Ventricular Septal Defect
... the defect lies close to the aortic valve cusps. These defects may be large and rarely undergo spontaneous closure. Because of proximity to the aortic valve, aortic regurgitation is more likely to occur than in other types. This defect is more common in infants of Asian descent. ...
... the defect lies close to the aortic valve cusps. These defects may be large and rarely undergo spontaneous closure. Because of proximity to the aortic valve, aortic regurgitation is more likely to occur than in other types. This defect is more common in infants of Asian descent. ...
Left Ventricular Function - St. Luke`s Roosevelt Ultrasound Division
... Directed bedside transthoracic echocardiography: preferred cardiac window for left ventricular ejection fraction estimation in critically ill patients. American Journal of Emergency Medicine Volume 25, Issue 8 (October 2007) - Copyright © 2007 W. B. Saunders Company ...
... Directed bedside transthoracic echocardiography: preferred cardiac window for left ventricular ejection fraction estimation in critically ill patients. American Journal of Emergency Medicine Volume 25, Issue 8 (October 2007) - Copyright © 2007 W. B. Saunders Company ...
Stroke Volume - emseducation.info
... • Defined: The period of time from the end of one cardiac contraction to the end of the next • Diastole: First phase; The relaxation phase; Ventricular filling begins, blood enters through the mitral and tricuspid valves; Pulmonic and aortic valves ...
... • Defined: The period of time from the end of one cardiac contraction to the end of the next • Diastole: First phase; The relaxation phase; Ventricular filling begins, blood enters through the mitral and tricuspid valves; Pulmonic and aortic valves ...
Cardiogenic Shock & Post Myocardial Infarction Complications
... The correct answer is A. During the first few days after a myocardial infarction, the heart is particularly susceptible to arrhythmia, which is the most common cause of death in the early ...
... The correct answer is A. During the first few days after a myocardial infarction, the heart is particularly susceptible to arrhythmia, which is the most common cause of death in the early ...
Cardiac Cycle
... • a wave represents atrial contraction, increasing atrial pressure. • c wave represents regurgitation of blood from ventricles into atrium due to sliding/closure of A.V. valves towards atrium due to increased ventricular pressure. • v wave represents the flow of blood from atria to ventricle after v ...
... • a wave represents atrial contraction, increasing atrial pressure. • c wave represents regurgitation of blood from ventricles into atrium due to sliding/closure of A.V. valves towards atrium due to increased ventricular pressure. • v wave represents the flow of blood from atria to ventricle after v ...
The time between S1 and S2
... never changes with breathing. It's fairly normal in children and athletes. In other people, it can indicate a non-specific impairment of ventricular function - listen with the bell to determine which ventricle is making the sound (left side at the apex, right side at the xiphoid process). ...
... never changes with breathing. It's fairly normal in children and athletes. In other people, it can indicate a non-specific impairment of ventricular function - listen with the bell to determine which ventricle is making the sound (left side at the apex, right side at the xiphoid process). ...
Model Pulmonary Edema
... < 1 month: Tetralogy of Fallot, Transposition of the great arteries, Coarctation of the aorta. 2 – 6 months: Ventricular septal defects (VSD), Atrioseptal defects (ASD). Any age: Myocarditis, Pericarditis, SVT, heart blocks. Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure / Pulmonary edema may vary depending ...
... < 1 month: Tetralogy of Fallot, Transposition of the great arteries, Coarctation of the aorta. 2 – 6 months: Ventricular septal defects (VSD), Atrioseptal defects (ASD). Any age: Myocarditis, Pericarditis, SVT, heart blocks. Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure / Pulmonary edema may vary depending ...
worldwide collaboration
... the U.S. alone. Available treatments for patients suffering from these forms of heart disease have been approved for other illnesses and only treat the symptoms of their disease. As their disease progresses, it can require invasive procedures including heart transplantation, and can lead to sudden c ...
... the U.S. alone. Available treatments for patients suffering from these forms of heart disease have been approved for other illnesses and only treat the symptoms of their disease. As their disease progresses, it can require invasive procedures including heart transplantation, and can lead to sudden c ...
Pre-heart questions
... All answers can be obtained via lab book 1. Area where the heart is located ...
... All answers can be obtained via lab book 1. Area where the heart is located ...
The Child with a Cardiovascular Disorder
... pulsations in neck veins tachycardia, dyspnea irregular pulse rate clubbing of fingers fatigue during feeding or activity excessive perspirations (esp. over forehead) ...
... pulsations in neck veins tachycardia, dyspnea irregular pulse rate clubbing of fingers fatigue during feeding or activity excessive perspirations (esp. over forehead) ...
Cardiac - CMA`s English Mastiffs
... phenotypically normal prior to use in a breeding program. For the purposes of the database, a phenotypically normal dog is defined as: 1. One without a cardiac murmur -or2. One with an innocent heart murmur that is found to be otherwise normal by virtue of an echocardiographic examination which incl ...
... phenotypically normal prior to use in a breeding program. For the purposes of the database, a phenotypically normal dog is defined as: 1. One without a cardiac murmur -or2. One with an innocent heart murmur that is found to be otherwise normal by virtue of an echocardiographic examination which incl ...
ERT Critical Care Consult
... Holter monitor annually (24 hour monitor) ECG and Holter if any syncope (fainting) or other symptoms concerning for arrhythmia ...
... Holter monitor annually (24 hour monitor) ECG and Holter if any syncope (fainting) or other symptoms concerning for arrhythmia ...
irregular pulse in a nine-year old girl
... structural defects such as L-transposition of the great arteries. It may be associated with matemallupus erythematosus.2 Autoimmune disease accounts for 60% to 70% of all congenital heart block and 80% of cases with a structurally normal heart. 2 ...
... structural defects such as L-transposition of the great arteries. It may be associated with matemallupus erythematosus.2 Autoimmune disease accounts for 60% to 70% of all congenital heart block and 80% of cases with a structurally normal heart. 2 ...
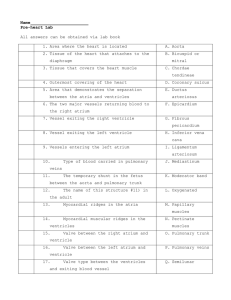
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines HEART
... and extent of coronary artery disease (CAD) as well as ventricular and valvular function. It can be used to perform various tests, including angiography, intravascular ultrasonography, and measurement of cardiac output (CO), detection and quantification of shunts, endomyocardial biopsy, and measurem ...
... and extent of coronary artery disease (CAD) as well as ventricular and valvular function. It can be used to perform various tests, including angiography, intravascular ultrasonography, and measurement of cardiac output (CO), detection and quantification of shunts, endomyocardial biopsy, and measurem ...
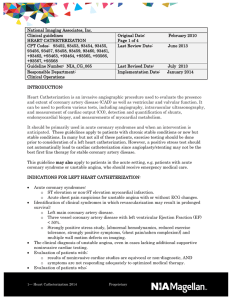
Lecture Note 3 - Heart Failure
... • Increased venous return increases the ventricular filling (end-diastolic volume) and therefore preload, which is the initial stretching of the cardiac myocytes prior to contraction. Myocyte stretching causes an increase in force generation. This mechanism enables the heart to eject the additional ...
... • Increased venous return increases the ventricular filling (end-diastolic volume) and therefore preload, which is the initial stretching of the cardiac myocytes prior to contraction. Myocyte stretching causes an increase in force generation. This mechanism enables the heart to eject the additional ...
Chest trauma Case Presentation
... • The paramedics arrived 5 minutes later and, found the patient to be in ventricular fibrillation. • The patient returned to spontaneus circulation with one 200 joule defibrilation. • A normal sinus rhythm was noted and the patient was noted to regain consciousness. ...
... • The paramedics arrived 5 minutes later and, found the patient to be in ventricular fibrillation. • The patient returned to spontaneus circulation with one 200 joule defibrilation. • A normal sinus rhythm was noted and the patient was noted to regain consciousness. ...
Ventricular Septal Defect PDF
... The defect can be small or large. The VSD may be termed muscular, perimembranous, inlet, outlet, apical or doublycommitted depending on its position and the surrounding substance of the heart. Where the VSD is small, there is no elevation of the low pressures found in the right ventricle (pumping ch ...
... The defect can be small or large. The VSD may be termed muscular, perimembranous, inlet, outlet, apical or doublycommitted depending on its position and the surrounding substance of the heart. Where the VSD is small, there is no elevation of the low pressures found in the right ventricle (pumping ch ...
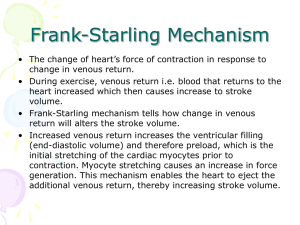
Heart sounds and murmurs
... 1. systolic murmur: harsh turbulent flow (from increase in turbulence) a. aortic stenosis: ejection murmur because the valves are too tight./don’t open completely b. pulmonary stenosis: ejection murmur + S2 splitting c. mitral/tricuspid regurgitation: not properly closed holosystolic d. mitral val ...
... 1. systolic murmur: harsh turbulent flow (from increase in turbulence) a. aortic stenosis: ejection murmur because the valves are too tight./don’t open completely b. pulmonary stenosis: ejection murmur + S2 splitting c. mitral/tricuspid regurgitation: not properly closed holosystolic d. mitral val ...
Time: Monday May 2nd, 2011 5:00pm Location: Buchanan A202
... Kelly Paton, University of British Columbia Cardiac arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia (VT) and fibrillation (VF) can be fatal if left untreated. In two dimensions, these reentrant arrhythmias can be modeled as one or more spiral waves in a system of excitable media. The appearance of spira ...
... Kelly Paton, University of British Columbia Cardiac arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia (VT) and fibrillation (VF) can be fatal if left untreated. In two dimensions, these reentrant arrhythmias can be modeled as one or more spiral waves in a system of excitable media. The appearance of spira ...
2. A condition in which one or both of the cusps of the mitral vlave is
... 18. Blood leaves the heart through the ____ valves. 20. Condition lacking a definite rhythm or no rhythm. 21. A heart valve with a abnormally narrow opening is called ____. 24. The large artery leaving the heart carry blood to the lungs is called the ___trunk. 27. Structurally descriptive name for t ...
... 18. Blood leaves the heart through the ____ valves. 20. Condition lacking a definite rhythm or no rhythm. 21. A heart valve with a abnormally narrow opening is called ____. 24. The large artery leaving the heart carry blood to the lungs is called the ___trunk. 27. Structurally descriptive name for t ...
Sudden Cardiac Death in Athletes and
... 1. Symptoms are usually absent (or denied) in athletes with CMPs! ...
... 1. Symptoms are usually absent (or denied) in athletes with CMPs! ...
ARVC Patient Information
... and is responsible for 20% of sudden deaths in young adults and 25% of sudden deaths among athletes. Since the condition may be inherited in about 30-50% cases, it is recommended that parents and brothers and sisters and the children of those affected should be screened for the ARVC. ARVC has been f ...
... and is responsible for 20% of sudden deaths in young adults and 25% of sudden deaths among athletes. Since the condition may be inherited in about 30-50% cases, it is recommended that parents and brothers and sisters and the children of those affected should be screened for the ARVC. ARVC has been f ...
Supplementary Material Online
... wave was used to obtain septal and lateral mitral annular velocities (e’). The tissue Doppler ...
... wave was used to obtain septal and lateral mitral annular velocities (e’). The tissue Doppler ...
Management of Diastolic Heart Failure Patients with Irbesartan
... end-diastolic pressure, either by invasive hemodynamic studies or, more conveniently, by Doppler echocardiography. Control of aetiological factors, particularly hypertension, coronary heart disease and arrhythmias, constitutes the mainstay of management of diastolic heart failure. Restriction of int ...
... end-diastolic pressure, either by invasive hemodynamic studies or, more conveniently, by Doppler echocardiography. Control of aetiological factors, particularly hypertension, coronary heart disease and arrhythmias, constitutes the mainstay of management of diastolic heart failure. Restriction of int ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.