World History Connections to Today
... Portugal used firepower to win control of the rich Indian Ocean spice trade. In less than 50 years, the Portuguese had built a trading empire with military and merchant outposts rimming the southern seas. Despite their sea power, the Portuguese were not strong enough to conquer much territory on lan ...
... Portugal used firepower to win control of the rich Indian Ocean spice trade. In less than 50 years, the Portuguese had built a trading empire with military and merchant outposts rimming the southern seas. Despite their sea power, the Portuguese were not strong enough to conquer much territory on lan ...
World History v12 Course Syllabus
... interconnectedness of world events and eras. Grab your passport for the adventure of a lifetime. In Segment I, students will learn how the Roman Empire developed in two very distinct directions. Next, students will discover the great intellectual and cultural contributions of Islamic Empires. Journe ...
... interconnectedness of world events and eras. Grab your passport for the adventure of a lifetime. In Segment I, students will learn how the Roman Empire developed in two very distinct directions. Next, students will discover the great intellectual and cultural contributions of Islamic Empires. Journe ...
French and Industrial Rev Unit guide 2016
... increasing lethality to war, and ecological destruction on the down side. The Industrial Revolution occurred first in Britain. We will ask why. After getting going in Britain, Industrialization spread to other centers of Europe, America, and by the end of the 19th Century to Japan. The British that ...
... increasing lethality to war, and ecological destruction on the down side. The Industrial Revolution occurred first in Britain. We will ask why. After getting going in Britain, Industrialization spread to other centers of Europe, America, and by the end of the 19th Century to Japan. The British that ...
BELLWORK
... BELLWORK: BLOCK 2 1. Why was it important for explorers to find a trade route to Asia? Explain! 2. How did the Exploration Era impact civilizations in the Americas? 3. What is circumnavigation? 4. THINKER: What was the Line of Demarcation? How did this impact the balance of power in Europe? (page 21 ...
... BELLWORK: BLOCK 2 1. Why was it important for explorers to find a trade route to Asia? Explain! 2. How did the Exploration Era impact civilizations in the Americas? 3. What is circumnavigation? 4. THINKER: What was the Line of Demarcation? How did this impact the balance of power in Europe? (page 21 ...
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
... Palestine, which they called Canaan. Their lifestyle was based on grazing flocks and herds. Because of a drought, they moved to Egypt. In Egypt they became slaves until Moses led them out. They wandered in tlie desert for many years and finally returned to Palestine. They were organized in tribes. B ...
... Palestine, which they called Canaan. Their lifestyle was based on grazing flocks and herds. Because of a drought, they moved to Egypt. In Egypt they became slaves until Moses led them out. They wandered in tlie desert for many years and finally returned to Palestine. They were organized in tribes. B ...
World History II: Final Exam Study Guide Unit 8—Exploration
... 1. Describe the causes and effects of the Age of Exploration. 2. Describe the relationship between the Renaissance & the Age of Exploration. 3. In what ways did the Ming Dynasty prosper and what was their relationship with Europeans. 4. What were the main characteristics of the Commercial Revolution ...
... 1. Describe the causes and effects of the Age of Exploration. 2. Describe the relationship between the Renaissance & the Age of Exploration. 3. In what ways did the Ming Dynasty prosper and what was their relationship with Europeans. 4. What were the main characteristics of the Commercial Revolution ...
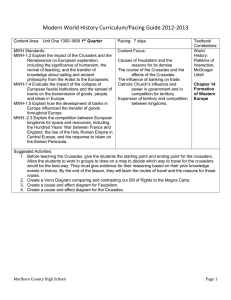
MCHS Modern World History Curriculum Pacing 1st Sem 2012
... renewal of international hostilities in the years leading to World War II. MWH-7.3 Describe major shifts in world geopolitics between 1900 and 1945, including the changing role of the United States in international affairs and the move from isolationism to an increased role as a world power. Suggest ...
... renewal of international hostilities in the years leading to World War II. MWH-7.3 Describe major shifts in world geopolitics between 1900 and 1945, including the changing role of the United States in international affairs and the move from isolationism to an increased role as a world power. Suggest ...
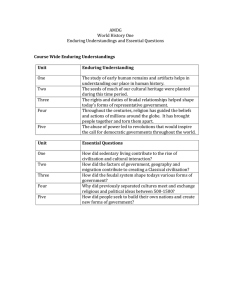
AMDG World History One Enduring Understandings and Essential
... How did sedentary living contribute to the rise of civilization and cultural interaction? How did the factors of government, geography and migration contribute to creating a Classical civilization? How did ...
... How did sedentary living contribute to the rise of civilization and cultural interaction? How did the factors of government, geography and migration contribute to creating a Classical civilization? How did ...
World_Hist_9_curriculum 6_1_09 - Pittsgrove Township School
... This course will focus on the time period between the late Middle Ages and the end of the 19th century. Students will investigate the emergence of the nations of Europe and the causes and results of major developments such as the Reformation, Renaissance, Enlightenment, and Industrial Revolution. Ad ...
... This course will focus on the time period between the late Middle Ages and the end of the 19th century. Students will investigate the emergence of the nations of Europe and the causes and results of major developments such as the Reformation, Renaissance, Enlightenment, and Industrial Revolution. Ad ...
HIST 107 World History Since 1500
... history since 1500. Using a global perspective, this course examines the intellectual, economic, political, social, and cultural forces that have linked and shaped the major world societies since 1500. Topics to be covered include: the development of global trade and new economic models; European ex ...
... history since 1500. Using a global perspective, this course examines the intellectual, economic, political, social, and cultural forces that have linked and shaped the major world societies since 1500. Topics to be covered include: the development of global trade and new economic models; European ex ...
File - Mr. Turpin`s Class Page
... from approximately 1450 to the present. The course has students investigate the content of European history for significant events, individuals, developments, and processes in four historical periods, and develop and use the same thinking skills and methods (analyzing primary and secondary sources, ...
... from approximately 1450 to the present. The course has students investigate the content of European history for significant events, individuals, developments, and processes in four historical periods, and develop and use the same thinking skills and methods (analyzing primary and secondary sources, ...
Topics List
... What was his view of "progress" within the context of Soviet history? 27) What is the 20th and 21st century history of “terrorism” and how has the term, its usage, and the responses to it by states changed over the century? 28) How can Protestant religious idealism be linked to apartheid in South Af ...
... What was his view of "progress" within the context of Soviet history? 27) What is the 20th and 21st century history of “terrorism” and how has the term, its usage, and the responses to it by states changed over the century? 28) How can Protestant religious idealism be linked to apartheid in South Af ...
Foundations: c. 8000 B.C.E.–600 C.E. 7 Weeks (19–20
... What are the issues involved in using “civilization” as an organizing principle in world history? What is the most common source of change: connection or diffusion versus independent invention? ...
... What are the issues involved in using “civilization” as an organizing principle in world history? What is the most common source of change: connection or diffusion versus independent invention? ...
CHY4U1 - Victoria Park Collegiate Institute
... including a huge increase in technological developments from approximately 1480--1715. Unit 2 Students explore fundamental changes in Western civilization and their impact on the non-Western world. The 18th Century is viewed here as an age of optimism and progress. The Reformation and Renaissance ga ...
... including a huge increase in technological developments from approximately 1480--1715. Unit 2 Students explore fundamental changes in Western civilization and their impact on the non-Western world. The 18th Century is viewed here as an age of optimism and progress. The Reformation and Renaissance ga ...
Advance Placement World History Objective: Your involvement in
... Latin American Independence Manifest Destiny Spanish American War Young Turks Abdul Hamid Boxer Rebellion Taiping Rebellion Matthew Perry Tokugawa Shogunate Meiji Restoration Emancipation of the Russian Serfs Bolsheviks Objectives Ø Compare European imperialism in the initial period after 1450 to t ...
... Latin American Independence Manifest Destiny Spanish American War Young Turks Abdul Hamid Boxer Rebellion Taiping Rebellion Matthew Perry Tokugawa Shogunate Meiji Restoration Emancipation of the Russian Serfs Bolsheviks Objectives Ø Compare European imperialism in the initial period after 1450 to t ...
View Backgrounder
... Holy Roman Empire in the East, sought to reduce Habsburg influence through a series of local wars.55 France’s involvement in the Thirty Years War can be interpreted as the result of their insecurity due to being surrounded on all sides by Habsburg territory. France consistently faced the possible th ...
... Holy Roman Empire in the East, sought to reduce Habsburg influence through a series of local wars.55 France’s involvement in the Thirty Years War can be interpreted as the result of their insecurity due to being surrounded on all sides by Habsburg territory. France consistently faced the possible th ...
Fall of Rome (Economic Crisis)
... 400 – Challenge to King Henry’s power came from where? Parliament ...
... 400 – Challenge to King Henry’s power came from where? Parliament ...
Putting American History into World History
... Known Vasco DaGama in India Asia and Europe—Why didn’t Asians Travel to Europe The Problem of Ignoring Geography The Problem of Ignoring Geography History works across space and well as over time Linear, Whiggish narratives ignore geography ...
... Known Vasco DaGama in India Asia and Europe—Why didn’t Asians Travel to Europe The Problem of Ignoring Geography The Problem of Ignoring Geography History works across space and well as over time Linear, Whiggish narratives ignore geography ...
AP EURO COS 2011-2012
... European history since 1450 is studied. The class introduces students to the social, political, religious, intellectual, technological, cultural, and economic developments that played a fundament role in the shaping of the western world we live in. The students will develop an understanding of the p ...
... European history since 1450 is studied. The class introduces students to the social, political, religious, intellectual, technological, cultural, and economic developments that played a fundament role in the shaping of the western world we live in. The students will develop an understanding of the p ...
topic - Perry Local Schools
... European history since 1450 is studied. The class introduces students to the social, political, religious, intellectual, technological, cultural, and economic developments that played a fundament role in the shaping of the western world we live in. The students will develop an understanding of the p ...
... European history since 1450 is studied. The class introduces students to the social, political, religious, intellectual, technological, cultural, and economic developments that played a fundament role in the shaping of the western world we live in. The students will develop an understanding of the p ...
Course Syllabus
... A survey of the political, economic, intellectual, cultural and religious development of the globe, from the Agricultural Revolution (c. 10,000 B.C.) to the sixteenth century A.D. Major topics will include, Ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt, the Hellenistic World, Ancient Indian Civilization, Imperial C ...
... A survey of the political, economic, intellectual, cultural and religious development of the globe, from the Agricultural Revolution (c. 10,000 B.C.) to the sixteenth century A.D. Major topics will include, Ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt, the Hellenistic World, Ancient Indian Civilization, Imperial C ...
Western Europe – Learning Outcomes Name World Geography
... Use the following list of statements to measure your understanding of Western Europe. If you answered “No” to any of the statements, explain “why not” after the statement(s). Ask your teacher to help clarify any that you are not confident with. World Geography Chapters 14-17 & Class Notes Yes ...
... Use the following list of statements to measure your understanding of Western Europe. If you answered “No” to any of the statements, explain “why not” after the statement(s). Ask your teacher to help clarify any that you are not confident with. World Geography Chapters 14-17 & Class Notes Yes ...
World History - Chicago Military Academy at Bronzeville
... Europe as the region slowly developed a new medieval culture? What political changes occurred during the rise of Europe and why are they important? What economic systems developed in Europe during the period 500-1300 and how are these economies different from the ancient economic systems? Why ...
... Europe as the region slowly developed a new medieval culture? What political changes occurred during the rise of Europe and why are they important? What economic systems developed in Europe during the period 500-1300 and how are these economies different from the ancient economic systems? Why ...
Early modern period

In history, the early modern period of modern history follows the late Middle Ages of the post-classical era. Although the chronological limits of the period are open to debate, the timeframe spans the period after the late portion of the post-classical age (c. 1500), known as the Middle Ages, through the beginning of the Age of Revolutions (c. 1800) and is variously demarcated by historians as beginning with the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, with the Renaissance period, and with the Age of Discovery (especially with the voyages of Christopher Columbus beginning in 1492, but also with the discovery of the sea route to the East in 1498), and ending around the French Revolution in 1789.Historians in recent decades have argued that from a worldwide standpoint, the most important feature of the early modern period was its globalizing character. The period witnessed the exploration and colonization of the Americas and the rise of sustained contacts between previously isolated parts of the globe. The historical powers became involved in global trade. This world trading of goods, plants, animals, and food crops saw exchange in the Old World and the New World. The Columbian exchange greatly affected the human environment.Economies and institutions began to appear, becoming more sophisticated and globally articulated over the course of the early modern period. This process began in the medieval North Italian city-states, particularly Genoa, Venice, and Milan. The early modern period also saw the rise and beginning of the dominance of the economic theory of mercantilism. It also saw the European colonization of the Americas, Asia, and Africa during the 15th to 19th centuries, which spread Christianity around the world.The early modern trends in various regions of the world represented a shift away from medieval modes of organization, politically and other-times economically. The period in Europe witnessed the decline of feudalism and includes the Reformation, the disastrous Thirty Years' War, the Commercial Revolution, the European colonization of the Americas, and the Golden Age of Piracy.Ruling China at the beginning of the early modern period, the Ming Dynasty was “one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history”. By the 16th century the Ming economy was stimulated by trade with the Portuguese, the Spanish, and the Dutch. The Azuchi-Momoyama period in Japan saw the Nanban trade after the arrival of the first European Portuguese.Other notable trends of the early modern period include the development of experimental science, the speedup of travel through improvements in mapping and ship design, increasingly rapid technological progress, secularized civic politics and the emergence of nation states. Historians typically date the end of the early modern period when the French Revolution of the 1790s began the ""modern"" period.