English
... There are two methods by which trees reproduce: seed reproduction and vegetative reproduction (sprouting, suckering, and layering). Most trees reproduce by seed, but many can also reproduce vegetatively. Broad-leaved trees will usually sprout from cut stems, but most needleleaved trees, or conifers, ...
... There are two methods by which trees reproduce: seed reproduction and vegetative reproduction (sprouting, suckering, and layering). Most trees reproduce by seed, but many can also reproduce vegetatively. Broad-leaved trees will usually sprout from cut stems, but most needleleaved trees, or conifers, ...
Justin Sexten Extension Specialist, Animal Systems/Beef
... outside there were ____ dead cattle. The incidence of accidental poisoning generally hits a seasonal high in the fall due to short pasture supply and accidental introduction of poisonous plants. Numerous landscape plants are commonly associated with livestock poisoning. One of the most common and mo ...
... outside there were ____ dead cattle. The incidence of accidental poisoning generally hits a seasonal high in the fall due to short pasture supply and accidental introduction of poisonous plants. Numerous landscape plants are commonly associated with livestock poisoning. One of the most common and mo ...
Study Guide 2: Bryophytes through Angiosperms and physiological
... Life cycles of: moss, fern, pine, angiosperm (eudicot). Know which stages are 2n, which are n, and where meiosis and mitosis occur. ...
... Life cycles of: moss, fern, pine, angiosperm (eudicot). Know which stages are 2n, which are n, and where meiosis and mitosis occur. ...
Growing Plants Using a Hydroponic Germinator
... -If conditions are right, germination will occur and a root will emerge from the seed. Eventually, stems produce leaves for photosynthesis and more roots push down to anchor the plant and gather nutrients. -Flowers develop and produce pollen. Pollination occurs by animals, insects, or the wind carry ...
... -If conditions are right, germination will occur and a root will emerge from the seed. Eventually, stems produce leaves for photosynthesis and more roots push down to anchor the plant and gather nutrients. -Flowers develop and produce pollen. Pollination occurs by animals, insects, or the wind carry ...
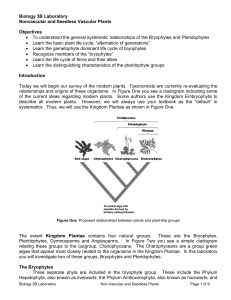
Biology 3B Laboratory Nonvascular and Seedless Vascular Plants
... and the Lycophyta, or club mosses. In these plants a vascular system connects the leaves, stems and roots. The sporophyte is dominant in all plants in this group. There are two groups identified within the pteridophytes based upon leaf size. The megaphylls (large leaves) includes the fern, which hav ...
... and the Lycophyta, or club mosses. In these plants a vascular system connects the leaves, stems and roots. The sporophyte is dominant in all plants in this group. There are two groups identified within the pteridophytes based upon leaf size. The megaphylls (large leaves) includes the fern, which hav ...
Chapter 6
... Meiosis I: the result is two daughter cells. Meiosis II: the result is four haploid cells, ...
... Meiosis I: the result is two daughter cells. Meiosis II: the result is four haploid cells, ...
8. Prairie Smoke - Friess Lake School District
... hairy leaflets that get progressively longer up the petiole. The leaflets are varied in shape. ...
... hairy leaflets that get progressively longer up the petiole. The leaflets are varied in shape. ...
phaius tankervilliae (grandifolius)
... A terrestrial orchid sometimes referred to as P. grandifolius is commonly called 'Nun's Orchid' or 'Nun's Hood Orchid'. Phaius offers an interesting "new" spring flowering pot plant for the tropical foliage grower or landscaper as well as a potential new cut flower crop. A vigorous plant with thin, ...
... A terrestrial orchid sometimes referred to as P. grandifolius is commonly called 'Nun's Orchid' or 'Nun's Hood Orchid'. Phaius offers an interesting "new" spring flowering pot plant for the tropical foliage grower or landscaper as well as a potential new cut flower crop. A vigorous plant with thin, ...
31. Rue Anemone - Friess Lake School District
... of the whorl of leaves. The flowering period is from March through June. The six petals on each flower are really sepals (parts that cover flower buds). The seedpods are very small and yellowish attached to the top and the center of the plant. ...
... of the whorl of leaves. The flowering period is from March through June. The six petals on each flower are really sepals (parts that cover flower buds). The seedpods are very small and yellowish attached to the top and the center of the plant. ...
Methods of Asexual Propagation: Growing Plants Without Seeds.
... Cutting apart rhizomes, tubers, runners, stolons, or suckers to get new plants ...
... Cutting apart rhizomes, tubers, runners, stolons, or suckers to get new plants ...
Many plants reproduce with flowers and fruit.
... Fertilization occurs when the pollen tube reaches the ovary and a sperm fertilizes the egg. The fertilized egg grows into an embryo and develops a seed coat. The ovary develops into a fruit. ...
... Fertilization occurs when the pollen tube reaches the ovary and a sperm fertilizes the egg. The fertilized egg grows into an embryo and develops a seed coat. The ovary develops into a fruit. ...
Text Like all other living organisms, land plants are also believed to
... The sporophyte performs vegetative as well as asexual reproduction. Vegetative propagation takes place by buds that develop on the rhizome, or by fragmentation of rhizome. Asexual reproduction takes place ...
... The sporophyte performs vegetative as well as asexual reproduction. Vegetative propagation takes place by buds that develop on the rhizome, or by fragmentation of rhizome. Asexual reproduction takes place ...
Chapter 8 * Section 3
... • Meets the Challenges – stand up straight, supply all cells with food and water. • Phloem – food moves through this tissue • Xylem – water and minerals travel through this tissue ...
... • Meets the Challenges – stand up straight, supply all cells with food and water. • Phloem – food moves through this tissue • Xylem – water and minerals travel through this tissue ...
Chestnut School of Herbal Medicine
... often a solid Plan B for plants if cross-pollination doesn’t occur. Pollination can be brought about by pollinators—butterflies, bees, flower flies, bats, and other species—or by the wind. Fertilization = Genetic exchange between plants that takes place in the ovary—this is where chromosomal exchang ...
... often a solid Plan B for plants if cross-pollination doesn’t occur. Pollination can be brought about by pollinators—butterflies, bees, flower flies, bats, and other species—or by the wind. Fertilization = Genetic exchange between plants that takes place in the ovary—this is where chromosomal exchang ...
Functions and Structures
... 2. Environment: Plants need light to make food, so they will bend toward a light source. What structures in plants enable them to move in this way? Raccoons feed at night, and deer feed during the day. They both use their eyes to see under very different conditions. In what ways are their eyes simil ...
... 2. Environment: Plants need light to make food, so they will bend toward a light source. What structures in plants enable them to move in this way? Raccoons feed at night, and deer feed during the day. They both use their eyes to see under very different conditions. In what ways are their eyes simil ...
Keeping Everyone Safe in the Ag Lab
... grows vegetative structures (roots, stems, leaves) in the first year and then after a period of dormancy during cold months, it will produce flowers and seeds before dying examples: carrot, parsley, onion, cabbage, hollyhock, Black-eyed Susan ...
... grows vegetative structures (roots, stems, leaves) in the first year and then after a period of dormancy during cold months, it will produce flowers and seeds before dying examples: carrot, parsley, onion, cabbage, hollyhock, Black-eyed Susan ...
Tradescantia spathacea
... Tradescantia spathacea O.P. Swartz Moses-In-The-Cradle (Rhoeo discolor, Rhoeo spathacea, Tradescantia bicolor, Tradescantia discolor) • Tradescantia spathacea is also known as Boat-Lily, Boat Plant, Man-In-A-Boat, Moses-In-A-Boat, Moses-In-ABasket, Moses-In-A-Raft, Moses-In-The-Bulrushes, Oyster Pla ...
... Tradescantia spathacea O.P. Swartz Moses-In-The-Cradle (Rhoeo discolor, Rhoeo spathacea, Tradescantia bicolor, Tradescantia discolor) • Tradescantia spathacea is also known as Boat-Lily, Boat Plant, Man-In-A-Boat, Moses-In-A-Boat, Moses-In-ABasket, Moses-In-A-Raft, Moses-In-The-Bulrushes, Oyster Pla ...
Dionaea - The Carnivorous Plant Society
... and often is the first example that many growers try out. The plant is a native of a very small area of boggy ground in North Carolina and is highly endangered in it’s native habitat due to a combination of over collection and habitat loss. These days they are produced in huge quantities commerciall ...
... and often is the first example that many growers try out. The plant is a native of a very small area of boggy ground in North Carolina and is highly endangered in it’s native habitat due to a combination of over collection and habitat loss. These days they are produced in huge quantities commerciall ...
Compact Japanese Fleeceflower
... Compact Japanese Fleeceflower is a dense herbaceous perennial with an upright spreading habit of growth. Its relatively coarse texture can be used to stand it apart from other garden plants with finer foliage. This is a high maintenance perennial that will require regular care and upkeep, and is bes ...
... Compact Japanese Fleeceflower is a dense herbaceous perennial with an upright spreading habit of growth. Its relatively coarse texture can be used to stand it apart from other garden plants with finer foliage. This is a high maintenance perennial that will require regular care and upkeep, and is bes ...
KINGDOM PLANTAE
... •ALL produce flowers and fruit •Do NOT produce flowers or fruit •Produce Cones ...
... •ALL produce flowers and fruit •Do NOT produce flowers or fruit •Produce Cones ...
Kingdom Protista
... Gametophyte, the green leafy base (haploid) Sporophyte, produces spores and grows from tip of leafy gametophyte (diploid) Seedless Vascular Plants (Ferns, and horsetails) Like the bryophytes, these plants require water for reproduction, due to motile sperm Also, produce spores for reproduction, ...
... Gametophyte, the green leafy base (haploid) Sporophyte, produces spores and grows from tip of leafy gametophyte (diploid) Seedless Vascular Plants (Ferns, and horsetails) Like the bryophytes, these plants require water for reproduction, due to motile sperm Also, produce spores for reproduction, ...
Water Soldier
... often rises seasonally to the water’s surface and is semi-emergent (above water surface) when fully flowering. Roots are unbranched and do not always attach to the substrate. Leaves Long, linear or narrowly triangular, stalkless, sharply serrated, length 40-110 cm (approx. 16-43 in.); leaves form a ...
... often rises seasonally to the water’s surface and is semi-emergent (above water surface) when fully flowering. Roots are unbranched and do not always attach to the substrate. Leaves Long, linear or narrowly triangular, stalkless, sharply serrated, length 40-110 cm (approx. 16-43 in.); leaves form a ...
Fantastic Flowers Pre-visit Package
... The joining together of a male and female reproductive cell to form a new organism Filament: The part of the stamen that holds the anther in position for pollen dispersal Flower: The reproductive structure of a flowering plant Nectar: Nectar, in botany, is a sugar-rich liquid produced by the flowers ...
... The joining together of a male and female reproductive cell to form a new organism Filament: The part of the stamen that holds the anther in position for pollen dispersal Flower: The reproductive structure of a flowering plant Nectar: Nectar, in botany, is a sugar-rich liquid produced by the flowers ...
Plant reproduction

Plant reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur. In seed plants, the offspring can be packaged in a protective seed, which is used as an agent of dispersal.