Life Science Chapter 1: How Plants Live and Grow Sequencing
... 1. mineral- a natural, nonliving material that can be found in soil 2. carbon dioxide- a gas in the air that plants use to make food Notes • Plant roots grow down into the soil. • The roots hold the plant tightly in the ground. • The roots take water and minerals from the soil. • The stems hold up t ...
... 1. mineral- a natural, nonliving material that can be found in soil 2. carbon dioxide- a gas in the air that plants use to make food Notes • Plant roots grow down into the soil. • The roots hold the plant tightly in the ground. • The roots take water and minerals from the soil. • The stems hold up t ...
1 Plant Characteristics Booklet Student Name
... Once a seed leaves the parent plant, it can either lay dormant OR germinate. If a seed lays dormant, that means it will wait until growing conditions are just right for it to grow. If a seed germinates, then it begins to grow. The roots grow down and stem & leaves grow up. This is called the process ...
... Once a seed leaves the parent plant, it can either lay dormant OR germinate. If a seed lays dormant, that means it will wait until growing conditions are just right for it to grow. If a seed germinates, then it begins to grow. The roots grow down and stem & leaves grow up. This is called the process ...
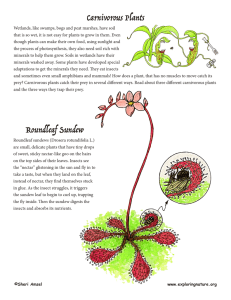
Carnivorous Plants Roundleaf Sundew
... prey? Carnivorous plants catch their prey in several different ways. Read about three different carnivorous plants and the three ways they trap their prey. ...
... prey? Carnivorous plants catch their prey in several different ways. Read about three different carnivorous plants and the three ways they trap their prey. ...
More Information on CLPW
... Habitat: Curly-leaf pondweed is found in the submersed plant community. Generally preferring soft sediments, it grows in waters that are shallow or deep, still or flowing. Curly-leaf thrives where many other aquatic plants do not, for example in waters that are shaded, disturbed, polluted or turbid. ...
... Habitat: Curly-leaf pondweed is found in the submersed plant community. Generally preferring soft sediments, it grows in waters that are shallow or deep, still or flowing. Curly-leaf thrives where many other aquatic plants do not, for example in waters that are shaded, disturbed, polluted or turbid. ...
Chapter 7 General Science The Plant Kingdom seed
... rigid, like the stems of trees and shrubs. These are woody stems. The wood is made of cells with thick walls. The stems of trees are called trunks. * You have probably eaten plant stems. Name all that you have tasted. Go. ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... rigid, like the stems of trees and shrubs. These are woody stems. The wood is made of cells with thick walls. The stems of trees are called trunks. * You have probably eaten plant stems. Name all that you have tasted. Go. ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
Plants
... important to plants Water- Plants need water. Water is essential to all life on earth. No known organism can exist without water. Plants use water to carry moisture and nutrients from the roots to he leaves and food from the leaves back down to the roots. Air- Plants most also have clean air. Gree ...
... important to plants Water- Plants need water. Water is essential to all life on earth. No known organism can exist without water. Plants use water to carry moisture and nutrients from the roots to he leaves and food from the leaves back down to the roots. Air- Plants most also have clean air. Gree ...
Plant Structure and Function
... First a root pushes through the seed coat and grows downward. The top part of the root grows upward and becomes the stem. The stem carries the seed coat and the seed leaves with it. The seed coat falls off. The seed leaves provide food for the plant. Two small leaves begin to grow from between the s ...
... First a root pushes through the seed coat and grows downward. The top part of the root grows upward and becomes the stem. The stem carries the seed coat and the seed leaves with it. The seed coat falls off. The seed leaves provide food for the plant. Two small leaves begin to grow from between the s ...
Planting and Planning: Warm Season Crops to
... Cucumbers: These trailing plants grow well from seed. Make sure you plant them according to the seed packet’s instructions, so each plant has the space it needs. To protect them from cucumber beetles, which carry bacterial wilt, cover the plants with fabric row cover (no need for wire hoops) until t ...
... Cucumbers: These trailing plants grow well from seed. Make sure you plant them according to the seed packet’s instructions, so each plant has the space it needs. To protect them from cucumber beetles, which carry bacterial wilt, cover the plants with fabric row cover (no need for wire hoops) until t ...
Taxonomy review session
... Seeds and their advantages • 1) Seed plants don’t depend on water to reproduce – Pollen (contains sperm) combines with egg – Egg hardens into a seed • 2) Nourishment and protection – Nourish: Nutrients inside seed for the embryo – Protection: Hard shell • 3) Allow dispersal – Carried by wind, water ...
... Seeds and their advantages • 1) Seed plants don’t depend on water to reproduce – Pollen (contains sperm) combines with egg – Egg hardens into a seed • 2) Nourishment and protection – Nourish: Nutrients inside seed for the embryo – Protection: Hard shell • 3) Allow dispersal – Carried by wind, water ...
PLANTS TEST
... Plants are organisms that make their own food, a simple sugar, for survival. The process by which they make this sugar is called photosynthesis. Chloroplasts, found in the cells of the leaf, contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs light energy. During this process, plants use carbon dioxid ...
... Plants are organisms that make their own food, a simple sugar, for survival. The process by which they make this sugar is called photosynthesis. Chloroplasts, found in the cells of the leaf, contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs light energy. During this process, plants use carbon dioxid ...
Plant and Animal Structure Unit
... Plants are made a small building blocks called cells. Different parts of a cell do different jobs. Ex: some cells may have the job of making food for the plant ...
... Plants are made a small building blocks called cells. Different parts of a cell do different jobs. Ex: some cells may have the job of making food for the plant ...
Class handout: Succulent propagation techniques
... Division is used for “clumping” plants that produce new shoots in a crowded mass, each with their own roots. Plants with fibrous roots and those with rhizomes (thick fleshy tubers) are also grown by division. Succulent plants suitable for dividing include shrubby aloes, gasterias, some yuccas, hawor ...
... Division is used for “clumping” plants that produce new shoots in a crowded mass, each with their own roots. Plants with fibrous roots and those with rhizomes (thick fleshy tubers) are also grown by division. Succulent plants suitable for dividing include shrubby aloes, gasterias, some yuccas, hawor ...
Beale`s barberry MABE2 Mahonia bealei (Fortune
... white waxy coated, light green turning robin’s egg blue and ripening purplish black, each with 2 to 3 seeds. Ecology. Moderate in growth rate in a full range of soil textures and light conditions, but prefers moist soils. Tolerates cold however young plants can be damaged by late frosts. Colonizes b ...
... white waxy coated, light green turning robin’s egg blue and ripening purplish black, each with 2 to 3 seeds. Ecology. Moderate in growth rate in a full range of soil textures and light conditions, but prefers moist soils. Tolerates cold however young plants can be damaged by late frosts. Colonizes b ...
Bookmark - Unit 4: Discovering Plants and Animals
... Skin – a protective covering around the outside of a creature or animal Habitat – the type of place where a creature lives and eats, examples are grasslands, forests, Polar Regions, streams, oceans, etc. Picture Walk & Prediction: What kind of animals do you think of live out in the grass and use it ...
... Skin – a protective covering around the outside of a creature or animal Habitat – the type of place where a creature lives and eats, examples are grasslands, forests, Polar Regions, streams, oceans, etc. Picture Walk & Prediction: What kind of animals do you think of live out in the grass and use it ...
Topic: Reproduction
... Topic: Reproduction Aim: Describe the structure of a flower and how it uses sexual reproduction. Do Now: Take out your HW and the Seeds ...
... Topic: Reproduction Aim: Describe the structure of a flower and how it uses sexual reproduction. Do Now: Take out your HW and the Seeds ...
Flowers
... Now, to drop the clerical simile, let us peep within the sheathing spathe, or, better still, strip it off altogether. Doctor Torrey states that the dark-striped spathes are the fertile plants, those with green and whitish lines, sterile. Within are smooth, glossy columns, and near the base of each ...
... Now, to drop the clerical simile, let us peep within the sheathing spathe, or, better still, strip it off altogether. Doctor Torrey states that the dark-striped spathes are the fertile plants, those with green and whitish lines, sterile. Within are smooth, glossy columns, and near the base of each ...
Range Plants Foundation of the Grazing Resource
... Rhizomes are actually creeping underground stems with joints and leanike scales. You may have seen quackgrass or western wheatgrass rhizomes producing a new plant. Rhizomes store food and reproduce new plants. Stolons are like rhizomes, except they grow above BCH-6050 ...
... Rhizomes are actually creeping underground stems with joints and leanike scales. You may have seen quackgrass or western wheatgrass rhizomes producing a new plant. Rhizomes store food and reproduce new plants. Stolons are like rhizomes, except they grow above BCH-6050 ...
The important things about life cycles is that organisms reproduce
... Living things need food, water, and air to live. Plants and animals live in an environment. The environment is everything around a living thing. An environment includes air, sunlight, water, and soil. An environment can change how a plant and animal grows. Plants need just the right amount of sunli ...
... Living things need food, water, and air to live. Plants and animals live in an environment. The environment is everything around a living thing. An environment includes air, sunlight, water, and soil. An environment can change how a plant and animal grows. Plants need just the right amount of sunli ...
Plants With A Purpose
... dense felt appearance (tomentose). Its striking colour can be used for contrast in mass flower colour or as a great contrast in between darker leaves. It would be a great addition to your horticultur ...
... dense felt appearance (tomentose). Its striking colour can be used for contrast in mass flower colour or as a great contrast in between darker leaves. It would be a great addition to your horticultur ...
The Seed Plants - FacultyWeb Support Center
... The sporophyte flower usually consists of four whorls of floral organs borne on the expanded end of a called the receptacle. The lowest and outermost structures, called sepals, are often leaflike and serve to protect the flower when it is a bud. Usually sepals are green; however, they may also be br ...
... The sporophyte flower usually consists of four whorls of floral organs borne on the expanded end of a called the receptacle. The lowest and outermost structures, called sepals, are often leaflike and serve to protect the flower when it is a bud. Usually sepals are green; however, they may also be br ...
Plant Diversity I: Colonization by Land Plants
... composition of sporopollenin is still not known! designed to protect the pollen grain on its “travels” ...
... composition of sporopollenin is still not known! designed to protect the pollen grain on its “travels” ...
Terminology Used With Plumeria - The Plumeria Society of America
... Petal. A unit of a corolla, usually showy and colored. Petiole. A leaf stalk. Pistil. The female, ovule-bearing organ of a flower, including the stigma, style, and ovary. Pollen. The fine, powder like material consisting of pollen grains that is produced by the anthers of seed plants. A structure th ...
... Petal. A unit of a corolla, usually showy and colored. Petiole. A leaf stalk. Pistil. The female, ovule-bearing organ of a flower, including the stigma, style, and ovary. Pollen. The fine, powder like material consisting of pollen grains that is produced by the anthers of seed plants. A structure th ...
Desert Pack - Birmingham Botanical Gardens and Glasshouses
... Here the stem is swollen with water inside a thick rubbery skin to prevent it being lost. To reduce the surface area from which water can be lost, there are no leaves. Therefore the stem is green to allow the plant to carry out photosynthesis. The barrelshaped cacti often use their ridges to change ...
... Here the stem is swollen with water inside a thick rubbery skin to prevent it being lost. To reduce the surface area from which water can be lost, there are no leaves. Therefore the stem is green to allow the plant to carry out photosynthesis. The barrelshaped cacti often use their ridges to change ...
Plant reproduction

Plant reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur. In seed plants, the offspring can be packaged in a protective seed, which is used as an agent of dispersal.