The Sensorimotor System
... Not all patients with this form of amnesia are unable form new explicit long-term memories, as was the case with H.M. ...
... Not all patients with this form of amnesia are unable form new explicit long-term memories, as was the case with H.M. ...
PAPER #3: EMBARGOED PRESS RELEASE STRICTLY UNDER
... Surprisingly, a single stimulation of the ventral subiculum (which lasts about 10 minutes in an anesthetized rat) had the same impact on the brain and dopamine neurons as a massive injection of cocaine. These effects lasted up to five days and raise the possibility that dopamine-producing neurons ca ...
... Surprisingly, a single stimulation of the ventral subiculum (which lasts about 10 minutes in an anesthetized rat) had the same impact on the brain and dopamine neurons as a massive injection of cocaine. These effects lasted up to five days and raise the possibility that dopamine-producing neurons ca ...
Ms. Setzer-The Brain!
... mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. -The right hemisphere houses most spatial abilities-the ability to precieve or organize things in a given space. Also helps make connections between words. ...
... mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. -The right hemisphere houses most spatial abilities-the ability to precieve or organize things in a given space. Also helps make connections between words. ...
Limbic System - WordPress.com
... A. Gray matter does not contain synapses; white matter does. B. White matter is largely composed of myelinated axons; gray matter is not. C. White matter functions primarily to transmit impulses to other areas of the CNS. ...
... A. Gray matter does not contain synapses; white matter does. B. White matter is largely composed of myelinated axons; gray matter is not. C. White matter functions primarily to transmit impulses to other areas of the CNS. ...
LAB 5 – CORONAL 1 (Jan 29)
... Any structure resembling an arch, especially the archlike band of white fibres in the limbic system at the base of the brain, projecting from the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies , involved in memory and the control of eating. Also called the vault. Optic Tract The part of each optic nerve betwe ...
... Any structure resembling an arch, especially the archlike band of white fibres in the limbic system at the base of the brain, projecting from the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies , involved in memory and the control of eating. Also called the vault. Optic Tract The part of each optic nerve betwe ...
CHAPTER 12 Learning and Memory Basic Outline with notes I. The
... behavior. We refer to these changes as memory. Experiences change the way we perceive, perform, think and plan. A. Learning can take 4 basic forms: 1. Perceptual Learning – The identification of objects and things. Changes in the perceptual systems that make it possible for us to recognize stimuli s ...
... behavior. We refer to these changes as memory. Experiences change the way we perceive, perform, think and plan. A. Learning can take 4 basic forms: 1. Perceptual Learning – The identification of objects and things. Changes in the perceptual systems that make it possible for us to recognize stimuli s ...
Nervous system
... The occipital cortex is the primary visual area of the brain. It receives projections from the retina from where different groups of neurons separately encode different visual information such as color, orientation, and motion. ...
... The occipital cortex is the primary visual area of the brain. It receives projections from the retina from where different groups of neurons separately encode different visual information such as color, orientation, and motion. ...
THE BRAIN DAMAGE IN FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME
... In nuclei in the hypothalamus (Figure 2), we also observed focuses of tissue rarefaction and cell dystrophic changes. Chromatolysis and pycnotic changes, as well as a decrease (and sometimes a complete absence) of neuroendocrine granules, were dominated. In the cerebellum (Figure 3) we observed thin ...
... In nuclei in the hypothalamus (Figure 2), we also observed focuses of tissue rarefaction and cell dystrophic changes. Chromatolysis and pycnotic changes, as well as a decrease (and sometimes a complete absence) of neuroendocrine granules, were dominated. In the cerebellum (Figure 3) we observed thin ...
Auditory information processing at the cortical level
... The primary auditory cortex appears to be well organised with respect to frequency and carries on its surface a “map” of the cochlea, as is found in the subcortical nuclei. High frequency excitation, orignating in the base of the cochlea, is received in neurons located in the more medial portion of ...
... The primary auditory cortex appears to be well organised with respect to frequency and carries on its surface a “map” of the cochlea, as is found in the subcortical nuclei. High frequency excitation, orignating in the base of the cochlea, is received in neurons located in the more medial portion of ...
Lecture 12
... (frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital, insula). Other gray matter found in the cerebrum is located in the basal nuclei and the limbic system. Basal nuclei are masses of gray matter located deep within the cerebral hemispheres. They relay motor impulses originating in the cerebral cortex, and a ...
... (frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital, insula). Other gray matter found in the cerebrum is located in the basal nuclei and the limbic system. Basal nuclei are masses of gray matter located deep within the cerebral hemispheres. They relay motor impulses originating in the cerebral cortex, and a ...
Step back and look at the Science
... Brain growth rate of foetus same… but… Human brain continues growth at rapid fetal rate for 2 yrs ...
... Brain growth rate of foetus same… but… Human brain continues growth at rapid fetal rate for 2 yrs ...
Chapter 3 Class Notes / Biological Foundations
... includes the two large lobes or left and right ‘hemispheres’ on the top of the brain. The cerebral cortex is responsible for thinking, memory processes, learning, reasoning, intelligence, creativity, sensory processing and awareness, and in general, our conscious experience. The two hemispheres (lef ...
... includes the two large lobes or left and right ‘hemispheres’ on the top of the brain. The cerebral cortex is responsible for thinking, memory processes, learning, reasoning, intelligence, creativity, sensory processing and awareness, and in general, our conscious experience. The two hemispheres (lef ...
NMSI - 4 Central Nervous System
... active when speech is generated • Wernicke’s area in the temporal lobe is active when speech is ...
... active when speech is generated • Wernicke’s area in the temporal lobe is active when speech is ...
Central nervous system
... active when speech is generated • Wernicke’s area in the temporal lobe is active when speech is ...
... active when speech is generated • Wernicke’s area in the temporal lobe is active when speech is ...
CNS lecture
... Parietal lobe: somatic sensory area : impulses from sensory receptors are localized and interpreted; path are X’d, able to interpret characteristics of objects feel with hand and to comprehend spoken and written language Occipital lobe: visual cortex, receives visual info via thalamus (primary visua ...
... Parietal lobe: somatic sensory area : impulses from sensory receptors are localized and interpreted; path are X’d, able to interpret characteristics of objects feel with hand and to comprehend spoken and written language Occipital lobe: visual cortex, receives visual info via thalamus (primary visua ...
Slide ()
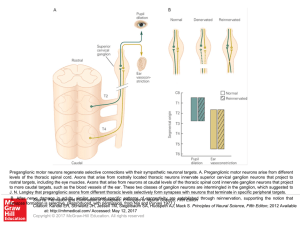
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
Module Four: The Brain
... - Protects brain cells from harmful substances and pathogens o Regulates what substances can move from the bloodstream into the interstitial fluid of the brain - Selectively permeable barrier formed by tight junctions that seal together the endothelial cells of brain capillaries o Permeable to liq ...
... - Protects brain cells from harmful substances and pathogens o Regulates what substances can move from the bloodstream into the interstitial fluid of the brain - Selectively permeable barrier formed by tight junctions that seal together the endothelial cells of brain capillaries o Permeable to liq ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... Second, the gates of the potassium channels open, and potassium flows outside the axon. This repolarizes the axon. Conduction of an Action Potential The action potential travels down an axon one small section at a time. Transmission across a Synapse Every axon branches into many fine endings, each t ...
... Second, the gates of the potassium channels open, and potassium flows outside the axon. This repolarizes the axon. Conduction of an Action Potential The action potential travels down an axon one small section at a time. Transmission across a Synapse Every axon branches into many fine endings, each t ...
Biological Bases
... appearance cause by the layer known as the cerebral cortex The brain’s versatility caused by the millions of different neural connections Our adaptability to different problems ranging from survival needs to abstract reasoning New connections forming in the brain to take over for damaged sections ...
... appearance cause by the layer known as the cerebral cortex The brain’s versatility caused by the millions of different neural connections Our adaptability to different problems ranging from survival needs to abstract reasoning New connections forming in the brain to take over for damaged sections ...
File
... health patients, is it fair to experiment on epileptic patients? • Soldiers? • FMRI allows this without experimentation ...
... health patients, is it fair to experiment on epileptic patients? • Soldiers? • FMRI allows this without experimentation ...
working memory
... In the resting old brain, granule cells, for example, had overall higher methylation levels, meaning that it was less likely that plasticity genes could be transcribed from the DNA (Barnes and Sweatt, see Barnes 2001). There may well be a number of changes that accumulate during aging via epigenetic ...
... In the resting old brain, granule cells, for example, had overall higher methylation levels, meaning that it was less likely that plasticity genes could be transcribed from the DNA (Barnes and Sweatt, see Barnes 2001). There may well be a number of changes that accumulate during aging via epigenetic ...
`synapse`.
... Impulse from the action potential opens ion channels for Ca++ The increased Ca++ concentration in the axon terminal initiates the release of the neurotransmitter (NT) NT is released from its vesicle and crosses the “gap” or synaptic cleft and attaches to a protein receptor on the dendrite ...
... Impulse from the action potential opens ion channels for Ca++ The increased Ca++ concentration in the axon terminal initiates the release of the neurotransmitter (NT) NT is released from its vesicle and crosses the “gap” or synaptic cleft and attaches to a protein receptor on the dendrite ...