What a Frog s Eye tells the Frog s brain
... 1. Local sharp edges and contrast 2. the curvature of edge of a dark contrast 3. the movement of edges 4. the local dimming produced by movement or rapid general darkening Each group of fibers serving one operation maps the retina continuously in a single sheet of endings in the frog’s brain. Th ...
... 1. Local sharp edges and contrast 2. the curvature of edge of a dark contrast 3. the movement of edges 4. the local dimming produced by movement or rapid general darkening Each group of fibers serving one operation maps the retina continuously in a single sheet of endings in the frog’s brain. Th ...
Organs-on-a-chip
... • Intact monolayers of cells linked by epithelial and endothelial junctional proteins. • Epithelial side produces surfactants to stay moist against air • Electrical resistance increased and protein transport decreased on the membrane formed at air-liquid interface as compared to fully liquid submerg ...
... • Intact monolayers of cells linked by epithelial and endothelial junctional proteins. • Epithelial side produces surfactants to stay moist against air • Electrical resistance increased and protein transport decreased on the membrane formed at air-liquid interface as compared to fully liquid submerg ...
Netter`s Atlas of Neuroscience - 9780323265119 | US Elsevier
... mainly through axonal terminations on the cell body and dendrites. These synapses are isolated and protected by astrocytic processes. The dendrites usually provide the greatest surface area of the neuron. Some protrusions from dendritic branches (dendritic spines) are sites of specific axo-dendritic ...
... mainly through axonal terminations on the cell body and dendrites. These synapses are isolated and protected by astrocytic processes. The dendrites usually provide the greatest surface area of the neuron. Some protrusions from dendritic branches (dendritic spines) are sites of specific axo-dendritic ...
Nervous System ch 11
... •Their plasma membrane function in: –Electrical signaling –Cell-to-cell signaling during development Dendrites of Motor Neurons •Short, tapered processes that diffusely branched out •They receive or input, to regions of the neuron •Electrical signals are graded potentials (not action potentials) Axo ...
... •Their plasma membrane function in: –Electrical signaling –Cell-to-cell signaling during development Dendrites of Motor Neurons •Short, tapered processes that diffusely branched out •They receive or input, to regions of the neuron •Electrical signals are graded potentials (not action potentials) Axo ...
BOX 2.2 CAJAL: ICONOCLAST TO ICON Santiago Ramón y Cajal
... Cajal saw immediately that it offered great hope in solving the most vexing problem of nineteenthcentury neuroscience: How do adult nerve cells interact with one another? This realization galvanized and directed the rest of his scientific life, which was extremely productive in terms of originality, ...
... Cajal saw immediately that it offered great hope in solving the most vexing problem of nineteenthcentury neuroscience: How do adult nerve cells interact with one another? This realization galvanized and directed the rest of his scientific life, which was extremely productive in terms of originality, ...
Study/Review * Nervous System Part 2 * CNS and PNS
... the synaptic cleft are called ____________________________ 2. These cells make myelin on axons of the CNS: _______________________ 3. _________________________ are gaps in the myelin sheath 4. A change in ion/charge distribution across the axon membrane is called ___________________________ ...
... the synaptic cleft are called ____________________________ 2. These cells make myelin on axons of the CNS: _______________________ 3. _________________________ are gaps in the myelin sheath 4. A change in ion/charge distribution across the axon membrane is called ___________________________ ...
Lecture - Lawrence Moon
... • These do not, however, spontaneously grow into zones of denervation • e.g. contralateral red nucleus • e.g. ipsilateral spinal cord • If we can understand why not, it may be possible to exploit spared axons to cause repair. • Possible new therapies! ...
... • These do not, however, spontaneously grow into zones of denervation • e.g. contralateral red nucleus • e.g. ipsilateral spinal cord • If we can understand why not, it may be possible to exploit spared axons to cause repair. • Possible new therapies! ...
Nervous System Student Notes
... carry information away from the cell in the form of a nerve impulse. Neurons commonly have only ____________ ____________ are simply bundles of axons. Axons are surrounded by a “Band-Aid” of cells called ____________. Multiple layers of these cells create __________________, around the axon called a ...
... carry information away from the cell in the form of a nerve impulse. Neurons commonly have only ____________ ____________ are simply bundles of axons. Axons are surrounded by a “Band-Aid” of cells called ____________. Multiple layers of these cells create __________________, around the axon called a ...
Central Tendency” - North Dakota State University
... to play a role in shaping dendritic growth b. axons grow faster than dendrites in order to reach a larger maximum size c. dendrite grow faster than axons in order to play a role in shaping axonal growth d. dendrite grow faster than axons in order to reach a larger maximum size ...
... to play a role in shaping dendritic growth b. axons grow faster than dendrites in order to reach a larger maximum size c. dendrite grow faster than axons in order to play a role in shaping axonal growth d. dendrite grow faster than axons in order to reach a larger maximum size ...
Plants and Pollinators
... • Light rays pass through lens and converge on retina at back of eye • The image that forms on the retina is upside down and reversed right to left ...
... • Light rays pass through lens and converge on retina at back of eye • The image that forms on the retina is upside down and reversed right to left ...
Document
... Best understood limbic center is the AMYGDALA AMYGDALA is required for experiencing both fearful and pleasurable responses and is required for generating memories associated with emotional experiences ...
... Best understood limbic center is the AMYGDALA AMYGDALA is required for experiencing both fearful and pleasurable responses and is required for generating memories associated with emotional experiences ...
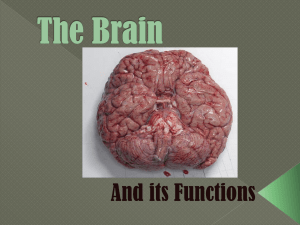
The Brain
... neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body and are covered with synapses. These receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma Cell Body - where the signals from the dendrites are joined and passed on. The cell body does not play an active rol ...
... neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body and are covered with synapses. These receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma Cell Body - where the signals from the dendrites are joined and passed on. The cell body does not play an active rol ...
Neural pathways
... Cell bodies form spiral ganglion within modiolus (Rosenthal’s canal) Terminate centrally in cochlear nucleus in brainstem (ipsilaterally only) Approximately 30,000 in man (in each ear) ...
... Cell bodies form spiral ganglion within modiolus (Rosenthal’s canal) Terminate centrally in cochlear nucleus in brainstem (ipsilaterally only) Approximately 30,000 in man (in each ear) ...
Nervous System Poster
... o Right and left cerebral hemispheres in humans Note: You DO NOT need to know the types of nervous systems, details of various structures and features of the brain parts, and details of specific neurologic processes. ...
... o Right and left cerebral hemispheres in humans Note: You DO NOT need to know the types of nervous systems, details of various structures and features of the brain parts, and details of specific neurologic processes. ...
action potential
... •Action potentials are based on the movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell •When an action potential occurs, a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... •Action potentials are based on the movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell •When an action potential occurs, a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel (the receptor), it opens and allows ions to diffuse across the membrane Result- postsynaptic potential (change in membrane potential) Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) membrane potential brought down to threshold Inhibitiory postsynaptic potentials (IPS ...
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel (the receptor), it opens and allows ions to diffuse across the membrane Result- postsynaptic potential (change in membrane potential) Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) membrane potential brought down to threshold Inhibitiory postsynaptic potentials (IPS ...
File
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
here
... The Structure and Function of Neurons Neurons are cells that are specialised to carry neural information throughout the body. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors. They are connected to the cell body (the control centre). The impulse travels from the cell body along the ...
... The Structure and Function of Neurons Neurons are cells that are specialised to carry neural information throughout the body. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors. They are connected to the cell body (the control centre). The impulse travels from the cell body along the ...
Neuronal Anatomy - VCC Library
... MOTOR NEURONS (a.k.a. efferent neurons) transmit commands from the CNS to muscles and glands in the body (the PNS). They usually have one long axon that is branched at the transmitting end. Like sensory neurons, their cell body is located close to the CNS and they usually have myelin on the axon. IN ...
... MOTOR NEURONS (a.k.a. efferent neurons) transmit commands from the CNS to muscles and glands in the body (the PNS). They usually have one long axon that is branched at the transmitting end. Like sensory neurons, their cell body is located close to the CNS and they usually have myelin on the axon. IN ...
4-Nervous system I: Structure and organization
... Harwood, P. 1963. Therapeutic dosage in small and large mammals . Science 139: 684-685. ...
... Harwood, P. 1963. Therapeutic dosage in small and large mammals . Science 139: 684-685. ...