File
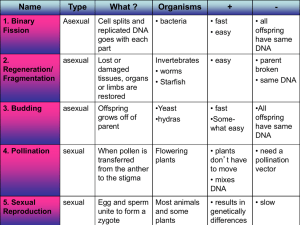
... • Sexual Reproduction: the union of an ovule (egg) and pollen (sperm) to create an egg. • Involves floral parts of one or two plants. • Quickest way of plant propagation • Only way to provide new varieties • Good way to avoid plant diseases • Asexual Reproduction: Part or parts of only one parent pl ...
... • Sexual Reproduction: the union of an ovule (egg) and pollen (sperm) to create an egg. • Involves floral parts of one or two plants. • Quickest way of plant propagation • Only way to provide new varieties • Good way to avoid plant diseases • Asexual Reproduction: Part or parts of only one parent pl ...
Blue Glow Agave - Pender Pines Garden Center
... Blue Glow Agave will grow to be about 24 inches tall at maturity extending to 6 feet tall with the flowers, with a spread of 3 feet. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. It grows at a slow rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live ...
... Blue Glow Agave will grow to be about 24 inches tall at maturity extending to 6 feet tall with the flowers, with a spread of 3 feet. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. It grows at a slow rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live ...
Plants and Places - Teacher DePaul
... live in the desert. Plants are very important. Every environment needs plants. Animals need them. Many herbivores eat them. Many animals use them to make homes. Some animals make nests in plants. If there were no plants in those environments, the animals would be homeless. When you see a plant you c ...
... live in the desert. Plants are very important. Every environment needs plants. Animals need them. Many herbivores eat them. Many animals use them to make homes. Some animals make nests in plants. If there were no plants in those environments, the animals would be homeless. When you see a plant you c ...
Unit 8
... Gibberellins: promotes cell growth, they are synthesized in young leaves, roots, and seeds. They are also involved in the promotion of fruit development and of seed germination, and the inhibition of again in leaves. Cytokinins: a hormone that stimulates cytokinesis (cell division). Are produced in ...
... Gibberellins: promotes cell growth, they are synthesized in young leaves, roots, and seeds. They are also involved in the promotion of fruit development and of seed germination, and the inhibition of again in leaves. Cytokinins: a hormone that stimulates cytokinesis (cell division). Are produced in ...
Plant Divisions - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • What did plants have to overcome to live on land? • What is the most primitive division of plants because they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular ...
... • What did plants have to overcome to live on land? • What is the most primitive division of plants because they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular ...
Plant Responses to Light
... Response to Gravity • Response of a plant to the gravitational field of the Earth • Shoots exhibit negative gravitropism • Roots have a positive gravitropic response ...
... Response to Gravity • Response of a plant to the gravitational field of the Earth • Shoots exhibit negative gravitropism • Roots have a positive gravitropic response ...
Lab 5: Plants: Nontracheophytes and Seedless Vascular Plants Part 2
... should notice a shift in the alternation of generations from a gametophyte dominant life cycle (mosses and liverworts) to a sporophyte dominant life cycle (ferns, conifers, and flowering plants). Importantly, remember that all the plants still exhibit a true alternation of generations. We will exami ...
... should notice a shift in the alternation of generations from a gametophyte dominant life cycle (mosses and liverworts) to a sporophyte dominant life cycle (ferns, conifers, and flowering plants). Importantly, remember that all the plants still exhibit a true alternation of generations. We will exami ...
3U 4.1 Vascular Plant Structure and Function PDF
... • Cells of all complex plants are organized into tissues, tissue systems, organs, and organ systems that enable the plants to carry out the basic processes of life such ...
... • Cells of all complex plants are organized into tissues, tissue systems, organs, and organ systems that enable the plants to carry out the basic processes of life such ...
Stained Glass Copper Coleus
... When grown in masses or used as a bedding plant, individual plants should be spaced approximately 20 inches apart. Although it's not a true annual, this fast-growing plant can be expected to behave as an annual in our climate if left outdoors over the winter, usually needing replacement the followin ...
... When grown in masses or used as a bedding plant, individual plants should be spaced approximately 20 inches apart. Although it's not a true annual, this fast-growing plant can be expected to behave as an annual in our climate if left outdoors over the winter, usually needing replacement the followin ...
Biology First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... The male reproductive structure of a flowering plant; consists of the anther and the filament The female reproductive structure of a flowering plant; consists of the stigma, style, and ovary The slender stalk-like portion of the male reproductive structure of a flowering plant; supports the anther T ...
... The male reproductive structure of a flowering plant; consists of the anther and the filament The female reproductive structure of a flowering plant; consists of the stigma, style, and ovary The slender stalk-like portion of the male reproductive structure of a flowering plant; supports the anther T ...
Fritillaria pudica species sheet (1
... area – usually flowering in April or May, or even early June in the higher elevations. It can be found in grassy sites, in sagebrush country or under stands of open ponderosa pine in the drier environments in all the Northwest states including northeast California. 1 to 3 bell-shaped flowers rise fr ...
... area – usually flowering in April or May, or even early June in the higher elevations. It can be found in grassy sites, in sagebrush country or under stands of open ponderosa pine in the drier environments in all the Northwest states including northeast California. 1 to 3 bell-shaped flowers rise fr ...
What Students Need to Know about
... Tropisms and turgor movements are two forms of plant movement that allow the plant to react to stimuli Geotropism is the term applied to the consequent orientation response of growing plant parts. Roots are positively geotropic, that is, they will bend and grow downwards, towards the center of t ...
... Tropisms and turgor movements are two forms of plant movement that allow the plant to react to stimuli Geotropism is the term applied to the consequent orientation response of growing plant parts. Roots are positively geotropic, that is, they will bend and grow downwards, towards the center of t ...
Kingdom
... The male parts of the flower are called the ________________________ and include the ________________________ and the _____________________________. The _________________________ contains the pollen and the __________________ supports the anther. The female parts of the flower are called the _______ ...
... The male parts of the flower are called the ________________________ and include the ________________________ and the _____________________________. The _________________________ contains the pollen and the __________________ supports the anther. The female parts of the flower are called the _______ ...
Desert Diversity - Electronic Field Trip
... Plant Adaptations In places that are not so dry, plants are known for their large leaves … like a maple tree’s. But in the desert, leaves must change so they will not lose water and dry up in the heat. These special changes for the desert environment are called adaptations. ...
... Plant Adaptations In places that are not so dry, plants are known for their large leaves … like a maple tree’s. But in the desert, leaves must change so they will not lose water and dry up in the heat. These special changes for the desert environment are called adaptations. ...
Plant Kingdom
... See page. 264—Read about seed structure and review seed structure pictures (figure 10) 11. How are seeds dispersed or spread? (pg. 265) a) Animals eat fruits and seeds pass through their digestive system and are deposited in various places. b) Animals and other organism pick up seeds and carry them ...
... See page. 264—Read about seed structure and review seed structure pictures (figure 10) 11. How are seeds dispersed or spread? (pg. 265) a) Animals eat fruits and seeds pass through their digestive system and are deposited in various places. b) Animals and other organism pick up seeds and carry them ...
Plant Kingdom
... See page. 264—Read about seed structure and review seed structure pictures (figure 10) How are seeds dispersed or spread? (pg. 265) a) Animals eat fruits and seeds pass through their digestive system and are deposited in various places. b) Animals and other organism pick up seeds and carry them to d ...
... See page. 264—Read about seed structure and review seed structure pictures (figure 10) How are seeds dispersed or spread? (pg. 265) a) Animals eat fruits and seeds pass through their digestive system and are deposited in various places. b) Animals and other organism pick up seeds and carry them to d ...
Article 53 Revisit Ailanthus Altisiima
... No doubt after a refreshing and inspiring break flavoured by happy reunions with friends and family we are all looking forward to an exciting and rewarding 2006. To keep our newcomers in the picture, we continue our series with revisits of the really persistent alien invasive flora in our area. Aila ...
... No doubt after a refreshing and inspiring break flavoured by happy reunions with friends and family we are all looking forward to an exciting and rewarding 2006. To keep our newcomers in the picture, we continue our series with revisits of the really persistent alien invasive flora in our area. Aila ...
Spring Grade 2 Nature Walk One-Page Summary
... without seeds, no new trees. The pines do not require insects to carry their pollen: the wind does it! (The pine cone holds the seeds.) Trees: Revisit the four trees from early walks (see map in packet). Talk about how trees grow from seed. All the seeds are not all produced at the same time. The tr ...
... without seeds, no new trees. The pines do not require insects to carry their pollen: the wind does it! (The pine cone holds the seeds.) Trees: Revisit the four trees from early walks (see map in packet). Talk about how trees grow from seed. All the seeds are not all produced at the same time. The tr ...
Educator Guide - The Field Museum
... plant. The embryo is surrounded by nutrients that help the seedling germinate. Non-seed plants such as ferns (pterophytes), liverworts and mosses (bryophytes) reproduce by spores. Spores are generally microscopic in size and are often located on stalks or the underside of the leaf. Unlike seeds, fer ...
... plant. The embryo is surrounded by nutrients that help the seedling germinate. Non-seed plants such as ferns (pterophytes), liverworts and mosses (bryophytes) reproduce by spores. Spores are generally microscopic in size and are often located on stalks or the underside of the leaf. Unlike seeds, fer ...
Viburnum acerifolium – Mapleleaf Viburnum
... SCIENTIFIC NAME: Viburnum acerifolium – comes from a Latin name of doubtful meaning with leaves like a maple ...
... SCIENTIFIC NAME: Viburnum acerifolium – comes from a Latin name of doubtful meaning with leaves like a maple ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.