- Experimental Neurobiology
... types, the location of cell body and axons, and internal neural circuits. Previous studies revealed that TCTP was expressed in the human nervous tissue [13]. However, the functional significance of TCTP in brain function has been speculated on the basis of information mostly from non-neuronal cells. ...
... types, the location of cell body and axons, and internal neural circuits. Previous studies revealed that TCTP was expressed in the human nervous tissue [13]. However, the functional significance of TCTP in brain function has been speculated on the basis of information mostly from non-neuronal cells. ...
Principles of Neural Science
... already seen how signals are propagated within a neuron, from its dendrites and cell body to its axonal terminal. Beginning with this chapter we consider the cellular mechanisms for signaling between neurons. The point at which one neuron communicates with another is called a synapse, and synaptic t ...
... already seen how signals are propagated within a neuron, from its dendrites and cell body to its axonal terminal. Beginning with this chapter we consider the cellular mechanisms for signaling between neurons. The point at which one neuron communicates with another is called a synapse, and synaptic t ...
Control of Muscular Contraction
... 3. Golgi Tendon Organs – Thin capsules of connective tissue which exist where muscle fibre and tendon meet. They cause a muscle to relax if high tensions within the muscle occur. ...
... 3. Golgi Tendon Organs – Thin capsules of connective tissue which exist where muscle fibre and tendon meet. They cause a muscle to relax if high tensions within the muscle occur. ...
biology lecture notes chapter 2
... Some neurotransmitters excite the next cell into firing and some inhibit the next cell from firing. Specific neurotransmitters “bind” with specific POSTSYNAPTIC RECEPTORS. 1. “Lock and Key” model 2. Neurotransmitter—receptor binding causes postsynaptic changes 3. ION CHANNEL: closely “tied” to a r ...
... Some neurotransmitters excite the next cell into firing and some inhibit the next cell from firing. Specific neurotransmitters “bind” with specific POSTSYNAPTIC RECEPTORS. 1. “Lock and Key” model 2. Neurotransmitter—receptor binding causes postsynaptic changes 3. ION CHANNEL: closely “tied” to a r ...
Nervous System - Seattle Central
... • Relay nuclei: – Reticular Formation: Share info between cerebrum & cerebellum ...
... • Relay nuclei: – Reticular Formation: Share info between cerebrum & cerebellum ...
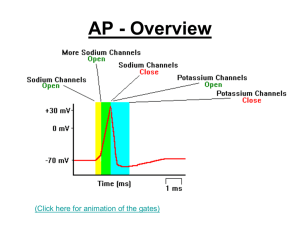
AP – All or nothing
... • There is a time after depolarisation where no new AP can start – called the refractory period. – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one ...
... • There is a time after depolarisation where no new AP can start – called the refractory period. – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... back toward -70 mV (a repolarization). Gradually, the ion concentrations go back to resting levels and the cell returns to -70 mV. ...
... back toward -70 mV (a repolarization). Gradually, the ion concentrations go back to resting levels and the cell returns to -70 mV. ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 13. Neuroglia outnumber neurons by about 10 to 1. In addition, neuroglia retain the ability to divide, unlike neurons. How do these two observations relate to the fact that most brain cancers begin in neuroglia? Cancers are cells that have lost the ability to regulate cell division. Cells have to d ...
... 13. Neuroglia outnumber neurons by about 10 to 1. In addition, neuroglia retain the ability to divide, unlike neurons. How do these two observations relate to the fact that most brain cancers begin in neuroglia? Cancers are cells that have lost the ability to regulate cell division. Cells have to d ...
Chapter 49 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... potential called a receptor potential. Specific receptor molecules of the membrane of a receptor cell open or close ion channels Amplification Stimulus energy that is too weak to be carried by the nervous system is strengthened or amplified. Amplification of the signal may occur in accessory structu ...
... potential called a receptor potential. Specific receptor molecules of the membrane of a receptor cell open or close ion channels Amplification Stimulus energy that is too weak to be carried by the nervous system is strengthened or amplified. Amplification of the signal may occur in accessory structu ...
CNS neurotransmitters
... Actions and Site of Actions Most of the serotonin in the brain is in the brainstem, specifically in the raphe nuclei; considerable amounts also are present in areas of the hypothalamus, the limbic system, and the pituitary gland. Current evidence indicates that serotonin is involved in the regula ...
... Actions and Site of Actions Most of the serotonin in the brain is in the brainstem, specifically in the raphe nuclei; considerable amounts also are present in areas of the hypothalamus, the limbic system, and the pituitary gland. Current evidence indicates that serotonin is involved in the regula ...
Nervous System Organization and Components
... Perikarya of most neurons are located in the CNS. The perikarya in the CNS are in clusters called nuclei form the gray matter of the spinal cord and brain. Perikarya outside, in the PNS, are grouped together in structures called ganglia. 2. Processes of the Neurons These are thin extensions of the c ...
... Perikarya of most neurons are located in the CNS. The perikarya in the CNS are in clusters called nuclei form the gray matter of the spinal cord and brain. Perikarya outside, in the PNS, are grouped together in structures called ganglia. 2. Processes of the Neurons These are thin extensions of the c ...
Physiology 2 - Sheet #6 - Dr.Loai Al-Zgoul - Done by: Yara
... exocytosis via synaptic vesicles which bind to their chemical receptors and transmits its effect on the postsynaptic neuron. Finally, the neurotransmitter is either reabsorbed by the presynaptic cell, and then repackaged for future release, or else it is broken down metabolically by enzymes. Synapse ...
... exocytosis via synaptic vesicles which bind to their chemical receptors and transmits its effect on the postsynaptic neuron. Finally, the neurotransmitter is either reabsorbed by the presynaptic cell, and then repackaged for future release, or else it is broken down metabolically by enzymes. Synapse ...
General Neurophysiology - Department of Physiology
... Receptors on the postsynaptic membrane • Excitatory receptors open Na+, Ca2+ channels membrane depolarization • Inhibitory receptors open K+, Cl- channels membrane hyperpolarization • EPSP – excitatory postsynaptic potential • IPSP – inhibitory postsynaptic potential ...
... Receptors on the postsynaptic membrane • Excitatory receptors open Na+, Ca2+ channels membrane depolarization • Inhibitory receptors open K+, Cl- channels membrane hyperpolarization • EPSP – excitatory postsynaptic potential • IPSP – inhibitory postsynaptic potential ...
Spinal nerves
... emerged that this is just one of many functions. It has been demonstrated that the Glia can send signals to each other and to the neurons, altering the neural transmission mechanisms. ...
... emerged that this is just one of many functions. It has been demonstrated that the Glia can send signals to each other and to the neurons, altering the neural transmission mechanisms. ...
Supplement to: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... mechanoreceptors) are not distant to the region of neurotransmitter release. At the vast majority of the remaining synaptic contacts, particularly in the mammalian nervous system, synaptic transmission is thought to occur through action potential-dependent triggered release. This action potential-de ...
... mechanoreceptors) are not distant to the region of neurotransmitter release. At the vast majority of the remaining synaptic contacts, particularly in the mammalian nervous system, synaptic transmission is thought to occur through action potential-dependent triggered release. This action potential-de ...
Frog Reflexes/synapses
... single synapses between sensory axons and motor neurons (a monosynaptic reflex). The required circuitry for this reflex is confined to the spinal cord, as shown in Figure 1. Sensory information also ascends to higher centers, but the brain is not necessary or required to perform the reflex. More com ...
... single synapses between sensory axons and motor neurons (a monosynaptic reflex). The required circuitry for this reflex is confined to the spinal cord, as shown in Figure 1. Sensory information also ascends to higher centers, but the brain is not necessary or required to perform the reflex. More com ...
Supplement: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... mechanoreceptors) are not distant to the region of neurotransmitter release. At the vast majority of the remaining synaptic contacts, particularly in the mammalian nervous system, synaptic transmission is thought to occur through action potential-dependent triggered release. This action potential-de ...
... mechanoreceptors) are not distant to the region of neurotransmitter release. At the vast majority of the remaining synaptic contacts, particularly in the mammalian nervous system, synaptic transmission is thought to occur through action potential-dependent triggered release. This action potential-de ...
ppt
... conduction because action potentials “jump” from one node of Ranvier to the next. Saltatory conduction is faster (120 m/s) than the conduction of nerve impulses in unmyelinated neurons (0.5 m/s). ...
... conduction because action potentials “jump” from one node of Ranvier to the next. Saltatory conduction is faster (120 m/s) than the conduction of nerve impulses in unmyelinated neurons (0.5 m/s). ...
Organization of the nervous system
... A Neuron is a very special cell: You have about 100 billion of them! •Cell body: Keeps the neuron alive and determines whether it will fire •Axon:Extending fiber that conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other cells. ...
... A Neuron is a very special cell: You have about 100 billion of them! •Cell body: Keeps the neuron alive and determines whether it will fire •Axon:Extending fiber that conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other cells. ...
Introduction to Neuroscience
... – convey sensory information into the brain – transmit commands from the brain to control organs and muscles, – thought, feeling, action – form complex circuits ...
... – convey sensory information into the brain – transmit commands from the brain to control organs and muscles, – thought, feeling, action – form complex circuits ...
B- Parietal
... What is the name of the fatty tissue that covers the axon to speed up the electric impulse message and hold it in? A- EIM layer B- Myelin C- Parietal D- None, the impulse is chemical in the axon ...
... What is the name of the fatty tissue that covers the axon to speed up the electric impulse message and hold it in? A- EIM layer B- Myelin C- Parietal D- None, the impulse is chemical in the axon ...
Nervous System - science
... peripheral nervous system? To connect the central nervous system, or brain and spinal cord, with all parts of the body ...
... peripheral nervous system? To connect the central nervous system, or brain and spinal cord, with all parts of the body ...
The Nervous System
... • groups of interneurons that make synaptic connections with each other • interneurons work together to perform a common function • each pool receives input from other neurons • each pool generates output to other neurons ...
... • groups of interneurons that make synaptic connections with each other • interneurons work together to perform a common function • each pool receives input from other neurons • each pool generates output to other neurons ...
Bio 211 Lecture 18
... • Begins at initial segment of axons (high density of voltageregulated Na+ channels) • all-or-none (think: finger on a gun’s trigger) • Does not weaken with distance ...
... • Begins at initial segment of axons (high density of voltageregulated Na+ channels) • all-or-none (think: finger on a gun’s trigger) • Does not weaken with distance ...