The Nervous System
... – Most cell bodies in CNS (except some autonomic neurons) • Interneurons (association neurons) – Lie between motor and sensory neurons – Shuttle signals through CNS pathways; most are entirely within CNS – 99% of body's neurons – Most confined in CNS ...
... – Most cell bodies in CNS (except some autonomic neurons) • Interneurons (association neurons) – Lie between motor and sensory neurons – Shuttle signals through CNS pathways; most are entirely within CNS – 99% of body's neurons – Most confined in CNS ...
Ch.10
... • groups of interneurons that make synaptic connections with each other • interneurons work together to perform a common function • each pool receives input from other neurons • each pool generates output to other neurons ...
... • groups of interneurons that make synaptic connections with each other • interneurons work together to perform a common function • each pool receives input from other neurons • each pool generates output to other neurons ...
L8_Nerve_tissue_and_organs
... network between the sensory and motor neurons Morphological classification is based on the number of processes: • Multipolar neurons have one axon and two or more dendrites • Bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite • Unipolar (pseudounipolar) neurons have one process, that divides close to th ...
... network between the sensory and motor neurons Morphological classification is based on the number of processes: • Multipolar neurons have one axon and two or more dendrites • Bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite • Unipolar (pseudounipolar) neurons have one process, that divides close to th ...
Reaching for the brain: stimulating neural activity as the big leap in
... is to make sure that a sufficient population of neurons survives the initial insult, where after they can regrow their axons. Besides being a fruitful approach for axonal regeneration, the treatment paradigm presented by Lim and co-workers also proved to have a profound neuroprotective effect (with ...
... is to make sure that a sufficient population of neurons survives the initial insult, where after they can regrow their axons. Besides being a fruitful approach for axonal regeneration, the treatment paradigm presented by Lim and co-workers also proved to have a profound neuroprotective effect (with ...
In This Issue - The Journal of Cell Biology
... Cofilin promotes the formation of actin filaments at the front of motile cells by binding to existing filaments and cutting them, creating barbed ends for new filament nucleation. Cofilin activation requires Ser3 dephosphorylation; however, this alone is not sufficient. Additional mechanisms—includi ...
... Cofilin promotes the formation of actin filaments at the front of motile cells by binding to existing filaments and cutting them, creating barbed ends for new filament nucleation. Cofilin activation requires Ser3 dephosphorylation; however, this alone is not sufficient. Additional mechanisms—includi ...
nerve impulse
... Insulate the electrical impulses Like electrical tape insulates electric wires this prevents “leaking” of electric signals ...
... Insulate the electrical impulses Like electrical tape insulates electric wires this prevents “leaking” of electric signals ...
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System - dr
... 2. What structures make up the brainstem, what is the function of each? 3. What structures make up the diencephalon, what is the function of each? 4. What are the four ventricles and what is their function? 5. What are the functions of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)? 6. Describe the following about the C ...
... 2. What structures make up the brainstem, what is the function of each? 3. What structures make up the diencephalon, what is the function of each? 4. What are the four ventricles and what is their function? 5. What are the functions of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)? 6. Describe the following about the C ...
File - Lucinda Supernavage
... • Sensory Nerves – conduct impulses into the brain or spinal cord from senses; AFFERENT nerves • Motor Nerves – carry impulses to muscles or glands; cause a response; EFFERENT nerves • Interneurons – connect sensory and motor nerves NEUROPATHY – damage to nerves in the PNS usually from underlying me ...
... • Sensory Nerves – conduct impulses into the brain or spinal cord from senses; AFFERENT nerves • Motor Nerves – carry impulses to muscles or glands; cause a response; EFFERENT nerves • Interneurons – connect sensory and motor nerves NEUROPATHY – damage to nerves in the PNS usually from underlying me ...
Exam 4
... -Describe the components and functions of somatic motor pathways - Identify the locations and functions of the different types of neurons in the somatic motor pathways (Describe the characteristics of first, second and third order neurons in somatic sensory pathways). -Understand wakefulness and sle ...
... -Describe the components and functions of somatic motor pathways - Identify the locations and functions of the different types of neurons in the somatic motor pathways (Describe the characteristics of first, second and third order neurons in somatic sensory pathways). -Understand wakefulness and sle ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION BSc Counselling Psychology
... d.Dendrites 2. ______________ help neurons by providing nutrition, removing waste products, and enhancing the speed of communication between neurons. a. Axons b. Dendrites ...
... d.Dendrites 2. ______________ help neurons by providing nutrition, removing waste products, and enhancing the speed of communication between neurons. a. Axons b. Dendrites ...
The Nervous System
... • Impulse goes from neuronal axon to another neuron or a receptor – This junction called ---synapse – neurotransmitters ...
... • Impulse goes from neuronal axon to another neuron or a receptor – This junction called ---synapse – neurotransmitters ...
Ch11AB
... Graded potentials are _________________, ____________________ changes in the membrane potential. Graded potentials can be __________________or _______________________. The ___________________ of a graded potential varies directly (is graded) with stimulus strength. (Slide 10) The ___________________ ...
... Graded potentials are _________________, ____________________ changes in the membrane potential. Graded potentials can be __________________or _______________________. The ___________________ of a graded potential varies directly (is graded) with stimulus strength. (Slide 10) The ___________________ ...
Slide ()
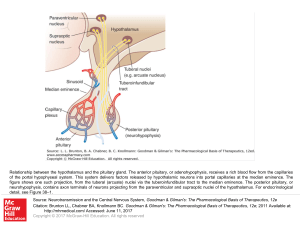
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
notes - Mrs. Blackmon`s Science Blackboard
... • White matter is a collection of myelinated fibers. • Gray matter is unmyelinated with only a single layer of Schwann cells. Gray matter is slow and found where distances are short. ...
... • White matter is a collection of myelinated fibers. • Gray matter is unmyelinated with only a single layer of Schwann cells. Gray matter is slow and found where distances are short. ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... 28.Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord to the effectors. 29. Within the spinal cord, motor and sensory neurons are connected byinterneurons 30. The 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system sympathetic ¶sympathetic 31 The above two divisions have a(n) antagonistic effects on the ...
... 28.Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord to the effectors. 29. Within the spinal cord, motor and sensory neurons are connected byinterneurons 30. The 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system sympathetic ¶sympathetic 31 The above two divisions have a(n) antagonistic effects on the ...
GROWTH
... • Directs growing symp nerve fibers toward target tissues – In fetal dev’t, correlation between [NGF], mRNA for nerve fiber prot’s, density nerve fiber prot’s – Synth’d by many cells ...
... • Directs growing symp nerve fibers toward target tissues – In fetal dev’t, correlation between [NGF], mRNA for nerve fiber prot’s, density nerve fiber prot’s – Synth’d by many cells ...
The Nervous System: Overview The nervous system Divisions of the
... processes, and contains two types of neuron: Motor neurons Sensory neurons ...
... processes, and contains two types of neuron: Motor neurons Sensory neurons ...
HBNervous
... 3. high metabolic rate - require OXYGEN and GLUCOSE at all times Dendrites are plasmamembrane extentions; this is the sensing end Cell body contains all organelles including nucleus with genetic information that directs synthesis. Dendritic end surrounds cell body. Axon is elongated region terminate ...
... 3. high metabolic rate - require OXYGEN and GLUCOSE at all times Dendrites are plasmamembrane extentions; this is the sensing end Cell body contains all organelles including nucleus with genetic information that directs synthesis. Dendritic end surrounds cell body. Axon is elongated region terminate ...
Unit 3A: Neural Processing and the Endocrine System Introduction
... 3. Axons are long “arms” that send info away from the cell body to other neurons or body parts. 1. Axons are insulated by the myelin sheath. This insulation helps control the impulses and speeds their travel. 2. Messages travel along neurons at between 2 and 200 mph (depending on the type of neuron) ...
... 3. Axons are long “arms” that send info away from the cell body to other neurons or body parts. 1. Axons are insulated by the myelin sheath. This insulation helps control the impulses and speeds their travel. 2. Messages travel along neurons at between 2 and 200 mph (depending on the type of neuron) ...
Chapter 1: Concepts and Methods in Biology - Rose
... B. Chemical synapses (fig. 48.12) 1. Synaptic cleft–separates presynaptic and postsynaptic cell 2. Electrical signal –> chemical signal –> electrical signal a. Presynaptic membrane depolarizes (due to arrival of action potential) b. Depolarization triggers an influx of Ca2+ c. Ca2+ influx causes syn ...
... B. Chemical synapses (fig. 48.12) 1. Synaptic cleft–separates presynaptic and postsynaptic cell 2. Electrical signal –> chemical signal –> electrical signal a. Presynaptic membrane depolarizes (due to arrival of action potential) b. Depolarization triggers an influx of Ca2+ c. Ca2+ influx causes syn ...
Notes Intro to Nervous System and Neurons
... Books says antagonistic, but they are more complimentary ...
... Books says antagonistic, but they are more complimentary ...