How a Flower is Pollinated
... What is the male part? • The male part of the flower is called the stamen • It has a long stalk called the filament • At the top of the filament is the anther ...
... What is the male part? • The male part of the flower is called the stamen • It has a long stalk called the filament • At the top of the filament is the anther ...
Powerpoint
... Need moisture for sexual reproduction to occur since flagellated sperm must swim to the egg life cycle includes alternation of generations between: haploid (n) phase (gametophyte) diploid (2n) phase (sporophyte) ...
... Need moisture for sexual reproduction to occur since flagellated sperm must swim to the egg life cycle includes alternation of generations between: haploid (n) phase (gametophyte) diploid (2n) phase (sporophyte) ...
Catchweed - Stevens County
... ¾ This plant is an introduced species from Europe ¾ Infests many acres in the western United States ¾ Does not compete well with grass, tends to mature and “dry up” relatively early in the growing season ...
... ¾ This plant is an introduced species from Europe ¾ Infests many acres in the western United States ¾ Does not compete well with grass, tends to mature and “dry up” relatively early in the growing season ...
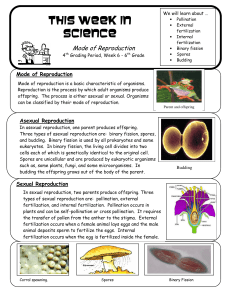
This week in science 6th - Reproduction
... Three types of asexual reproduction are: binary fission, spores, and budding. Binary fission is used by all prokaryotes and some eukaryotes. In binary fission, the living cell divides into two cells each of which is genetically identical to the original cell. Spores are unicellular and are produced ...
... Three types of asexual reproduction are: binary fission, spores, and budding. Binary fission is used by all prokaryotes and some eukaryotes. In binary fission, the living cell divides into two cells each of which is genetically identical to the original cell. Spores are unicellular and are produced ...
Plants
... • Seeds protected by a layer of tissue • Flowers are the reproductive organs • Ovaries surround and protect seed inside the flower • Many times the ovaries will develop into fruit ...
... • Seeds protected by a layer of tissue • Flowers are the reproductive organs • Ovaries surround and protect seed inside the flower • Many times the ovaries will develop into fruit ...
Module B: Unit 2, Lesson 4 - Plant Processes
... • The light energy captured in chloroplasts is changed and stored in the bonds of a sugar called glucose. • In the same process, oxygen gas is released. • In plants, extra glucose is stored as starch or changed to other types of sugar such as fructose or sucrose. • In cellular respiration, cells use ...
... • The light energy captured in chloroplasts is changed and stored in the bonds of a sugar called glucose. • In the same process, oxygen gas is released. • In plants, extra glucose is stored as starch or changed to other types of sugar such as fructose or sucrose. • In cellular respiration, cells use ...
Plant Unit
... There are two (2) types of autotrophs, those that use ______________, and those that use __________________. _______________- turns carbon dioxide and inorganic substances like nitrogen and sulfur into the food they need. __________________- turns light, carbon dioxide and water (ingredients/raw mat ...
... There are two (2) types of autotrophs, those that use ______________, and those that use __________________. _______________- turns carbon dioxide and inorganic substances like nitrogen and sulfur into the food they need. __________________- turns light, carbon dioxide and water (ingredients/raw mat ...
Ch 22- Plant Diversity
... without standing water? – Flowers or cones- allow transfer of sperm by pollination and protection of embryos in seeds ...
... without standing water? – Flowers or cones- allow transfer of sperm by pollination and protection of embryos in seeds ...
the process of converting light energy into chemical energy using
... leaves vascular tissue that transports food (glucose) from photosynthetic cells to other parts of the plant for growth and storage the waxy, waterproof layer that covers the leaf to prevent water loss plants that shed their leaves seasonally seed plants that reproduce using "naked" seeds like cones ...
... leaves vascular tissue that transports food (glucose) from photosynthetic cells to other parts of the plant for growth and storage the waxy, waterproof layer that covers the leaf to prevent water loss plants that shed their leaves seasonally seed plants that reproduce using "naked" seeds like cones ...
Angiosperms
... Ability to float, allowing dispersal by water (coconut) 7. List the characteristics of an angiosperm. Flowers, Fruit, double fertilization, vascular tissue, seeds, true roots, true leaves 8. Draw and label the three parts to a seed. ...
... Ability to float, allowing dispersal by water (coconut) 7. List the characteristics of an angiosperm. Flowers, Fruit, double fertilization, vascular tissue, seeds, true roots, true leaves 8. Draw and label the three parts to a seed. ...
Plant Unit Test Study Guide Biology 112 What are 5 characteristics
... What are 5 characteristics an organism must have to be considered a Plant? ...
... What are 5 characteristics an organism must have to be considered a Plant? ...
Ch27
... Another sperm joins the two polar nuclei forming the triploid (3n) nutritive tissue called the endosperm. See figure 27-12, page 581, for details. Seeds develop from the ovule following fertilization. The ovary enlarges and forms the fruit. In some instances other tissues also enlarge and become par ...
... Another sperm joins the two polar nuclei forming the triploid (3n) nutritive tissue called the endosperm. See figure 27-12, page 581, for details. Seeds develop from the ovule following fertilization. The ovary enlarges and forms the fruit. In some instances other tissues also enlarge and become par ...
Basic Plant Structure
... Plant Reproductive Structure • Tomorrow you will be dissecting a flower, identifying the parts, and discussing how plants interact with their environment. • So let’s take a few minutes to talk about the structure of flowers… ...
... Plant Reproductive Structure • Tomorrow you will be dissecting a flower, identifying the parts, and discussing how plants interact with their environment. • So let’s take a few minutes to talk about the structure of flowers… ...
Figure 38.2 Simplified overview of angiosperm life cycle
... • A huge variety of adaptations have evolved in plants to ensure successful pollination, including biotic (via animals) and abiotic (via wind or water) mechanisms ...
... • A huge variety of adaptations have evolved in plants to ensure successful pollination, including biotic (via animals) and abiotic (via wind or water) mechanisms ...
Reproduction in Plants 1. Fill in the blanks propagation.
... c. Bisexual Flowers- The flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexual flowers. Examples- Mustard, Rose and Petunia produce bisexual flowers. d. Pollination- The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination. e. Self Pollination- If the polle ...
... c. Bisexual Flowers- The flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexual flowers. Examples- Mustard, Rose and Petunia produce bisexual flowers. d. Pollination- The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination. e. Self Pollination- If the polle ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... chlorophyll breaks down and the colors of accessory pigments can be seen. ...
... chlorophyll breaks down and the colors of accessory pigments can be seen. ...
Std. VII
... structures called sori. The spores are tiny, single-celled asexual reproductive units. They are surrounded by a tough coat for protection. When these spores mature, the sori burst and release ...
... structures called sori. The spores are tiny, single-celled asexual reproductive units. They are surrounded by a tough coat for protection. When these spores mature, the sori burst and release ...
THE PLANT KINGDOM - Welcome to Cherokee High School
... other tough materials • Cells are connected to each other by shared cytoplasm • Large central vacuoles ...
... other tough materials • Cells are connected to each other by shared cytoplasm • Large central vacuoles ...
Document
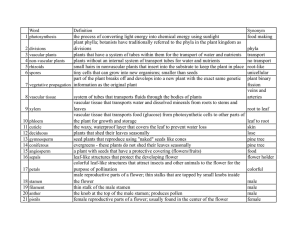
... Xylem – carries water and minerals from roots to rest of plants, composed of dead cells Phloem – is composed of living cells, ...
... Xylem – carries water and minerals from roots to rest of plants, composed of dead cells Phloem – is composed of living cells, ...
2.3 Sexual Reproduction in Plants
... of the plant. Each part of the flower has a specific function during the different stages of sexual reproduction; namely pollination, fertilisation and fruit formation with seeds. The flower is arranged in whorls (rings) of modified leaves each performing a specific function. These whorls are arrang ...
... of the plant. Each part of the flower has a specific function during the different stages of sexual reproduction; namely pollination, fertilisation and fruit formation with seeds. The flower is arranged in whorls (rings) of modified leaves each performing a specific function. These whorls are arrang ...
Plants
... - Fertilization occurs when the sperm from the pollen grain fuses (joins) with the egg inside the ovule. ...
... - Fertilization occurs when the sperm from the pollen grain fuses (joins) with the egg inside the ovule. ...
Kingdom Plantae - Smyth County Schools
... Seedless Vascular Plants • Have a vascular system • Sporophyte is larger & photosynthetic • Do need water to reproduce • Have droughtresistant spores • Example: Ferns ...
... Seedless Vascular Plants • Have a vascular system • Sporophyte is larger & photosynthetic • Do need water to reproduce • Have droughtresistant spores • Example: Ferns ...
Plant reproduction

Plant reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur. In seed plants, the offspring can be packaged in a protective seed, which is used as an agent of dispersal.