dictionary of Biology, 1990). Many small plants bearing ...
... in both damp (including freshwater) and drier situations. Mosses possess erect or prostrate leafless stems, which give rise to leafless stalks bearing capsules. Spores formed in the capsules are released and grow to produce new plants. (Concise Dictionary of Biology, 1990). Many small plants bearing ...
Life Science Journal 2014;11(7)
... Abstract: The concentrations of PCDDs, PCDFs, and DL-PCBs were determined in samples of eight commonly used medicinal plants, namely "caraway, cumin, anise, sage, rosemary, black tea, ginger and cinnamon" collected randomly from the Jeddah central market between the periods of July and August 2013. ...
... Abstract: The concentrations of PCDDs, PCDFs, and DL-PCBs were determined in samples of eight commonly used medicinal plants, namely "caraway, cumin, anise, sage, rosemary, black tea, ginger and cinnamon" collected randomly from the Jeddah central market between the periods of July and August 2013. ...
Inborn Errors of Metabolism A Hospitalist`s Approach
... E to F. C ispath notD.present the enzyme make Bthat to C is defective, pathways to Also, if the apoenzyme and cofactors form the enzyme of reactions are moot (transport defect) B accumulates anddefective, further shunts down alternate pathways to D. converting B to C are B backs up and diverts down ...
... E to F. C ispath notD.present the enzyme make Bthat to C is defective, pathways to Also, if the apoenzyme and cofactors form the enzyme of reactions are moot (transport defect) B accumulates anddefective, further shunts down alternate pathways to D. converting B to C are B backs up and diverts down ...
Direct Interference with Rhamnogalacturonan I Biosynthesis in Golgi
... aqueous solution (Cros et al., 1994), whereas 13CNMR studies by Renard and Jarvis (1999) demonstrate that they are also very mobile molecules in muro. The authors concluded that arabinans are not structural components; rather, they propose a role for them as plasticizers and water binding agents in ...
... aqueous solution (Cros et al., 1994), whereas 13CNMR studies by Renard and Jarvis (1999) demonstrate that they are also very mobile molecules in muro. The authors concluded that arabinans are not structural components; rather, they propose a role for them as plasticizers and water binding agents in ...
1. One of the earliest cultures to use flowers were the Egyptians
... To complain about it C After you have tried a solution *D With alternative solutions ...
... To complain about it C After you have tried a solution *D With alternative solutions ...
Effects of Amino Acids Replacing Nitrate on Growth - dl.edi
... During the experiment, pH in nutrient solutions was maintained at about 6.0 by addition of either 1 mmol L−1 NaOH or H2 SO4 , and the nutrient solutions were replaced every four days. The solutions in pots were aerated throughout the experimental period. Twenty-four days after application of the tre ...
... During the experiment, pH in nutrient solutions was maintained at about 6.0 by addition of either 1 mmol L−1 NaOH or H2 SO4 , and the nutrient solutions were replaced every four days. The solutions in pots were aerated throughout the experimental period. Twenty-four days after application of the tre ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.