Chapter 22: Introduction to Plants
... embryo, keeps it from drying out The embryo begins to grow when conditions are right Uses nutrients from stored food supply until it can carry out photosynthesis on its own ...
... embryo, keeps it from drying out The embryo begins to grow when conditions are right Uses nutrients from stored food supply until it can carry out photosynthesis on its own ...
invasives information - Mill River Wetland Committee
... Reproduces aggressively through the spread of rhizomes (underground stem system) up to 10 feet horizontally a year under good conditions Rhizomes (stems that grow horizontally at or above soil level) can grow to a length of 17 to 34 feet. The rhizomes can break off and spread with water curren ...
... Reproduces aggressively through the spread of rhizomes (underground stem system) up to 10 feet horizontally a year under good conditions Rhizomes (stems that grow horizontally at or above soil level) can grow to a length of 17 to 34 feet. The rhizomes can break off and spread with water curren ...
CONTACT: Nancy Freeman 361-790
... number of different plants. Some of their favorites are mistflowers, boneset, gayfeather, blanket flower, pentas, goldenrod, phlox, purple coneflower, golden-eye, lantana, and sunflowers. A flower that provides a landing area where they can perch while they drink nectar gives them the chance to drin ...
... number of different plants. Some of their favorites are mistflowers, boneset, gayfeather, blanket flower, pentas, goldenrod, phlox, purple coneflower, golden-eye, lantana, and sunflowers. A flower that provides a landing area where they can perch while they drink nectar gives them the chance to drin ...
Unit A Plant Structure and Function Chapter 1 Lesson 1 How Are
... Unit A Plant Structure and Function Chapter 1 Lesson 1 How Are Plants Grouped? ...
... Unit A Plant Structure and Function Chapter 1 Lesson 1 How Are Plants Grouped? ...
Kahili ginger - Horizons Regional Council
... Is Kahili ginger on your property? Kahili ginger is included in Horizon’s Regional Plant Pest Management Strategy as a ‘containment’ plant. This means that it occurs too frequently to make eradication a practical possibility. The areas where it has become a problem are recorded in the strategy and t ...
... Is Kahili ginger on your property? Kahili ginger is included in Horizon’s Regional Plant Pest Management Strategy as a ‘containment’ plant. This means that it occurs too frequently to make eradication a practical possibility. The areas where it has become a problem are recorded in the strategy and t ...
Photosynthesis
... Plants contain nondifferentiated meristem tissue Allows them to reproduce asexually by vegetative ...
... Plants contain nondifferentiated meristem tissue Allows them to reproduce asexually by vegetative ...
Tropism - My Teacher Site
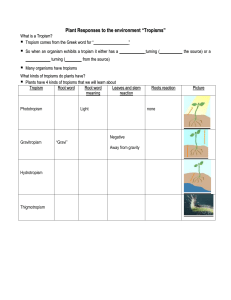
... Plants have 4 kinds of tropisms that we will learn about Tropism Root word Root word Leaves and stem meaning reaction Phototropism ...
... Plants have 4 kinds of tropisms that we will learn about Tropism Root word Root word Leaves and stem meaning reaction Phototropism ...
Horticulture Edition - July 2015
... This is a picture from this year. The root goes to China and round up does not touch the root. Also supposed to have a lovely pink variegation—it did the first year, but never again. Just don’t plant it—I beg of you. Hedera helix—English Ivy, it also is environmentally invasive and extremely difficu ...
... This is a picture from this year. The root goes to China and round up does not touch the root. Also supposed to have a lovely pink variegation—it did the first year, but never again. Just don’t plant it—I beg of you. Hedera helix—English Ivy, it also is environmentally invasive and extremely difficu ...
system
... are adapted hold catch water. more sunlight. plant grow to toward live on land. sun. and animals Camouflage = adaptations? blending ineating them. Why domore plants need remain in place. speed keep to predators catch food. from catch dinner! Mimicry = copying something that increases chances of surv ...
... are adapted hold catch water. more sunlight. plant grow to toward live on land. sun. and animals Camouflage = adaptations? blending ineating them. Why domore plants need remain in place. speed keep to predators catch food. from catch dinner! Mimicry = copying something that increases chances of surv ...
Lab Manual - UBC Blogs
... Capsicum peppers (Levetin and McMahon, pages 287 - 289) are the most widely cultivated spices in the world. They originated in South America and have become the most important component of a number of cuisines including Mexican, Thai, and Indian. There are five different species and many varieties. ...
... Capsicum peppers (Levetin and McMahon, pages 287 - 289) are the most widely cultivated spices in the world. They originated in South America and have become the most important component of a number of cuisines including Mexican, Thai, and Indian. There are five different species and many varieties. ...
Sunset Magenta Rockrose
... Sunset Magenta Rockrose will grow to be about 3 feet tall at maturity, with a spread of 5 feet. It tends to fill out right to the ground and therefore doesn't necessarily require facer plants in front. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 ...
... Sunset Magenta Rockrose will grow to be about 3 feet tall at maturity, with a spread of 5 feet. It tends to fill out right to the ground and therefore doesn't necessarily require facer plants in front. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 ...
Project Lifescape-11 Hunter Plants
... Hunter plants are among the curiosities of nature, being very different from normal plants in their mode of nutrition. They, however, never prey upon humans or large animals as often depicted in fiction or fables. They are specialised in trapping insects and are popularly known as insectivorous plan ...
... Hunter plants are among the curiosities of nature, being very different from normal plants in their mode of nutrition. They, however, never prey upon humans or large animals as often depicted in fiction or fables. They are specialised in trapping insects and are popularly known as insectivorous plan ...
Ruffles Bordeaux Coleus
... Plant Characteristics: Ruffles Bordeaux Coleus will grow to be about 18 inches tall at maturity, with a spread of 18 inches. Although it's not a true annual, this fast-growing plant can be expected to behave as an annual in our climate if left outdoors over the winter, usually needing replacement th ...
... Plant Characteristics: Ruffles Bordeaux Coleus will grow to be about 18 inches tall at maturity, with a spread of 18 inches. Although it's not a true annual, this fast-growing plant can be expected to behave as an annual in our climate if left outdoors over the winter, usually needing replacement th ...
1 2006S Bio153 Lab 4: Seedless Vascular Plants July 11th / July
... evidence shows that these early plants contained elongated cells organized into tissues. These cells had walls thickened with an extremely strong substance called lignin. These lignin rings would have allowed these plants to support erect stems and conduct water throughout the plant. By about 380 mi ...
... evidence shows that these early plants contained elongated cells organized into tissues. These cells had walls thickened with an extremely strong substance called lignin. These lignin rings would have allowed these plants to support erect stems and conduct water throughout the plant. By about 380 mi ...
Camassia_quamash - University of Washington
... Suggested spacing for bulbs in naturalized landscapes vary from 7.5 to 20 cm (3 to 8 in) apart. Others recommend 6 to 8 bulbs every 30 cm (12 in) for outdoor gardens. A dense “natural” stand may have 100 plants per m2 (9/ft2) or more. (Anonymous 2001) Care requirements after installed (water weekly, ...
... Suggested spacing for bulbs in naturalized landscapes vary from 7.5 to 20 cm (3 to 8 in) apart. Others recommend 6 to 8 bulbs every 30 cm (12 in) for outdoor gardens. A dense “natural” stand may have 100 plants per m2 (9/ft2) or more. (Anonymous 2001) Care requirements after installed (water weekly, ...
Late-Season Scouting – Why are Weeds Present in a Field??
... The presence of weeds late into the growing season can be caused by many things. The following list represents potential causes of weeds being present late in the growing season: 1. Sprayer skips. Caused by skips between sprayer passes or near end-rows/head-lands and from plugged nozzles. In these s ...
... The presence of weeds late into the growing season can be caused by many things. The following list represents potential causes of weeds being present late in the growing season: 1. Sprayer skips. Caused by skips between sprayer passes or near end-rows/head-lands and from plugged nozzles. In these s ...
THE RHIZOMATOUS GROUP Rhizomatous begonias form the
... The ground level rhizomes are the most common, and as their rhizomes grow forward the back section dies, with the vigorous part being the growing tip. When garden planted these rhizomatous begonias have a ‘life’ of two to three years, after which time they are likely to become straggly and unattract ...
... The ground level rhizomes are the most common, and as their rhizomes grow forward the back section dies, with the vigorous part being the growing tip. When garden planted these rhizomatous begonias have a ‘life’ of two to three years, after which time they are likely to become straggly and unattract ...
Stoller Enterprises, Inc.
... Considering this concept, diseases do not take down plants; plants decompose their tissue and invite disease to invade them. In our farming practices, we encourage this process by applying high rates of nitrogen. And, when it comes to calcium, we often rely on soil reserves to be sufficient. But wha ...
... Considering this concept, diseases do not take down plants; plants decompose their tissue and invite disease to invade them. In our farming practices, we encourage this process by applying high rates of nitrogen. And, when it comes to calcium, we often rely on soil reserves to be sufficient. But wha ...
Invader Weapons
... Many invasive plants arrived in an area because they were introduced as ornamental plants. These showy flowers can steal pollinators from native plants. We all know that the many flowers of an invasive plant will turn into many seeds. The seeds are really the secret behind invader spread! Seeds: ...
... Many invasive plants arrived in an area because they were introduced as ornamental plants. These showy flowers can steal pollinators from native plants. We all know that the many flowers of an invasive plant will turn into many seeds. The seeds are really the secret behind invader spread! Seeds: ...
Blueweed - Montana State University Extension
... vegetative parts of blueweed, causing considerable damage and reducing seed production. The larval stage (caterpillar) of E. bipunctella also feeds on the vegetative blueweed. This species has expanded its range in the northeastern United States as far south as Maryland and west into West Virginia. ...
... vegetative parts of blueweed, causing considerable damage and reducing seed production. The larval stage (caterpillar) of E. bipunctella also feeds on the vegetative blueweed. This species has expanded its range in the northeastern United States as far south as Maryland and west into West Virginia. ...
European Mistletoe
... Has been one of the most magical, mysterious and sacred of all the European plants Associated with Celtic rituals & Greek festivals The tradition of kissing under the mistletoe was first associated with primitive marriage rights due to its believed power of fertility ...
... Has been one of the most magical, mysterious and sacred of all the European plants Associated with Celtic rituals & Greek festivals The tradition of kissing under the mistletoe was first associated with primitive marriage rights due to its believed power of fertility ...
Santa Claus Fuchsia
... Santa Claus Fuchsia will grow to be about 3 feet tall at maturity, with a spread of 3 feet. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. Although it's not a true annual, this fast-growing plant can be expected to behave as an annual in our climate if le ...
... Santa Claus Fuchsia will grow to be about 3 feet tall at maturity, with a spread of 3 feet. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. Although it's not a true annual, this fast-growing plant can be expected to behave as an annual in our climate if le ...
Dutch Growers Garden Centre (Saskatoon)
... Butterfly Pink Star Flower will grow to be about 24 inches tall at maturity, with a spread of 24 inches. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. Although it's not a true annual, this fast-growing plant can be expected to behave as an annual in our ...
... Butterfly Pink Star Flower will grow to be about 24 inches tall at maturity, with a spread of 24 inches. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. Although it's not a true annual, this fast-growing plant can be expected to behave as an annual in our ...
European black alder
... have been observed on European alder. Those known to cause significant damage include striped alder sawfly (Hernichroa crocea), European alder leafminer (Fenusa dohrnii), alder flea beetle (Altica ambiens alni) and woolly alder aphid (Prociphilus tessalatus). ...
... have been observed on European alder. Those known to cause significant damage include striped alder sawfly (Hernichroa crocea), European alder leafminer (Fenusa dohrnii), alder flea beetle (Altica ambiens alni) and woolly alder aphid (Prociphilus tessalatus). ...
Erigenia bulbosa
... Basal Leaves: Its basal leaves are numerous Stem Leaves: Its 1-2 stem leaves are alternate, palmately compound, and are twice divided into 3 delicate, fern-like leaflets. Each leaflet is over 1½ inches wide and is divided into narrow oval, oblong, or lobed toothless segments with rounded tips. These ...
... Basal Leaves: Its basal leaves are numerous Stem Leaves: Its 1-2 stem leaves are alternate, palmately compound, and are twice divided into 3 delicate, fern-like leaflets. Each leaflet is over 1½ inches wide and is divided into narrow oval, oblong, or lobed toothless segments with rounded tips. These ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.