Ch26
... 1. Small plants found in moist environments, lack woody tissue and usually form mats spread over the ground. 2. Gametophyte generation is dominant; sporophyte is parasitic on the gametophyte. 3. Bryophytes have cuticle, stomata and multicellular gametangia that allow them to survive on land. 4. Bry ...
... 1. Small plants found in moist environments, lack woody tissue and usually form mats spread over the ground. 2. Gametophyte generation is dominant; sporophyte is parasitic on the gametophyte. 3. Bryophytes have cuticle, stomata and multicellular gametangia that allow them to survive on land. 4. Bry ...
Perennials - PowerPoint file - OSU Phenology Garden Network
... Brilliant yellow, daisy-like flowers. Fine for cutting in early spring. Plant is dormant in midsummer, the foliage partially disappearing. One of the earliest blooming perennials and an excellent ground cover under shrubs and trees if the soil is kept moist in the summer. ...
... Brilliant yellow, daisy-like flowers. Fine for cutting in early spring. Plant is dormant in midsummer, the foliage partially disappearing. One of the earliest blooming perennials and an excellent ground cover under shrubs and trees if the soil is kept moist in the summer. ...
Slide 1
... microliters DMSO incubated with 180 microliters of S. aureus culture for 2 and 24 hours at 37°C Incubation mixtures diluted 10,000-fold and 1,000,000-fold and spread plates prepared with 100 microliters of S. ...
... microliters DMSO incubated with 180 microliters of S. aureus culture for 2 and 24 hours at 37°C Incubation mixtures diluted 10,000-fold and 1,000,000-fold and spread plates prepared with 100 microliters of S. ...
Imagine you are walking through a tropical rain forest. The air feels
... birds calling. You brush against a small, green, feathery plant. As you look around, there are lots of these plants growing on the forest floor. The plants described above are called ferns. There are many different kinds of ferns. They range in size from low-lying plants that can cover a forest floo ...
... birds calling. You brush against a small, green, feathery plant. As you look around, there are lots of these plants growing on the forest floor. The plants described above are called ferns. There are many different kinds of ferns. They range in size from low-lying plants that can cover a forest floo ...
Plant Processes PowerPoint
... One type of artificial reproduction that helps improve the stock of fruit trees is called __________. ...
... One type of artificial reproduction that helps improve the stock of fruit trees is called __________. ...
Inniswood Hosta
... flowers, with a spread of 3 feet. Its foliage tends to remain low and dense right to the ground. It grows at a slow rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. This perennial does best in partial shade to shade. It prefers to grow in average to moist conditio ...
... flowers, with a spread of 3 feet. Its foliage tends to remain low and dense right to the ground. It grows at a slow rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. This perennial does best in partial shade to shade. It prefers to grow in average to moist conditio ...
ANGIOSPERMS - E
... Plants using the water to help them with pollination must live in the water (they are aquatic plants). The pollen is released and floats on top of the water. The stigmas of another plant must be close to the surface of the water so that they can catch the pollen as it floats by. Why is pollination i ...
... Plants using the water to help them with pollination must live in the water (they are aquatic plants). The pollen is released and floats on top of the water. The stigmas of another plant must be close to the surface of the water so that they can catch the pollen as it floats by. Why is pollination i ...
Topic 9: Plant Nutrition, Growth and Development (Chs. 36-39)
... Topic 9: Plant Nutrition, Growth and Development (Chs. 36-39) ...
... Topic 9: Plant Nutrition, Growth and Development (Chs. 36-39) ...
Lectures 17-24 (word)
... • one with terminal sporangia • one with lateral sporangia and flaps of tissue (non -vascularized) ▼ extant vascular cryptogams - 2 divisions (phyla) ▼ Lycophyta (club mosses) • leaves are microphylls - arose from vascularized flaps (enations) • sporangia are lateral, associated with leaves and ofte ...
... • one with terminal sporangia • one with lateral sporangia and flaps of tissue (non -vascularized) ▼ extant vascular cryptogams - 2 divisions (phyla) ▼ Lycophyta (club mosses) • leaves are microphylls - arose from vascularized flaps (enations) • sporangia are lateral, associated with leaves and ofte ...
The LECHUZA (Dream)Team of the month for August
... and offices – one you can find at any reputable retailer. Houseplants are natural air fresheners that filter pollutants and release oxygen. Their fresh green color adds harmony to any environment puts people in a good mood and makes them feel comfortable. LECHUZA planters bring out the beauty of pla ...
... and offices – one you can find at any reputable retailer. Houseplants are natural air fresheners that filter pollutants and release oxygen. Their fresh green color adds harmony to any environment puts people in a good mood and makes them feel comfortable. LECHUZA planters bring out the beauty of pla ...
owen BOTANY - Kowenscience.com
... If the pollen is from the right kind of plant, and lands on the flower, the pollen grain will break open and its content produce a tube that grows down through the style into the ovule. ...
... If the pollen is from the right kind of plant, and lands on the flower, the pollen grain will break open and its content produce a tube that grows down through the style into the ovule. ...
Intro to Plants
... • On land, most plants take nutrients from the soil with their roots. • Fungi have helped land plants to get nutrients from Earth’s rocky surface. – Symbiotic relationships referred to as mutualism between fungi and the roots of plants are called mycorrhizae. – Today, about 80% of all plant species ...
... • On land, most plants take nutrients from the soil with their roots. • Fungi have helped land plants to get nutrients from Earth’s rocky surface. – Symbiotic relationships referred to as mutualism between fungi and the roots of plants are called mycorrhizae. – Today, about 80% of all plant species ...
Linnaea borealis
... Storage Behaviour: Most likely orthodox; dry seed to low relative humidity and store cold but this is unproven (Royal Botanic Gardens Kew 2008). Storage: Store cool and dry (Luna et al. 2008). Longevity: Unknown but does not remain viable in soil seed banks for long periods of time (Howard 1993); sh ...
... Storage Behaviour: Most likely orthodox; dry seed to low relative humidity and store cold but this is unproven (Royal Botanic Gardens Kew 2008). Storage: Store cool and dry (Luna et al. 2008). Longevity: Unknown but does not remain viable in soil seed banks for long periods of time (Howard 1993); sh ...
Powerpoint - Colorado FFA
... made just below the node Remove lower leaves Apply rooting hormone Insert in media deep enough to be self supporting 1 node must be below the surface of the media for root growth to occur ...
... made just below the node Remove lower leaves Apply rooting hormone Insert in media deep enough to be self supporting 1 node must be below the surface of the media for root growth to occur ...
1d. Plantstaxonomy,reprod,response
... asymmetrical distribution of auxin cells on darker side elongate faster than cells on brighter side ...
... asymmetrical distribution of auxin cells on darker side elongate faster than cells on brighter side ...
Young Plant Flowering Plant
... A seedling starts to grow leaves and begins to make its own food. As the plant grows more leaves, there will be less need for the cotyledons. The cotyledons will eventually be shed. (Think of cotyledons as the plant version of baby teeth.) ...
... A seedling starts to grow leaves and begins to make its own food. As the plant grows more leaves, there will be less need for the cotyledons. The cotyledons will eventually be shed. (Think of cotyledons as the plant version of baby teeth.) ...
Golgi- Packages and transports proteins outside the cell
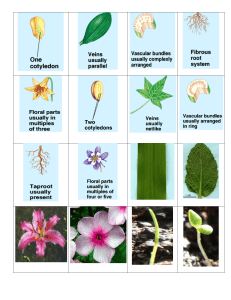
... The big difference that most people note about monocots and dicots is the formation of the plants’ veins on leaves. ...
... The big difference that most people note about monocots and dicots is the formation of the plants’ veins on leaves. ...
Hybridizing Lotuses
... find new plants and knowledgeable people we take notice. One such man is Stephen Garton; he has a passion and knowledge for Nelumbos. Stephen first saw them growing to perfection at Davis Creek Nurseries, which peaked his interest. He then studied the native Nelumbo lutea growing wild in some Alabam ...
... find new plants and knowledgeable people we take notice. One such man is Stephen Garton; he has a passion and knowledge for Nelumbos. Stephen first saw them growing to perfection at Davis Creek Nurseries, which peaked his interest. He then studied the native Nelumbo lutea growing wild in some Alabam ...
$doc.title
... 2. Dig a hole about two >mes wider than the plant's container, but no deeper than the plant’s root ball. 3. Tap the sides of the container firmly with a trowel to ...
... 2. Dig a hole about two >mes wider than the plant's container, but no deeper than the plant’s root ball. 3. Tap the sides of the container firmly with a trowel to ...
Chapter 18
... • In seed plants the gametophytes are microscopic in size. • The desiccation-tolerant pollen grains are the male, sperm-producing gametophyte. • Pollination occurs when the pollen grain fertilizes the female gametophyte. ...
... • In seed plants the gametophytes are microscopic in size. • The desiccation-tolerant pollen grains are the male, sperm-producing gametophyte. • Pollination occurs when the pollen grain fertilizes the female gametophyte. ...
Comparative Phenology of Five Dominant Plant Species
... renosterbos — S. Africa) are open dwarf-scrub ones. Both these groups of the mediterranean type vegetation, under the conditions of the mediterranean climate, have evolved several adaptations in their life cycles in order to cope with them. Concerning the phenology of Mediterranean plant species, st ...
... renosterbos — S. Africa) are open dwarf-scrub ones. Both these groups of the mediterranean type vegetation, under the conditions of the mediterranean climate, have evolved several adaptations in their life cycles in order to cope with them. Concerning the phenology of Mediterranean plant species, st ...
chapter 38 - Course Notes
... researchers from visualizing fertilization in plants, but recently, scientists have been able to isolate sperm cells and eggs and observe fertilization in vitro. The first cellular event after gamete fusion is an increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels, which also occurs during animal gamete fusion. ...
... researchers from visualizing fertilization in plants, but recently, scientists have been able to isolate sperm cells and eggs and observe fertilization in vitro. The first cellular event after gamete fusion is an increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels, which also occurs during animal gamete fusion. ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.