Perioperative Management of DORV Case
... catheterization data, and other imaging studies (MRI, CT). It is vital to recognize the presence of ventricular dysfunction since this may impact the anesthetic technique utilized. The EKG and any previous history of rhythm abnormalities should be reviewed. Patient allergies, medications, and a his ...
... catheterization data, and other imaging studies (MRI, CT). It is vital to recognize the presence of ventricular dysfunction since this may impact the anesthetic technique utilized. The EKG and any previous history of rhythm abnormalities should be reviewed. Patient allergies, medications, and a his ...
Pediatric Cardiovascular Disorders
... (overload right side of heart causing backflow) leads to… Cardiac hypertrophy leads to… One-sided cardiac failure→ bilateral failure ...
... (overload right side of heart causing backflow) leads to… Cardiac hypertrophy leads to… One-sided cardiac failure→ bilateral failure ...
Mathematical Modelling of Human Heart as a
... and deformation have been simulated [1]. The excitation propagation has been simulated by electrical heart model, and the resultant active forces have been used to study the ventricular wall motion during systole. The simulation results are found to be compatible with the models theoretical results ...
... and deformation have been simulated [1]. The excitation propagation has been simulated by electrical heart model, and the resultant active forces have been used to study the ventricular wall motion during systole. The simulation results are found to be compatible with the models theoretical results ...
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF HEART FAILURE
... In normal conditions, the ryanoid channel in SR is stabilized, but in heart failure abnormal calcium leak is induced. In heart failure, channel gating is hypersensitized to calcium: at a lower concentration of calcium, the channel is more activated. ...
... In normal conditions, the ryanoid channel in SR is stabilized, but in heart failure abnormal calcium leak is induced. In heart failure, channel gating is hypersensitized to calcium: at a lower concentration of calcium, the channel is more activated. ...
Pericardium and external features of Heart
... Mainly formed by right atrium and right ventricle. Diaphragmatic surface (Inferior surface): Mainly formed by right and left ventricles. Small portion is formed by right atrium. Base (Posterior surface): Mainly formed by left atrium. Apex: formed by left ventricle ...
... Mainly formed by right atrium and right ventricle. Diaphragmatic surface (Inferior surface): Mainly formed by right and left ventricles. Small portion is formed by right atrium. Base (Posterior surface): Mainly formed by left atrium. Apex: formed by left ventricle ...
Non-cardiac Surgery in the Adult Congenital Heart Patient
... Cardiac output is determined by the transpulmonary gradient in Fontan physiology. This means that the gradient between central venous pressure and the end diastolic pressure of the systemic ventricle is ...
... Cardiac output is determined by the transpulmonary gradient in Fontan physiology. This means that the gradient between central venous pressure and the end diastolic pressure of the systemic ventricle is ...
Critical Congenital Heart Disease
... 1. Narrowing is severe enough to cause a decrease in right ventricular output ...
... 1. Narrowing is severe enough to cause a decrease in right ventricular output ...
ostium primum defect: factors causing deterioration in - Heart
... and increasing heart size (Fig. 3). Right ventriostium primum defect related to age of the patients. cular failure was excluded by cardiac catheterization which in 4 patients revealed a normal end-diastolic pressure in the right ventricle. However, as well as some mitral incompetence, gross tricuspi ...
... and increasing heart size (Fig. 3). Right ventriostium primum defect related to age of the patients. cular failure was excluded by cardiac catheterization which in 4 patients revealed a normal end-diastolic pressure in the right ventricle. However, as well as some mitral incompetence, gross tricuspi ...
Chapter 18 - The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
... Heart is inhibited by the parasympathetic cardioinhibitory center ...
... Heart is inhibited by the parasympathetic cardioinhibitory center ...
Stroke volume and Cardiac output
... 1. Place the cones and outline the basic chambers of the heart. Ensure that you use red for oxygenated and blue for de-oxygenated transport of blood. Label each of the sections of the heart. Once this is complete each take a photo from on the balcony. 2. Using the diagram write the names of the valv ...
... 1. Place the cones and outline the basic chambers of the heart. Ensure that you use red for oxygenated and blue for de-oxygenated transport of blood. Label each of the sections of the heart. Once this is complete each take a photo from on the balcony. 2. Using the diagram write the names of the valv ...
Circulatory system
... The atrioventricular valves (AV valve) separate the atrium and ventricle on each side of the heart. The AV valves have flaps of tissues, called leaflets or cusps, which open and close to ensure that the blood flows only in one direction and does not backflow into the atriums. The AV valve on the r ...
... The atrioventricular valves (AV valve) separate the atrium and ventricle on each side of the heart. The AV valves have flaps of tissues, called leaflets or cusps, which open and close to ensure that the blood flows only in one direction and does not backflow into the atriums. The AV valve on the r ...
Surgical Ventricular Restoration
... ventricle to its normal, spherical shape and size in patients with akinetic segments of the heart, secondary to either dilated cardiomyopathy or post-infarction left ventricular aneurysm. The SVR procedure is usually performed after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and may proceed or be follow ...
... ventricle to its normal, spherical shape and size in patients with akinetic segments of the heart, secondary to either dilated cardiomyopathy or post-infarction left ventricular aneurysm. The SVR procedure is usually performed after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and may proceed or be follow ...
Twelve-lead
... ST segment may be elevated and T wave may be inverted Infarction (Age Unknown)—abnormal Q wave, ST segment and T wave returned to normal ...
... ST segment may be elevated and T wave may be inverted Infarction (Age Unknown)—abnormal Q wave, ST segment and T wave returned to normal ...
Congenital Heart Defects
... •Because of the increased affinity of fetal hemoglobin for oxygen, PO2 values at a given level of oxygen saturation are often lower in newborns than adults. •An elevated arterial PCO2 value often indicates the presence of pulmonary disease. PCO2 may also be increased in heart failure. •A reduced pH ...
... •Because of the increased affinity of fetal hemoglobin for oxygen, PO2 values at a given level of oxygen saturation are often lower in newborns than adults. •An elevated arterial PCO2 value often indicates the presence of pulmonary disease. PCO2 may also be increased in heart failure. •A reduced pH ...
Invasive Hemodynamic for Prep and Recove
... Bedside monitor – amplifier is located inside. The amplifier increases the size of signal Transducer – changes the mechanical energy or pressures of pulse into electrical energy; should be level with the phlebostatic axis[ you can estimate this by intersecting lines from the 4th ICS,mid axillary lin ...
... Bedside monitor – amplifier is located inside. The amplifier increases the size of signal Transducer – changes the mechanical energy or pressures of pulse into electrical energy; should be level with the phlebostatic axis[ you can estimate this by intersecting lines from the 4th ICS,mid axillary lin ...
INVASIVE HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING
... Bedside monitor – amplifier is located inside. The amplifier increases the size of signal Transducer – changes the mechanical energy or pressures of pulse into electrical energy; should be level with the phlebostatic axis[ you can estimate this by intersecting lines from the 4th ICS,mid axillary lin ...
... Bedside monitor – amplifier is located inside. The amplifier increases the size of signal Transducer – changes the mechanical energy or pressures of pulse into electrical energy; should be level with the phlebostatic axis[ you can estimate this by intersecting lines from the 4th ICS,mid axillary lin ...
Cardiac Purkinje Fiber Imaging
... Thus, detailed insight into the anatomy of the conduction system would be of great importance for the understanding of the homogeneous cardiac performance arising from well-coordinated electro-mechanical activity and further for the investigation of cardiac function in a (an) normal and abnormal sta ...
... Thus, detailed insight into the anatomy of the conduction system would be of great importance for the understanding of the homogeneous cardiac performance arising from well-coordinated electro-mechanical activity and further for the investigation of cardiac function in a (an) normal and abnormal sta ...
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
... About 15% to 30% of patients with CHF and LV systolic dysfunction have conduction system disease. The resulting conduction abnormalities alter the normal pattern of heart contraction, causing different parts of the heart to contract at different times. This dyssynchrony leads to abnormal wall stress ...
... About 15% to 30% of patients with CHF and LV systolic dysfunction have conduction system disease. The resulting conduction abnormalities alter the normal pattern of heart contraction, causing different parts of the heart to contract at different times. This dyssynchrony leads to abnormal wall stress ...
Arrhythmias 2
... identifiable reversible cause (e.g. acute myocardial infarction, severe metabolic disturbance), at high risk of sudden death. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) are first-line therapy ...
... identifiable reversible cause (e.g. acute myocardial infarction, severe metabolic disturbance), at high risk of sudden death. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) are first-line therapy ...
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
... Inferior Vena Cava ~ from lower body Coronary Sinus ~ from myocardium itself Receives “unoxygenated” blood from body Pumps blood into Right Ventricle through Right AV Valve Right AV Valve ~ Tricuspid Valve Heart ~ Chapter 20~5/1/2017 ...
... Inferior Vena Cava ~ from lower body Coronary Sinus ~ from myocardium itself Receives “unoxygenated” blood from body Pumps blood into Right Ventricle through Right AV Valve Right AV Valve ~ Tricuspid Valve Heart ~ Chapter 20~5/1/2017 ...
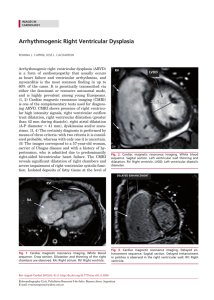
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
... Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD) is a form of cardiomyopathy that usually occurs as heart failure and ventricular arrhythmias, and myocarditis is the most common finding in up to 60% of the cases. It is genetically transmitted via either the dominant or recessive autosomal mode, and ...
... Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD) is a form of cardiomyopathy that usually occurs as heart failure and ventricular arrhythmias, and myocarditis is the most common finding in up to 60% of the cases. It is genetically transmitted via either the dominant or recessive autosomal mode, and ...
Murmurs - National Heart Centre Singapore
... of the heart and its related structures (e.g. valves). From these pictures, cardiologists can measure the size and function of heart chambers, study the motion of heart valves, and evaluate the blood flow pattern across the valves and within the heart chambers. Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) is ...
... of the heart and its related structures (e.g. valves). From these pictures, cardiologists can measure the size and function of heart chambers, study the motion of heart valves, and evaluate the blood flow pattern across the valves and within the heart chambers. Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) is ...
Lecture Notes - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... A. The heart is a double pump; the right side pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation, i.e., the pulmonary circuit; the left side pumps blood throughout the body to nourish tissues, i.e., the systemic circuit (p. 500, Fig. 18.1). B. The four chambers are the right and left atria (receiving chambers ...
... A. The heart is a double pump; the right side pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation, i.e., the pulmonary circuit; the left side pumps blood throughout the body to nourish tissues, i.e., the systemic circuit (p. 500, Fig. 18.1). B. The four chambers are the right and left atria (receiving chambers ...
Chapter 19 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Rising pressure opens semilunar valves Rapid ejection of blood Reduced ejection of blood (less pressure) Stroke volume: amount ejected, 70 ml at rest • SV/EDV= ejection fraction, at rest ~ 54%, during vigorous exercise as high as 90%, diseased heart < 50% • End-systolic volume: amount left in heart ...
... Rising pressure opens semilunar valves Rapid ejection of blood Reduced ejection of blood (less pressure) Stroke volume: amount ejected, 70 ml at rest • SV/EDV= ejection fraction, at rest ~ 54%, during vigorous exercise as high as 90%, diseased heart < 50% • End-systolic volume: amount left in heart ...
Chapter 19
... Rising pressure opens semilunar valves Rapid ejection of blood Reduced ejection of blood (less pressure) Stroke volume: amount ejected, 70 ml at rest • SV/EDV= ejection fraction, at rest ~ 54%, during vigorous exercise as high as 90%, diseased heart < 50% • End-systolic volume: amount left in heart ...
... Rising pressure opens semilunar valves Rapid ejection of blood Reduced ejection of blood (less pressure) Stroke volume: amount ejected, 70 ml at rest • SV/EDV= ejection fraction, at rest ~ 54%, during vigorous exercise as high as 90%, diseased heart < 50% • End-systolic volume: amount left in heart ...
Mitral insufficiency

Mitral insufficiency (MI), mitral regurgitation or mitral incompetence is a disorder of the heart in which the mitral valve does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood. It is the abnormal leaking of blood backwards from the left ventricle, through the mitral valve, into the left atrium, when the left ventricle contracts, i.e. there is regurgitation of blood back into the left atrium. MI is the most common form of valvular heart disease.