course syllabus
... Course Goals: By the end of this course, the student will: Identify the major civilizations, empires, leaders, and political ideals of the past and their continuing contributions to the world as it exists today. Students will focus on the different aspects of influence ranging from geographical, soc ...
... Course Goals: By the end of this course, the student will: Identify the major civilizations, empires, leaders, and political ideals of the past and their continuing contributions to the world as it exists today. Students will focus on the different aspects of influence ranging from geographical, soc ...
World History Pacing Guide, Themes of World History
... SSWH1 The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BCE to 500 BCE. a. Describe the development of Mesopotamian societies; include the religious, cultural, economic, and political facets of society, with attenti ...
... SSWH1 The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BCE to 500 BCE. a. Describe the development of Mesopotamian societies; include the religious, cultural, economic, and political facets of society, with attenti ...
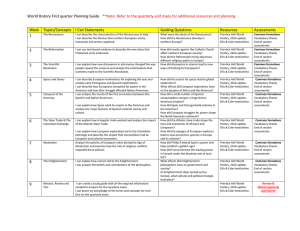
Major Turning Points in World History Before 1800
... animals, start of small villages along rivers ...
... animals, start of small villages along rivers ...
Major Turning Points in World History Before 1800
... animals, start of small villages along rivers ...
... animals, start of small villages along rivers ...
World History II - Pittsfield High School
... WHII.26 Describe the background, course, and consequences of the Holocaust, including its roots in the long tradition of Christian anti-Semitism, 19th century ideas about race and nation, and Nazi dehumanization of the Jews. (H) WHII.27 Explain the reasons for the dropping of atom bombs on Japan and ...
... WHII.26 Describe the background, course, and consequences of the Holocaust, including its roots in the long tradition of Christian anti-Semitism, 19th century ideas about race and nation, and Nazi dehumanization of the Jews. (H) WHII.27 Explain the reasons for the dropping of atom bombs on Japan and ...
ADM 1324 - History of Civilizations
... examine continuity and change over time. The large scope of this course will encourage more synthesis of ideas and integration of knowledge than thorough information on particular topics. The course is arranged so as to avoid two common pitfalls of teaching and learning about civilizations. First, i ...
... examine continuity and change over time. The large scope of this course will encourage more synthesis of ideas and integration of knowledge than thorough information on particular topics. The course is arranged so as to avoid two common pitfalls of teaching and learning about civilizations. First, i ...
Englewood Public School District United States History Grade 6
... Three large Islamic empires formed the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal. Muslim scholars and artists made important contributions to science, art, and literature. Geography, resources, culture, and trade influenced the growth of societies in West Africa. Rulers of Ghana built an empire by controlling th ...
... Three large Islamic empires formed the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal. Muslim scholars and artists made important contributions to science, art, and literature. Geography, resources, culture, and trade influenced the growth of societies in West Africa. Rulers of Ghana built an empire by controlling th ...
World History Connections to Today
... b) Germany quickly achieved unity. c) German nobles grew more independent. d) the French invaded and conquered Germany. ...
... b) Germany quickly achieved unity. c) German nobles grew more independent. d) the French invaded and conquered Germany. ...
Study guide due: Tuesday October 9th
... 4. Church & State: How have the church and state affected European class and government? Who was in charge of each? How did each affect the governments and politics of Europe as a whole and various countries—be specific with regard to England, France, Italy, Spain, Russia, and Germany (Holy Roman Em ...
... 4. Church & State: How have the church and state affected European class and government? Who was in charge of each? How did each affect the governments and politics of Europe as a whole and various countries—be specific with regard to England, France, Italy, Spain, Russia, and Germany (Holy Roman Em ...
World History Unit 5
... other classmates, students will again work individually to answer this question: Which artist/scientist, Michelangelo or da Vinci was more influential on today’s society? Why do you think so? Students will trace the changes and constants in Europe’s church from medieval times through the Renaissance ...
... other classmates, students will again work individually to answer this question: Which artist/scientist, Michelangelo or da Vinci was more influential on today’s society? Why do you think so? Students will trace the changes and constants in Europe’s church from medieval times through the Renaissance ...
Chapter 17 - Mr. Sadow`s History Class Website
... Even with these changes, British government remained an oligarchy, a government where a few powerful nobles and rich landowners controlled Parliament. Only male property owners could vote. A small middle class controlled the towns and cities. Most people were poor farmers who struggled to survive. ...
... Even with these changes, British government remained an oligarchy, a government where a few powerful nobles and rich landowners controlled Parliament. Only male property owners could vote. A small middle class controlled the towns and cities. Most people were poor farmers who struggled to survive. ...
ENGL 5720 Literature and Science: Enlightenment and Environment
... ENGL 5720 Literature and Science: Enlightenment and Environment in America The exploration and discovery of America has traditionally been viewed as a key point in the “Scientific Revolution”: the shift away from privileging classical philosophies to empirical information and evidence. For example, ...
... ENGL 5720 Literature and Science: Enlightenment and Environment in America The exploration and discovery of America has traditionally been viewed as a key point in the “Scientific Revolution”: the shift away from privileging classical philosophies to empirical information and evidence. For example, ...
Foundations: c. 8000 b.c.e.–600 c.e. 6 Weeks (19–20%) What
... Compare major religious and philosophical systems including some underlying similarities in cementing a social hierarchy, e.g., Hinduism contrasted with Confucianism Compare the role of women in different belief systems—Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, and Hinduism Understand how and why the co ...
... Compare major religious and philosophical systems including some underlying similarities in cementing a social hierarchy, e.g., Hinduism contrasted with Confucianism Compare the role of women in different belief systems—Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, and Hinduism Understand how and why the co ...
Study Sheet for the Final Exam
... Nomadic migrations and their impacts: Arabs, Turks, Vikings, Mongols Portuguese role in maritime trade vs. Chinese maritime voyages with Zheng He Aztec and Inca – process of empire building Feudalism in Japan and Europe – basic comparisons Various political structures of the time period: Western Eur ...
... Nomadic migrations and their impacts: Arabs, Turks, Vikings, Mongols Portuguese role in maritime trade vs. Chinese maritime voyages with Zheng He Aztec and Inca – process of empire building Feudalism in Japan and Europe – basic comparisons Various political structures of the time period: Western Eur ...
Period 4: Global Interactions, c. 1450 to c. 1750
... II. As new social and political elites changed, they also restructured new ethnic, racial, and gender hierarchies. A. Both imperial conquests and widening global economic opportunities contributed to the formation of new political and economic elites. Example of new elites: The Manchus in China, Cre ...
... II. As new social and political elites changed, they also restructured new ethnic, racial, and gender hierarchies. A. Both imperial conquests and widening global economic opportunities contributed to the formation of new political and economic elites. Example of new elites: The Manchus in China, Cre ...
World History First quarter Planning Guide **Note: Refer to the
... on the peoples of Africa and the Americas? How did a small number of Spanish conquistadors conquer a huge Native American empires? How did Spain and Portugal build colonies in the Americas? How did European struggles for power shape the North American continent? How did the Atlantic slave trade shap ...
... on the peoples of Africa and the Americas? How did a small number of Spanish conquistadors conquer a huge Native American empires? How did Spain and Portugal build colonies in the Americas? How did European struggles for power shape the North American continent? How did the Atlantic slave trade shap ...
Eastern Europe - Supplementary Notes
... Redistribution of the Eastern European Map ■ Consequences of WWII (1945) • The Second World War had important consequences on the political geography of Eastern Europe. • Poland was “moved” to the west to the gain of the Soviet Union and the loss of Germany. • Germany also lost Koenisburg (Eastern ...
... Redistribution of the Eastern European Map ■ Consequences of WWII (1945) • The Second World War had important consequences on the political geography of Eastern Europe. • Poland was “moved” to the west to the gain of the Soviet Union and the loss of Germany. • Germany also lost Koenisburg (Eastern ...
Timothy Brook, Vermeer`s Hat
... This short, evocative book uses a selection of paintings by Johannes Vermeer (1632-1675) as vantage points from whence to observe the emergence of the modern, interconnected world. Vermeer’s Hat owes its title to a prominent object in the painting entitled “Officer and Laughing Girl,” one of the man ...
... This short, evocative book uses a selection of paintings by Johannes Vermeer (1632-1675) as vantage points from whence to observe the emergence of the modern, interconnected world. Vermeer’s Hat owes its title to a prominent object in the painting entitled “Officer and Laughing Girl,” one of the man ...
The Indian Ocean Trade Network
... hold of trade routes in S.E Asia for a time. Angkor Wat and Borobudur. Malacca - Connected I.O.B with China Conquered by Portugal @ end of period in 1511. ...
... hold of trade routes in S.E Asia for a time. Angkor Wat and Borobudur. Malacca - Connected I.O.B with China Conquered by Portugal @ end of period in 1511. ...
ap world history syllabus - Gull Lake Community Schools
... to develop a framework for identifying significant aspects of a given culture: politics, military, economics, society, technology, philosophy, religion, and art to use such a framework to describe a culture as it exists within a specific area of geography and time, to understand how change may have ...
... to develop a framework for identifying significant aspects of a given culture: politics, military, economics, society, technology, philosophy, religion, and art to use such a framework to describe a culture as it exists within a specific area of geography and time, to understand how change may have ...
AP European History Syllabus - Anderson School District Five
... Disaster and the Black Plague (causes as well as economic, religious, cultural and social effects) The Hundred Years War – changes in politics, society and military strategy Problems of the Church – the Babylonian Captivity and the Great Schism Medieval Society (unrest and tension) Changes in Litera ...
... Disaster and the Black Plague (causes as well as economic, religious, cultural and social effects) The Hundred Years War – changes in politics, society and military strategy Problems of the Church – the Babylonian Captivity and the Great Schism Medieval Society (unrest and tension) Changes in Litera ...
***9th GRADE CUTOFF*** Topics for Questions 20-25
... In Eastern Europe (The Balkans) after World War I, the greatest obstacle to national unity in many nation-states was the 1. great ethnic diversity found in the region 2. economic dependence of Eastern Europe on Japan 3. acceptance of democratic traditions by most Eastern ...
... In Eastern Europe (The Balkans) after World War I, the greatest obstacle to national unity in many nation-states was the 1. great ethnic diversity found in the region 2. economic dependence of Eastern Europe on Japan 3. acceptance of democratic traditions by most Eastern ...
temple christian school
... Garden of Eden – Creation, Fall, Civilization Mesopotamia – Sumerians, Amorites Egypt – Old, Middle, New Kingdoms Canaan – Hittites, Phoenicians, Arameans, Hebrews Near Eastern Empires – Assyrians, Chaldeans, Persians Neolithic Agricultural Revolution – the beginnings of plant and animal ...
... Garden of Eden – Creation, Fall, Civilization Mesopotamia – Sumerians, Amorites Egypt – Old, Middle, New Kingdoms Canaan – Hittites, Phoenicians, Arameans, Hebrews Near Eastern Empires – Assyrians, Chaldeans, Persians Neolithic Agricultural Revolution – the beginnings of plant and animal ...
The Byzantine Empire
... By 395 AD, the Roman Empire was formally divided into two empires: East and West. With the invasion of Germanic forces from the north, the Western Roman Empire was conquered and further divided. This left the eastern part of the Roman empire to carry on the Greco-Roman tradition. ...
... By 395 AD, the Roman Empire was formally divided into two empires: East and West. With the invasion of Germanic forces from the north, the Western Roman Empire was conquered and further divided. This left the eastern part of the Roman empire to carry on the Greco-Roman tradition. ...
AP World History: Syllabus 2015-2016
... • Short Answer: The later Middle Ages was a period of great intellectual and artistic achievement marked by what is often called the renaissance. What was the renaissance, and what were some of its most important and lasting cultural and artistic achievements? • Discussion: Does the label “Renaissan ...
... • Short Answer: The later Middle Ages was a period of great intellectual and artistic achievement marked by what is often called the renaissance. What was the renaissance, and what were some of its most important and lasting cultural and artistic achievements? • Discussion: Does the label “Renaissan ...
Early modern period

In history, the early modern period of modern history follows the late Middle Ages of the post-classical era. Although the chronological limits of the period are open to debate, the timeframe spans the period after the late portion of the post-classical age (c. 1500), known as the Middle Ages, through the beginning of the Age of Revolutions (c. 1800) and is variously demarcated by historians as beginning with the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, with the Renaissance period, and with the Age of Discovery (especially with the voyages of Christopher Columbus beginning in 1492, but also with the discovery of the sea route to the East in 1498), and ending around the French Revolution in 1789.Historians in recent decades have argued that from a worldwide standpoint, the most important feature of the early modern period was its globalizing character. The period witnessed the exploration and colonization of the Americas and the rise of sustained contacts between previously isolated parts of the globe. The historical powers became involved in global trade. This world trading of goods, plants, animals, and food crops saw exchange in the Old World and the New World. The Columbian exchange greatly affected the human environment.Economies and institutions began to appear, becoming more sophisticated and globally articulated over the course of the early modern period. This process began in the medieval North Italian city-states, particularly Genoa, Venice, and Milan. The early modern period also saw the rise and beginning of the dominance of the economic theory of mercantilism. It also saw the European colonization of the Americas, Asia, and Africa during the 15th to 19th centuries, which spread Christianity around the world.The early modern trends in various regions of the world represented a shift away from medieval modes of organization, politically and other-times economically. The period in Europe witnessed the decline of feudalism and includes the Reformation, the disastrous Thirty Years' War, the Commercial Revolution, the European colonization of the Americas, and the Golden Age of Piracy.Ruling China at the beginning of the early modern period, the Ming Dynasty was “one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history”. By the 16th century the Ming economy was stimulated by trade with the Portuguese, the Spanish, and the Dutch. The Azuchi-Momoyama period in Japan saw the Nanban trade after the arrival of the first European Portuguese.Other notable trends of the early modern period include the development of experimental science, the speedup of travel through improvements in mapping and ship design, increasingly rapid technological progress, secularized civic politics and the emergence of nation states. Historians typically date the end of the early modern period when the French Revolution of the 1790s began the ""modern"" period.