Squawroot - Bruce Trail
... its nutrients from a host plant as a parasite on the root structures of the host trees, mainly oaks. This parasitic activity generally does not affect the health of the host tree, as the nutrient extraction is relatively minor and the number of individual Squawroot shoots is not extensive. The sucke ...
... its nutrients from a host plant as a parasite on the root structures of the host trees, mainly oaks. This parasitic activity generally does not affect the health of the host tree, as the nutrient extraction is relatively minor and the number of individual Squawroot shoots is not extensive. The sucke ...
Anatomy and Physiology of Vegetable Plants
... Sexual Reproduction in Plants: Two parents (meiosis) • The stamen releases pollen. • Pollen is carried by wind, gravity, animals, or insects to the stigma of another flower. (This is when pollination occurs) • The pollen moves from the stigma down through in a pollen tube the style depositing sper ...
... Sexual Reproduction in Plants: Two parents (meiosis) • The stamen releases pollen. • Pollen is carried by wind, gravity, animals, or insects to the stigma of another flower. (This is when pollination occurs) • The pollen moves from the stigma down through in a pollen tube the style depositing sper ...
Bio 1B, Spring, 2008, Evolution section 1 of 3 Updated 3/13/08 11
... other mechanisms that result in new combinations of alleles. Sexual reproduction is an evolved trait There is great variety in modes of sexual reproduction • Isogamy vs. aniogamy: isogamous species produce gametes of the same size and form; anisogamous species produce gametes that differ in size ...
... other mechanisms that result in new combinations of alleles. Sexual reproduction is an evolved trait There is great variety in modes of sexual reproduction • Isogamy vs. aniogamy: isogamous species produce gametes of the same size and form; anisogamous species produce gametes that differ in size ...
Plants, Bacteria, Viruses and Fungi
... things as they are not made of cells • Viruses are very small, approximately 100nm across (1nm = 1/1000 000 of a mm) ...
... things as they are not made of cells • Viruses are very small, approximately 100nm across (1nm = 1/1000 000 of a mm) ...
the cyclamen mite - University of Guelph Laboratory Services
... larkspur, petunia, snapdragon, etc. Under certain conditions, field strawberries can also be affected. The cyclamen mite is extremely small (0.2 mm) and usually inflicts heavy damage before it is detected. The foliage of infested plants develops a streaked or blotched appearance. Leaves and leaflets ...
... larkspur, petunia, snapdragon, etc. Under certain conditions, field strawberries can also be affected. The cyclamen mite is extremely small (0.2 mm) and usually inflicts heavy damage before it is detected. The foliage of infested plants develops a streaked or blotched appearance. Leaves and leaflets ...
Growing Beans - Communication4All
... plant begins to develop a stem, roots and leaves. The stem grows upwards, towards the light, while the roots are beneath the ground. ...
... plant begins to develop a stem, roots and leaves. The stem grows upwards, towards the light, while the roots are beneath the ground. ...
a) Reproduction - iGCSE Science Courses
... 3.5 understand the conditions needed for seed germination 3.6 understand how germinating seeds utilise food reserves until the seedling can carry out photosynthesis 3.7 understand that plants can reproduce asexually by natural methods (illustrated by runners) and by artificial methods (illustrated b ...
... 3.5 understand the conditions needed for seed germination 3.6 understand how germinating seeds utilise food reserves until the seedling can carry out photosynthesis 3.7 understand that plants can reproduce asexually by natural methods (illustrated by runners) and by artificial methods (illustrated b ...
Practice Exam I
... A. ferns, horsetails, and clubmosses B. horsetails and mosses C. mosses and clubmosses D. ferns and bryophytes E. mosses and ferns 27. All bryophytes (mosses, liverworts & hronworts) share certain characteritics. These are: A. reproductive cells in gametangia; embryos B. branched sprorphytes C. seed ...
... A. ferns, horsetails, and clubmosses B. horsetails and mosses C. mosses and clubmosses D. ferns and bryophytes E. mosses and ferns 27. All bryophytes (mosses, liverworts & hronworts) share certain characteritics. These are: A. reproductive cells in gametangia; embryos B. branched sprorphytes C. seed ...
S/Reed and Ginger - Botanical Society of South Africa
... named cultivars were introduced to the local trade during the 1980’s. These cultivars were superior to the originals because the propagation technique of using cuttings rather than seed ensured that the plants grew true to form. Growing from seed often resulted in poor flower colour. It is worthwhil ...
... named cultivars were introduced to the local trade during the 1980’s. These cultivars were superior to the originals because the propagation technique of using cuttings rather than seed ensured that the plants grew true to form. Growing from seed often resulted in poor flower colour. It is worthwhil ...
Yucca rostrata.pub
... the finest yuccas for ornamental landscapes. Yucca rostrata forms a trunk to about 10 feet tall. Young plants are usually unbranched, but older plants may develop multiple heads near the top. The narrow blue leaves are up to 2 feet long by ½ inch wide, and end in a sharp terminal spine. Yucca rostra ...
... the finest yuccas for ornamental landscapes. Yucca rostrata forms a trunk to about 10 feet tall. Young plants are usually unbranched, but older plants may develop multiple heads near the top. The narrow blue leaves are up to 2 feet long by ½ inch wide, and end in a sharp terminal spine. Yucca rostra ...
Biology First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... The male reproductive structure of a flowering plant; consists of the anther and the filament The female reproductive structure of a flowering plant; consists of the stigma, style, and ovary The slender stalk-like portion of the male reproductive structure of a flowering plant; supports the anther T ...
... The male reproductive structure of a flowering plant; consists of the anther and the filament The female reproductive structure of a flowering plant; consists of the stigma, style, and ovary The slender stalk-like portion of the male reproductive structure of a flowering plant; supports the anther T ...
Article 149 Updated List_Limonium sinuatum
... branched panicles or corymbs (clusters). These can be up to half a metre tall. The individual flowers are very small (4-10 mm long) with a five-lobed calyx and corolla (flower tube). Colours are pink, violet to purple in most species and white or yellow in a few others. A number of species (mainly f ...
... branched panicles or corymbs (clusters). These can be up to half a metre tall. The individual flowers are very small (4-10 mm long) with a five-lobed calyx and corolla (flower tube). Colours are pink, violet to purple in most species and white or yellow in a few others. A number of species (mainly f ...
Name - XTEC Blocs
... f. Which part of the plant forms the fruit and seeds? ____The flower___________________________________________ g. Which part of the plant contains seeds? _____The fruits__________________________________________ h. Which part of the plant contains an embryo plant? ___The seed_______________________ ...
... f. Which part of the plant forms the fruit and seeds? ____The flower___________________________________________ g. Which part of the plant contains seeds? _____The fruits__________________________________________ h. Which part of the plant contains an embryo plant? ___The seed_______________________ ...
Gymnosperms - cloudfront.net
... 4) What are male cones called and what do they produce? 5) What are female cones called and what do they produce? 6) What is created when the sperm and egg fuse: sporophyte or gametophyte? ...
... 4) What are male cones called and what do they produce? 5) What are female cones called and what do they produce? 6) What is created when the sperm and egg fuse: sporophyte or gametophyte? ...
Invasive Species: Garlic Mustard Alliaria petiolata
... seeds that can spread several meters from the parent plant. Seeds are dispersed mainly by humans and animals although they can be carried in water flow. Wind dispersal is not as common as the seeds do not drift well. By the end of June most of the leaves have died leaving stalks and siliques that ma ...
... seeds that can spread several meters from the parent plant. Seeds are dispersed mainly by humans and animals although they can be carried in water flow. Wind dispersal is not as common as the seeds do not drift well. By the end of June most of the leaves have died leaving stalks and siliques that ma ...
plant identification - Arizona Section, Society for Range Management
... Broad leaves and showy flowers Above-ground growth dies back each year Veins in the leaves are net veins although some forbs have veins that are parallel Range wildflowers and weeds ...
... Broad leaves and showy flowers Above-ground growth dies back each year Veins in the leaves are net veins although some forbs have veins that are parallel Range wildflowers and weeds ...
Slides
... young cotton plants at Maricopa, AZ. Replicated sets of sensors allow simultaneous measurement of plant height, foliage temperature, and foliage ...
... young cotton plants at Maricopa, AZ. Replicated sets of sensors allow simultaneous measurement of plant height, foliage temperature, and foliage ...
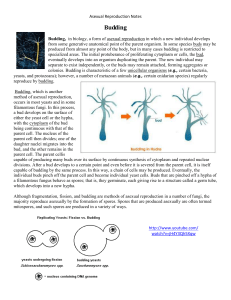
Asexual Reproduction Jigsaw
... parent cell. The nucleus of the parent cell then divides; one of the daughter nuclei migrates into the bud, and the other remains in the parent cell. The parent cellis capable of producing many buds over its surface by continuous synthesis of cytoplasm and repeated nuclear divisions. After a bud dev ...
... parent cell. The nucleus of the parent cell then divides; one of the daughter nuclei migrates into the bud, and the other remains in the parent cell. The parent cellis capable of producing many buds over its surface by continuous synthesis of cytoplasm and repeated nuclear divisions. After a bud dev ...
Plants
... along veins, often near leaf margins, or scattered on underside of leaf blade (abaxially) Indusia absent, or when present, a false indusium formed by the recurved pinnule margin Spores uniform in size, small; globose to globose-tetrahedral or trigonal Gametophytes bisexual, aboveground, thin, green, ...
... along veins, often near leaf margins, or scattered on underside of leaf blade (abaxially) Indusia absent, or when present, a false indusium formed by the recurved pinnule margin Spores uniform in size, small; globose to globose-tetrahedral or trigonal Gametophytes bisexual, aboveground, thin, green, ...
Flower and Fruit Drop - The University of Arizona Extension
... plants. Plants in this group include tomato, pepper, and snap bean. Pecan also are wind pollinated. In greenhouses bees are often introduced to facilitate pollination. Physiological Differences Vegetable and melon plants that require the transfer of pollen from separate male to female flowers (such ...
... plants. Plants in this group include tomato, pepper, and snap bean. Pecan also are wind pollinated. In greenhouses bees are often introduced to facilitate pollination. Physiological Differences Vegetable and melon plants that require the transfer of pollen from separate male to female flowers (such ...
spread the word not the weed! - Natural Resources South Australia
... • Plant natives from your local area. • Remove known sleeper weeds from your garden. • Don’t share or sell sleeper weeds. ...
... • Plant natives from your local area. • Remove known sleeper weeds from your garden. • Don’t share or sell sleeper weeds. ...
Plant Devel L1.indd
... horticulturist should concentrate on these three. Others are also highlighted here since they are referred to in the syllabus. Some additional categories are also included. The definitions presented here are assessment criteria within the syllabus. Let us now consider the Order and further classific ...
... horticulturist should concentrate on these three. Others are also highlighted here since they are referred to in the syllabus. Some additional categories are also included. The definitions presented here are assessment criteria within the syllabus. Let us now consider the Order and further classific ...
Incomplete Dominance
... Incomplete Dominance 1. In Japanese four-o-clocks, the gene controlling flower colour has alleles that are neither dominant nor recessive. Plants that have two red alleles (CRCR) have red flowers. Plants with two white alleles (CWCW) have white flowers. However, plants with one red allele and one wh ...
... Incomplete Dominance 1. In Japanese four-o-clocks, the gene controlling flower colour has alleles that are neither dominant nor recessive. Plants that have two red alleles (CRCR) have red flowers. Plants with two white alleles (CWCW) have white flowers. However, plants with one red allele and one wh ...
Plant reproduction

Plant reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur. In seed plants, the offspring can be packaged in a protective seed, which is used as an agent of dispersal.