The vertebrate nervous system is regionally specialized
... nervous systems having complicated brains and ventral nerve cords. In vertebrates, the central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord, which is located dorsally. Information processing Nervous systems process information in three stages: sensory input, integration, and motor ...
... nervous systems having complicated brains and ventral nerve cords. In vertebrates, the central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord, which is located dorsally. Information processing Nervous systems process information in three stages: sensory input, integration, and motor ...
Andrew Rosen - Chapter 3: The Brain and Nervous System Intro
... Sensitive to activity level in each neuron and increase blood flow whenever the neurons in one area become more active Control brain development When new neurons are made during development, they migrate from one position to another, and this is controlled by glia o Glia produce chemicals to shut do ...
... Sensitive to activity level in each neuron and increase blood flow whenever the neurons in one area become more active Control brain development When new neurons are made during development, they migrate from one position to another, and this is controlled by glia o Glia produce chemicals to shut do ...
Norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter
... • Classsified chemically as purines; bind to purinergic receptors a. P1 receptor for ATP b. P2 receptor for adenosine • Released with norepinephrine to stimulate blood vessel constriction and with ACh to stimulate intestinal contraction • Released by nonneural cells; act as paracrine regulators in b ...
... • Classsified chemically as purines; bind to purinergic receptors a. P1 receptor for ATP b. P2 receptor for adenosine • Released with norepinephrine to stimulate blood vessel constriction and with ACh to stimulate intestinal contraction • Released by nonneural cells; act as paracrine regulators in b ...
Chapter 4 – Sensation
... Rods – Photoreceptors in the retina that respond to lower light intensities and give rise to achromatic (colorless) sensations Cones – Visual receptors that respond to greater light intensities and give rise to chromatic sensations Fovea – The area roughly at the retina’s center where cones ar ...
... Rods – Photoreceptors in the retina that respond to lower light intensities and give rise to achromatic (colorless) sensations Cones – Visual receptors that respond to greater light intensities and give rise to chromatic sensations Fovea – The area roughly at the retina’s center where cones ar ...
nervoussystemwebquest
... Sensory neuron transmits information from a sensory receptor to a motor neuron, which signals an effector cell to carry out the response. The knee jerking reaction goes through the sensory neurons which relays the information to the stretch receptor in the thigh muscle, to interneurons in the spinal ...
... Sensory neuron transmits information from a sensory receptor to a motor neuron, which signals an effector cell to carry out the response. The knee jerking reaction goes through the sensory neurons which relays the information to the stretch receptor in the thigh muscle, to interneurons in the spinal ...
Nervous System - wondersofscience
... • carries information from the various parts of the body to the brain. It is also the reflex center. – A reflex is a rapid and involuntary reaction to a stimulus – A reflex arc is the path taken by a nerve impulse during a reflex ...
... • carries information from the various parts of the body to the brain. It is also the reflex center. – A reflex is a rapid and involuntary reaction to a stimulus – A reflex arc is the path taken by a nerve impulse during a reflex ...
Nerve Growth Factor-7S (N0513) - Datasheet - Sigma
... may be involved in fetal development8,9 and nerve regeneration.10 NGF may also play a physiological role within the central nervous system.8,11,12 Cellular receptors for NGF have been found in a variety of cell lines13 and tissues, including cholinergic neurons of the brain14,15 and Schwann cells of ...
... may be involved in fetal development8,9 and nerve regeneration.10 NGF may also play a physiological role within the central nervous system.8,11,12 Cellular receptors for NGF have been found in a variety of cell lines13 and tissues, including cholinergic neurons of the brain14,15 and Schwann cells of ...
The Nervous System
... – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
... – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
The Nervous System - Ione Community Charter School
... – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
... – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
The Nervous System
... – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
... – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
Ch. 10 Outline
... A. One neuron sends impulses to several neurons B. Can amplify an impulse C. Impulse from a single neuron in CNS may be amplified to activate enough motor units needed for muscle contraction Outcomes to be Assessed 10.1: Introduction Describe the general functions of the nervous system. Identify ...
... A. One neuron sends impulses to several neurons B. Can amplify an impulse C. Impulse from a single neuron in CNS may be amplified to activate enough motor units needed for muscle contraction Outcomes to be Assessed 10.1: Introduction Describe the general functions of the nervous system. Identify ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes the membrane to become more positive. This starts an action potential, or nerve impulse. They follow the all or none law!!! • The membrane will repolarize when K+ ...
... depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes the membrane to become more positive. This starts an action potential, or nerve impulse. They follow the all or none law!!! • The membrane will repolarize when K+ ...
brain - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... pianist, for example, can play a complex piece of music without thinking about which notes to play next. In fact, stopping to think about the task can actually interfere with a flawless performance. This is what musicians, athletes and others often refer to as being “in the zone.” Spreng’s findings ...
... pianist, for example, can play a complex piece of music without thinking about which notes to play next. In fact, stopping to think about the task can actually interfere with a flawless performance. This is what musicians, athletes and others often refer to as being “in the zone.” Spreng’s findings ...
BOX 42.2 WHY BRAIN SIZE IS IMPORTANT Larger brains are
... Larger brains are generally thought to be computationally better because they usually have more neurons. However, growing bigger brains with more neurons creates a need for modifications in brain organization, and some solutions are likely to be common across taxa, allowing predictions about brain o ...
... Larger brains are generally thought to be computationally better because they usually have more neurons. However, growing bigger brains with more neurons creates a need for modifications in brain organization, and some solutions are likely to be common across taxa, allowing predictions about brain o ...
Chapter 12 Nervous System
... o herniated disc Fig. 8-8 - symptom is typically sciatica: radiating pain from the hip - correctable via diskectomy (Fig. 8-19) or spondylosyndesis (Fig. 8-21) VI. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) A. Cranial nerves -- 12 pairs B. Spinal nerves -- 31 pairs, usually named after body region they suppl ...
... o herniated disc Fig. 8-8 - symptom is typically sciatica: radiating pain from the hip - correctable via diskectomy (Fig. 8-19) or spondylosyndesis (Fig. 8-21) VI. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) A. Cranial nerves -- 12 pairs B. Spinal nerves -- 31 pairs, usually named after body region they suppl ...
Document
... • Based on number of processes found on cell body – multipolar = several dendrites & one axon • most common cell type in the brain and SC ...
... • Based on number of processes found on cell body – multipolar = several dendrites & one axon • most common cell type in the brain and SC ...
Neuron Anatomy
... chemical synapses are, for the most part, unidirectional. • There is a delay of a msec or more between the arrival of information at the presynaptic terminal and its transfer to the postsynaptic cell. This delay may reflect the several steps required for the release and action of the ...
... chemical synapses are, for the most part, unidirectional. • There is a delay of a msec or more between the arrival of information at the presynaptic terminal and its transfer to the postsynaptic cell. This delay may reflect the several steps required for the release and action of the ...
ANATOMICAL TERMS
... o The soma usually gives rise to the dendrites, long, thin like branches They are the primary site for receiving signals from other neurons The more dendrite a neuron has the more information it can receive 5 to 135 micro metres in diameter o Axon - a cylindrical and relatively unbranched for ...
... o The soma usually gives rise to the dendrites, long, thin like branches They are the primary site for receiving signals from other neurons The more dendrite a neuron has the more information it can receive 5 to 135 micro metres in diameter o Axon - a cylindrical and relatively unbranched for ...
New Title
... Epithelial tissue covers body surfaces. Connective tissue supports the body and connects its parts. Nervous tissue carries messages throughout the body. Muscle tissue allows movement. • Groups of tissues that work together to perform complex functions are called organs. • Organs form organ systems. ...
... Epithelial tissue covers body surfaces. Connective tissue supports the body and connects its parts. Nervous tissue carries messages throughout the body. Muscle tissue allows movement. • Groups of tissues that work together to perform complex functions are called organs. • Organs form organ systems. ...
HISTOLOGY REVISIT: NEURONS AND NEUROGLIA LEARNING
... Afferent processes of neurons Have primary secondary and tertiary branches. Contains all the components of perikayon except golgi apparatus Nissal substance restricted to main stem Outer surface shows numerous small spines or knobbed out growths called gemmules these are sites of synaptic contacts. ...
... Afferent processes of neurons Have primary secondary and tertiary branches. Contains all the components of perikayon except golgi apparatus Nissal substance restricted to main stem Outer surface shows numerous small spines or knobbed out growths called gemmules these are sites of synaptic contacts. ...
Document
... Olfactory Bulbs The olfactory bulbs relay sensory signals to the olfactory tract. small axons from the olfactory epithelium synapse with receptor neurons and interneurons in the olfactory bulbs. ...
... Olfactory Bulbs The olfactory bulbs relay sensory signals to the olfactory tract. small axons from the olfactory epithelium synapse with receptor neurons and interneurons in the olfactory bulbs. ...
Test yourself on lesions in section pictures
... Specific Lesions Loss of pain and temperature in the ipsilateral face is due to elimination of the spinal trigeminal tract and nucleus. This pathway has not yet crossed, since these are the primary afferents and cell bodies of the second order neurons. Loss of pain and temperature in the contralate ...
... Specific Lesions Loss of pain and temperature in the ipsilateral face is due to elimination of the spinal trigeminal tract and nucleus. This pathway has not yet crossed, since these are the primary afferents and cell bodies of the second order neurons. Loss of pain and temperature in the contralate ...
NERVOUS TISSUE The nervous system consists of all nervous
... that are mitotically inactive, i.e. can not divide. They have conducting pathways, and act as site of integration and analysis of nerve impulses. Neurons have large cell body (perikaryo) and nucleus surrounded by the cytoplasm. The cell body could be spherical, ovoid, or angular with variable diamet ...
... that are mitotically inactive, i.e. can not divide. They have conducting pathways, and act as site of integration and analysis of nerve impulses. Neurons have large cell body (perikaryo) and nucleus surrounded by the cytoplasm. The cell body could be spherical, ovoid, or angular with variable diamet ...
Slide ()
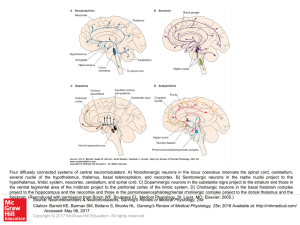
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...