The Nervous System
... In many ways, the cell body is similar to other types of cells. It has a nucleus with at least one nucleolus and contains many of the typical cytoplasmic organelles. It lacks centrioles, however. Because centrioles function in cell division, the fact that neurons lack these organelles is consistent ...
... In many ways, the cell body is similar to other types of cells. It has a nucleus with at least one nucleolus and contains many of the typical cytoplasmic organelles. It lacks centrioles, however. Because centrioles function in cell division, the fact that neurons lack these organelles is consistent ...
Biology 3201 - s3.amazonaws.com
... causing them to “leak” out. This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This furth ...
... causing them to “leak” out. This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This furth ...
The Nervous System
... Control center for all body activities Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... Control center for all body activities Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
Results: Mitochondrial transport in dendrites and axons Maximum
... mRNA. In general, mitochondria were less mobile in axons, though there were more moving particles at day 7 (76%) compared to days 4 and 12 (63% and 55%, respectively). Of the unidirectionally moving particles, there were more retrograde particles than anterograde particles at days 4 and 7. Significa ...
... mRNA. In general, mitochondria were less mobile in axons, though there were more moving particles at day 7 (76%) compared to days 4 and 12 (63% and 55%, respectively). Of the unidirectionally moving particles, there were more retrograde particles than anterograde particles at days 4 and 7. Significa ...
Ch 11 Part 1 - Groch Biology
... 5. A major subdivision of the nervous system that interprets incoming information and issues orders. ______ 6. A major subdivision of the nervous system that serves as the communication lines, linking all parts of the body to the CNS. ____ 3) T/F. If the statement is false, write the correct word(s) ...
... 5. A major subdivision of the nervous system that interprets incoming information and issues orders. ______ 6. A major subdivision of the nervous system that serves as the communication lines, linking all parts of the body to the CNS. ____ 3) T/F. If the statement is false, write the correct word(s) ...
Nerve tissue File
... Nodes of Ranvier are widely spaced There is no neurilemma, one oli covers many axons ...
... Nodes of Ranvier are widely spaced There is no neurilemma, one oli covers many axons ...
Assignment: Sensing mechanical changes in firing neurons
... milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical field strength over this membrane. It is our hypothesis that this change in electrical field causes small mechanical deformations in the cell membrane. The cell membrane can be regarded as a capacitor, composed of two conductors separated by an ...
... milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical field strength over this membrane. It is our hypothesis that this change in electrical field causes small mechanical deformations in the cell membrane. The cell membrane can be regarded as a capacitor, composed of two conductors separated by an ...
Exercise 17
... Nerves: tracts in the PNS Neurofibrils: cytoskeletal elements that support and transport inside the cell Nissl bodies: elaborate type of rough ER; involved in the metabolic activity of the the cell Dendrites: are receptive regions that bear receptors for neurotransmitters released by other neurons A ...
... Nerves: tracts in the PNS Neurofibrils: cytoskeletal elements that support and transport inside the cell Nissl bodies: elaborate type of rough ER; involved in the metabolic activity of the the cell Dendrites: are receptive regions that bear receptors for neurotransmitters released by other neurons A ...
THE NEuRoN - Big Picture
... (A) that diffuses across the synaptic gap (B) and binds to proteins (C) on the surface of the receiving neuron. This binding causes an influx of ions, changing the membrane voltage and initiating an electrical signal in the second neuron. ...
... (A) that diffuses across the synaptic gap (B) and binds to proteins (C) on the surface of the receiving neuron. This binding causes an influx of ions, changing the membrane voltage and initiating an electrical signal in the second neuron. ...
Nervous System
... processes to other neurons or to muscles and glands. ◦ The complex patterns in which the neurons connect with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integrate many body functions. ...
... processes to other neurons or to muscles and glands. ◦ The complex patterns in which the neurons connect with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integrate many body functions. ...
What is a neuron?
... • include most neurons including all motor neurons and most CNS neurons • have multiple dendrites and a single axon ...
... • include most neurons including all motor neurons and most CNS neurons • have multiple dendrites and a single axon ...
What is a neuron?
... • include most neurons including all motor neurons and most CNS neurons • have multiple dendrites and a single axon ...
... • include most neurons including all motor neurons and most CNS neurons • have multiple dendrites and a single axon ...
Chapter 12- Intro to NS
... II. Nervous TissueNervous tissue develops from the embryonic neural tube and neuro crest. Two types of cells form: neurons and glial cells (supporting cells) A. The Neuron- these types of cells are excitable and can send an impulse (electrical signal). Neurons have three major parts: cell body, de ...
... II. Nervous TissueNervous tissue develops from the embryonic neural tube and neuro crest. Two types of cells form: neurons and glial cells (supporting cells) A. The Neuron- these types of cells are excitable and can send an impulse (electrical signal). Neurons have three major parts: cell body, de ...
Development and Plasticity of the Brain
... Sprouting-when nearby, uninjured cells form new branches to the vacant synapses Denervation Supersensitivity-heightened sensitivity to a neurotransmitter after the destruction of an incoming axon Reorganized Sensory Representations and the Phantom Limb Effects of Age Older people do not recover as w ...
... Sprouting-when nearby, uninjured cells form new branches to the vacant synapses Denervation Supersensitivity-heightened sensitivity to a neurotransmitter after the destruction of an incoming axon Reorganized Sensory Representations and the Phantom Limb Effects of Age Older people do not recover as w ...
Nervous System
... channels regenerate the action potential at each point along the axon, so voltage does not decay. Conduction is slow because movements of ions and of the gates of channel proteins take time and must occur before voltage regeneration occurs. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... channels regenerate the action potential at each point along the axon, so voltage does not decay. Conduction is slow because movements of ions and of the gates of channel proteins take time and must occur before voltage regeneration occurs. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
t1review
... 8. Knee jerk reflexes are controlled by? 9. Understand the Endocrine system, what it consist of and it's chemical messengers. 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What st ...
... 8. Knee jerk reflexes are controlled by? 9. Understand the Endocrine system, what it consist of and it's chemical messengers. 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What st ...
eating spaghetti!
... into ATP (Energy). Neurons demand a lot of energy because they’re always in a state of metabolic activity. Neurons are manufacturing enzymes and neurotransmitters that are transported out to very ends of their nerve-branches. Chemo ...
... into ATP (Energy). Neurons demand a lot of energy because they’re always in a state of metabolic activity. Neurons are manufacturing enzymes and neurotransmitters that are transported out to very ends of their nerve-branches. Chemo ...
Psychology 300 Instructor: Sylvia S. Spencer Ph.D. TEST 1 REVIEW
... 8. Knee jerk reflexes are controlled by? 9. Understand the Endocrine system, what it consist of and it's chemical messengers. 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What st ...
... 8. Knee jerk reflexes are controlled by? 9. Understand the Endocrine system, what it consist of and it's chemical messengers. 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What st ...
Slide ()
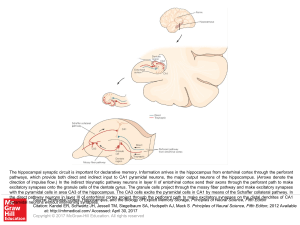
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
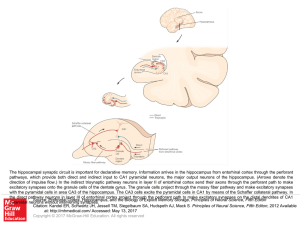
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
File
... communication. There are 100 billion neurons present from birth (actually from 24 weeks’ gestation). Commonly thought that once neurons die, they’re lost forever, but some scientists are challenging this assumption, saying that neurons can be regenerated. It’s currently unknown whether neurons can b ...
... communication. There are 100 billion neurons present from birth (actually from 24 weeks’ gestation). Commonly thought that once neurons die, they’re lost forever, but some scientists are challenging this assumption, saying that neurons can be regenerated. It’s currently unknown whether neurons can b ...
Part1
... Resting potential maintained by concentration differences of ions inside and outside of cell There are channels in membrane selective to different ions. Channels may be open or closed. ...
... Resting potential maintained by concentration differences of ions inside and outside of cell There are channels in membrane selective to different ions. Channels may be open or closed. ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In this activity, students will learn about neurons and their unique structure a ...
... made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In this activity, students will learn about neurons and their unique structure a ...
STRUCTURE OF NEURON AND NEUROGLIA NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Transmit electrical signals toward the cell body Function as receptive sites for receiving signals from other neurons ...
... Transmit electrical signals toward the cell body Function as receptive sites for receiving signals from other neurons ...