Dear Colleagues - Centre for Rare Cardiovascular Diseases
... pulmonary to systemic flow was 2:1). Other findings included mild pulmonary hypertension (mean pulmonary artery pressure, 29 mmHg) increased pulmonary vascular resistance - 203,9 ARU and increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure - 16 mmHg. Discussion, Patients with transannular patch repair of ri ...
... pulmonary to systemic flow was 2:1). Other findings included mild pulmonary hypertension (mean pulmonary artery pressure, 29 mmHg) increased pulmonary vascular resistance - 203,9 ARU and increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure - 16 mmHg. Discussion, Patients with transannular patch repair of ri ...
Dear Colleagues, - Centre for Rare Cardiovascular Diseases
... Apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (AHCM) is a rare variant of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), in which thickening predominantly involves the apex of the left ventricle (LV) [1]. It is observed in 3-15% of HCM cases, more commonly in Asian population [2]. Fistulae between coronary arteries and he ...
... Apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (AHCM) is a rare variant of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), in which thickening predominantly involves the apex of the left ventricle (LV) [1]. It is observed in 3-15% of HCM cases, more commonly in Asian population [2]. Fistulae between coronary arteries and he ...
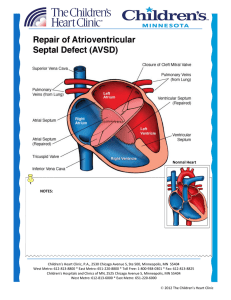
(AVSD) Repair - Children`s Heart Clinic
... AVSD is usually repaired within the first two years of life. Partial AVSD is usually repaired later when the child is 2-3 years of age, because they lack the VSD component. During surgery, a median sternotomy (incision through the middle of the chest) is performed. The patient is placed on cardiopul ...
... AVSD is usually repaired within the first two years of life. Partial AVSD is usually repaired later when the child is 2-3 years of age, because they lack the VSD component. During surgery, a median sternotomy (incision through the middle of the chest) is performed. The patient is placed on cardiopul ...
Transfer of NYHA 1-2 Heart Failure Patients to Primary Care
... Moderate pulmonary hypertension (estimated RV systolic pressure 45-50mm Hg). No pericardial disease. Other Investigations: Cardiac MRI was performed at St George's Hospital on 24 October 2014. This showed a dilated left ventricle with mild concentric hypertrophy and basal septal bulge. Severe systol ...
... Moderate pulmonary hypertension (estimated RV systolic pressure 45-50mm Hg). No pericardial disease. Other Investigations: Cardiac MRI was performed at St George's Hospital on 24 October 2014. This showed a dilated left ventricle with mild concentric hypertrophy and basal septal bulge. Severe systol ...
File
... Ventricle fills with blood and contracts pumping blood to the aorta and pulmonary arteries 3. Atrial & Ventricle _____________________ – 0.40 sec Both atria & ventricles are diastole (relaxed) as blood from the body fills the atria What is that sound? ___________: closing of the bicuspid and ...
... Ventricle fills with blood and contracts pumping blood to the aorta and pulmonary arteries 3. Atrial & Ventricle _____________________ – 0.40 sec Both atria & ventricles are diastole (relaxed) as blood from the body fills the atria What is that sound? ___________: closing of the bicuspid and ...
The cardiopulmonary simulator proven to teach skills Harvey The Cardiopulmonary Patient Simulator
... Harvey currently trains thousands of learners annually at hundreds of medical centers worldwide.The all-new Harvey, the Cardiopulmonary Patient Simulator, has made some dramatic changes which result in a more portable, versatile and less costly Harvey. The full-size manikin realistically simulates n ...
... Harvey currently trains thousands of learners annually at hundreds of medical centers worldwide.The all-new Harvey, the Cardiopulmonary Patient Simulator, has made some dramatic changes which result in a more portable, versatile and less costly Harvey. The full-size manikin realistically simulates n ...
aortic valve opens.
... CO is the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute CO is the product of heart rate (HR) and stroke volume (SV) HR is the number of heart beats per minute SV is the amount of blood pumped out by a ventricle with each beat Cardiac reserve is the difference between resting and maximal CO ...
... CO is the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute CO is the product of heart rate (HR) and stroke volume (SV) HR is the number of heart beats per minute SV is the amount of blood pumped out by a ventricle with each beat Cardiac reserve is the difference between resting and maximal CO ...
Brain and CranialNerves
... CO is the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute CO is the product of heart rate (HR) and stroke volume (SV) HR is the number of heart beats per minute SV is the amount of blood pumped out by a ventricle with each beat Cardiac reserve is the difference between resting and maximal CO ...
... CO is the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute CO is the product of heart rate (HR) and stroke volume (SV) HR is the number of heart beats per minute SV is the amount of blood pumped out by a ventricle with each beat Cardiac reserve is the difference between resting and maximal CO ...
Familial Subvalvular Aortic Stenosis in Rottweilers
... • SAS is a life threatening disease • Appears to be inherited in the Rottweiler • Pattern of inheritance is still unclear • Screening is important in reducing prevalence • Genetic studies are underway to identify possible ...
... • SAS is a life threatening disease • Appears to be inherited in the Rottweiler • Pattern of inheritance is still unclear • Screening is important in reducing prevalence • Genetic studies are underway to identify possible ...
HEART SOUNDS
... • Murmurs are abnormal sounds produced due to abnormal flow of blood [turbulent blood flow] through abnormal heart valves e.g.. stenosis or incompetence. • Stenosis means narrow or stiff, valve that does not open completely. • Incompetent means valve which does not close properly and remains open. ...
... • Murmurs are abnormal sounds produced due to abnormal flow of blood [turbulent blood flow] through abnormal heart valves e.g.. stenosis or incompetence. • Stenosis means narrow or stiff, valve that does not open completely. • Incompetent means valve which does not close properly and remains open. ...
Double Outlet Right Ventricle
... artery exit from the right ventricle. In the normal heart, the aorta leaves the left ventricle and the pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle. In addition, there is a large ventricular septal defect (VSD), or hole in the muscle wall (septum) that separates the right and left ventricles. ...
... artery exit from the right ventricle. In the normal heart, the aorta leaves the left ventricle and the pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle. In addition, there is a large ventricular septal defect (VSD), or hole in the muscle wall (septum) that separates the right and left ventricles. ...
DRUG DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Ajmaline 1 mg/kg over 5
... disease) or in the presence of wide QRS, wide P waves, or prolonged PR intervals (i.e. infranodal conduction disease) to avoid the risk of precipitating complete AV block. Electro‐mechanical dissociation has been encountered in isolated cases. Isoprenaline and ...
... disease) or in the presence of wide QRS, wide P waves, or prolonged PR intervals (i.e. infranodal conduction disease) to avoid the risk of precipitating complete AV block. Electro‐mechanical dissociation has been encountered in isolated cases. Isoprenaline and ...
Mechanism of Action
... Compare and contrast left-sided heart failure to right Describe special considerations for older adults with heart failure Discuss the prevention of complications for patients with heart failure Prioritize nursing care for clients with heart failure Identify common nursing diagnoses and collaborativ ...
... Compare and contrast left-sided heart failure to right Describe special considerations for older adults with heart failure Discuss the prevention of complications for patients with heart failure Prioritize nursing care for clients with heart failure Identify common nursing diagnoses and collaborativ ...
Cardiac Function in Ultramarathoners
... “One possible explanation for the U-shaped curve observed by Lavie and colleagues is that the authors adjust for body mass index, hypertension and hypercholesterolaemia. Running has been shown to lower those risk factors in a dose-dependent fashion with no sign of negative returns until at least 50 ...
... “One possible explanation for the U-shaped curve observed by Lavie and colleagues is that the authors adjust for body mass index, hypertension and hypercholesterolaemia. Running has been shown to lower those risk factors in a dose-dependent fashion with no sign of negative returns until at least 50 ...
P-59 Frequency of associated congenital heart defects in Down
... the Institute of Child Health, Lahore, in year 2015. Fifty-eight phenotypically Down syndrome children coming to the cardiology department for echocardiography from birth to 13 years were included in this study. The 2 –dimension echocardiography had been done after detailed history and physical exam ...
... the Institute of Child Health, Lahore, in year 2015. Fifty-eight phenotypically Down syndrome children coming to the cardiology department for echocardiography from birth to 13 years were included in this study. The 2 –dimension echocardiography had been done after detailed history and physical exam ...
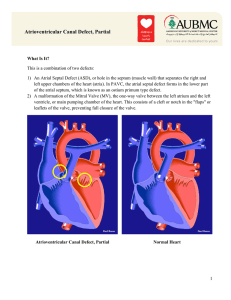
Atrioventricular Canal Defect, Partial
... pumped to the lungs via the right ventricle, reducing the efficiency of the circulatory system. This may lead to heart failure with congestion of the lungs. Eventually, the atrial septal defect will cause the enlargement (dilatation) of the right atrium and right ventricle, which may lead to irregul ...
... pumped to the lungs via the right ventricle, reducing the efficiency of the circulatory system. This may lead to heart failure with congestion of the lungs. Eventually, the atrial septal defect will cause the enlargement (dilatation) of the right atrium and right ventricle, which may lead to irregul ...
Cardiovascular Disease
... • ASDs are some of the most common congenital defects, representing 10%to l7% • a higher prevalence in women (6o%) • Defects are classified according to their location in the interatrial septum : • 1- primary ostium defect : 20%, defect in ...
... • ASDs are some of the most common congenital defects, representing 10%to l7% • a higher prevalence in women (6o%) • Defects are classified according to their location in the interatrial septum : • 1- primary ostium defect : 20%, defect in ...
Ventricular Late potentials
... T wave alternans testing requires exercise or atrial pacing to achieve a heart rate of 100 to 120 beats/min with relatively little atrial or ventricular ectopic activity The test is less useful in patients with wide QRS complex(longer than 120 milliseconds). ...
... T wave alternans testing requires exercise or atrial pacing to achieve a heart rate of 100 to 120 beats/min with relatively little atrial or ventricular ectopic activity The test is less useful in patients with wide QRS complex(longer than 120 milliseconds). ...
right ventricular myxoma infiltrating the tricuspid valve and
... right heart, was also heard. There was a grade 3/6 harsh systolic ejection murmur at the second and third left intercostal spaces. No diastolic murmur was audible. The chest radiograph showed a mildly enlarged right heart silhouette and a prominent pulmonary conus with normal pulmonary vascularity. ...
... right heart, was also heard. There was a grade 3/6 harsh systolic ejection murmur at the second and third left intercostal spaces. No diastolic murmur was audible. The chest radiograph showed a mildly enlarged right heart silhouette and a prominent pulmonary conus with normal pulmonary vascularity. ...
Curriculum based assessment tool for basic training in
... Coronary anatomy and correlation with 2D views of left ventricle. Segmentation of the left ventricle Wall motion Measurements of global systolic function. (LVOT VTI, stroke volume, fractional shortening Doppler mitral valve filling patterns & normal range Appearance of complications afte ...
... Coronary anatomy and correlation with 2D views of left ventricle. Segmentation of the left ventricle Wall motion Measurements of global systolic function. (LVOT VTI, stroke volume, fractional shortening Doppler mitral valve filling patterns & normal range Appearance of complications afte ...
Heart Physiology Cardiac Conduction System Electrical System
... · stroke volume - volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per heartbeat · cardiac output - volume of blood pumped per minute by the heart (both ventricles) ...
... · stroke volume - volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per heartbeat · cardiac output - volume of blood pumped per minute by the heart (both ventricles) ...
FASMED - Sudden Cardiac Death
... • Autosomal dominant disease of sarcomeres; increased proliferation and disorganized arrangement • Prevalence of 0.050.2% of the population ...
... • Autosomal dominant disease of sarcomeres; increased proliferation and disorganized arrangement • Prevalence of 0.050.2% of the population ...
Percutaneous ventricular restoration in a chronic
... often failing left ventricle. Fifty seven percent of patients with an anterior infarction develop heart failure one year after thrombolytic therapy for an acute MI4. Heart failure after myocardial infarction (MI) is a progressive disease5. There have been many advances in medical treatment the last ...
... often failing left ventricle. Fifty seven percent of patients with an anterior infarction develop heart failure one year after thrombolytic therapy for an acute MI4. Heart failure after myocardial infarction (MI) is a progressive disease5. There have been many advances in medical treatment the last ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.