Name: Date: Honor Code: Stearns Chapter 2: Classical China (Due
... Section III – In Depth: Use the document to answer in COMPLETE SENTENCES. Women in Patriarchal Societies (page 45) 1. How do you think most women reared in a patriarchal society would react to their conditions? ...
... Section III – In Depth: Use the document to answer in COMPLETE SENTENCES. Women in Patriarchal Societies (page 45) 1. How do you think most women reared in a patriarchal society would react to their conditions? ...
Stearns Chapter 2: Classical China
... Section III – In Depth: Use the document to answer in COMPLETE SENTENCES. Women in Patriarchal Societies (page 45) 1. How do you think most women reared in a patriarchal society would react to their conditions? ...
... Section III – In Depth: Use the document to answer in COMPLETE SENTENCES. Women in Patriarchal Societies (page 45) 1. How do you think most women reared in a patriarchal society would react to their conditions? ...
Name - davis.k12.ut.us
... 26. Why do you think 2 small European kingdoms accomplished what no major empire/power ever had previously done? ...
... 26. Why do you think 2 small European kingdoms accomplished what no major empire/power ever had previously done? ...
... money prices, while unemployment and other real variables are largely determined by market forces and institutions. Stagflation should have taught us that monetary stimulus can backfire. Indeed, QE2 is already backfiring, as seen by its heavy criticism. German Finance Minister Wolfgang Schäuble summ ...
Population
... The Great Escape from what? The Great Escape is from hunger, disease and premature death [Fogel, 2004] This is the “natural” condition of humanity up to the industrial revolution: the normalcy of the past the low average growth rate of population (0.2 pc/year) is a measure of both instability (crops ...
... The Great Escape from what? The Great Escape is from hunger, disease and premature death [Fogel, 2004] This is the “natural” condition of humanity up to the industrial revolution: the normalcy of the past the low average growth rate of population (0.2 pc/year) is a measure of both instability (crops ...
Global Age - Tioga Central School District
... as slaves; portion of the Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade ...
... as slaves; portion of the Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade ...
How did China`s involvement in international trade change at the
... No. China increasingly began an import market. ...
... No. China increasingly began an import market. ...
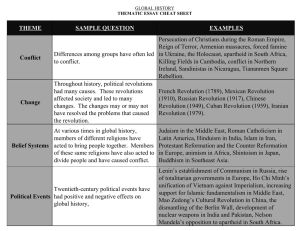
THEME SAMPLE QUESTION EXAMPLES Conflict Differences
... These beliefs and achievements have had Isabella, Leonardo da Vinci, John Locke, Catherine History positive and negative effects on society. the great, Simón Bolívar, Nelson Mandela, ...
... These beliefs and achievements have had Isabella, Leonardo da Vinci, John Locke, Catherine History positive and negative effects on society. the great, Simón Bolívar, Nelson Mandela, ...
Survey of American History Name: TIAN Xiansheng Nationality
... China: Identity, Assimilation, and Resistance (2015), Discovering History in America (2008), Society, Modernity, and Cultural Identity in Taiwan: A Historical Revisit (2001), Asia’s Crisis and New Paradigm (2000), Taiwan in Historical Perspective: Post-War Economy, Politics, Culture, Education, and ...
... China: Identity, Assimilation, and Resistance (2015), Discovering History in America (2008), Society, Modernity, and Cultural Identity in Taiwan: A Historical Revisit (2001), Asia’s Crisis and New Paradigm (2000), Taiwan in Historical Perspective: Post-War Economy, Politics, Culture, Education, and ...
Chapter 11 China, Technology, and Change
... studying for the exams, and thousands of inexpensive books were required. Without printing, such a system would not have been possible. The development of this alternative to aristocratic rule was one of the most radical changes in world history. Since the examinations were ultimately open to 98 per ...
... studying for the exams, and thousands of inexpensive books were required. Without printing, such a system would not have been possible. The development of this alternative to aristocratic rule was one of the most radical changes in world history. Since the examinations were ultimately open to 98 per ...
History and Culture of China
... 3. rulers called emperors 4. between dynasties kingdoms and warlords fought for power ...
... 3. rulers called emperors 4. between dynasties kingdoms and warlords fought for power ...
Kenneth Pomeranz, The Great Divergence
... a source of land-intensive goods such as cotton and grain, while at the same time providing a market for its manufactured goods. In China, where coal reserves were not as readily available, and a policy of coercive colonization, which could provide it with free land, was absent, ecological constrain ...
... a source of land-intensive goods such as cotton and grain, while at the same time providing a market for its manufactured goods. In China, where coal reserves were not as readily available, and a policy of coercive colonization, which could provide it with free land, was absent, ecological constrain ...
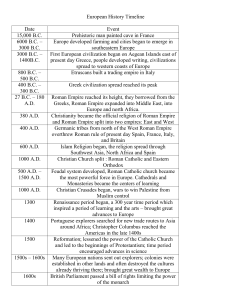
European History Timeline
... Portuguese explorers searched for new trade routes to Asia around Africa; Christopher Columbus reached the Americas in the late 1400s Reformation; lessened the power of the Catholic Church and led to the beginnings of Protestantism; time period encouraged advances in science Many European nations se ...
... Portuguese explorers searched for new trade routes to Asia around Africa; Christopher Columbus reached the Americas in the late 1400s Reformation; lessened the power of the Catholic Church and led to the beginnings of Protestantism; time period encouraged advances in science Many European nations se ...
Crash Course #32. World History
... x an abundance of rivers and canals; access to foreign resources; and x the accumulation of capital. B. The development of machines, including steam engines and the internal combustion engine, made it possible to exploit vast new resources of energy stored in fossil fuels, specifically coal and o ...
... x an abundance of rivers and canals; access to foreign resources; and x the accumulation of capital. B. The development of machines, including steam engines and the internal combustion engine, made it possible to exploit vast new resources of energy stored in fossil fuels, specifically coal and o ...
WHAP Review for Year
... political/social institutions in Eastern and Western Europe Analyze role and function of cities Islam and Christianity Analyze gender systems and changes (impact of Islam) Aztec and Incan empires European contacts and sub-Saharan contacts with Islamic world nomadic invasion and effects ...
... political/social institutions in Eastern and Western Europe Analyze role and function of cities Islam and Christianity Analyze gender systems and changes (impact of Islam) Aztec and Incan empires European contacts and sub-Saharan contacts with Islamic world nomadic invasion and effects ...
Review: AP World History Exam 1750
... – Need for raw materials (exploitations) – Coerced labor – Europe Dominating ...
... – Need for raw materials (exploitations) – Coerced labor – Europe Dominating ...
WH Fall Review
... populations. Cultural __________ happened since Africans brought their knowledge and customs to the New World. Triangular trade describes how slaves were brought here on the _________ Passage. ____ materials were brought to Europe to make things in factories. Then ____________ goods such as guns and ...
... populations. Cultural __________ happened since Africans brought their knowledge and customs to the New World. Triangular trade describes how slaves were brought here on the _________ Passage. ____ materials were brought to Europe to make things in factories. Then ____________ goods such as guns and ...
Unit III Test
... growth of cities during the late 1800s and early 1900s. 29. The Great Depression of the 1920s and 1930s never affected the United States since America had adopted isolationist foreign policies following World War I. 30. During the Medieval Age groups of craftspeople would often join together to form ...
... growth of cities during the late 1800s and early 1900s. 29. The Great Depression of the 1920s and 1930s never affected the United States since America had adopted isolationist foreign policies following World War I. 30. During the Medieval Age groups of craftspeople would often join together to form ...
Final Exam Study Guide: AP World History Fall-Winter 2013-14
... Types of commerce along the Silk Road Variance in Silk/Sea/Sand Road commerce Consequences of cross‐cultural interaction Chinese history during the era of regionalism following the Han Dynasty Golden Ages in China o Tang o Song Chinese tributary system Longevity of Byzantium Impact of th ...
... Types of commerce along the Silk Road Variance in Silk/Sea/Sand Road commerce Consequences of cross‐cultural interaction Chinese history during the era of regionalism following the Han Dynasty Golden Ages in China o Tang o Song Chinese tributary system Longevity of Byzantium Impact of th ...
Chapter 20 Reading Guide
... 2. Analyze the changes and continuities in Ming/Qing governments (1500-1800) in TWO of the following areas: Political, Social, Economic. Include reasons and global context. 3. Analyzes the changes and continuities in Tokugawa Japan (1500-1800) in TWO of the following areas: Political, Social, Econom ...
... 2. Analyze the changes and continuities in Ming/Qing governments (1500-1800) in TWO of the following areas: Political, Social, Economic. Include reasons and global context. 3. Analyzes the changes and continuities in Tokugawa Japan (1500-1800) in TWO of the following areas: Political, Social, Econom ...
Great Divergence
The Great Divergence, a term coined by Samuel Huntington (also known as the European miracle, a term coined by Eric Jones in 1981), referring to the process by which the Western world (i.e. Western Europe and the parts of the New World where its people became the dominant populations) overcame pre-modern growth constraints and emerged during the 19th century as the most powerful and wealthy world civilization of the time, eclipsing Qing China, Mughal India, Tokugawa Japan, and the Ottoman Empire.The process was accompanied and reinforced by the Age of Discovery and the subsequent rise of the colonial empires, the Age of Enlightenment, the Commercial Revolution, the Scientific Revolution and finally the Industrial Revolution. Scholars have proposed a wide variety of theories to explain why the Great Divergence happened, including lack of government intervention, geography, colonialism, and customary traditions.Before the Great Divergence, the core developed areas included Europe, East Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and the Middle East. In each of these core areas, differing political and cultural institutions allowed varying degrees of development. Western Europe, China, and Japan had developed to a relatively high level and began to face constraints on energy and land use, while India still possessed large amounts of unused resources. Shifts in government policy from mercantilism to laissez-faire liberalism aided Western development.Technological advances, such as railroads, steamboats, mining, and agriculture were embraced to a higher degree in the West than the East during the Great Divergence. Technology led to increased industrialization and economic complexity in the areas of agriculture, trade, fuel and resources, further separating the East and the West. Europe's use of coal as an energy substitute for wood in the mid-19th century gave Europe a major head start in modern energy production. Although China had used coal earlier during the Song and Ming, its use declined due to the shift of Chinese industry to the south, far from major deposits, during the destruction of Mongol and Jurchen invasions between 1100 and 1400. The West also had the advantage of larger quantities of raw materials and a substantial trading market. China and Asia did participate in trading, but colonization brought a distinct advantage to the West. ""In the twentieth century, the Great Divergence peaked before the First World War and continued until the early 1970s, then, after two decades of indeterminate fluctuations, in the late 1980s it was replaced by the Great Convergence as the majority of Third World countriesreached economic growth rates significantly higher than those in most First World countries"".