Lecture 11b Neurophysiology
... • The sum of the two gradients, chemical and electrical. This “overall” gradient is valid for an individual ion (e.g. “the electrochemical gradient for Na+” or “the electrochemical gradient for K+”) • The electrochemical gradient tells you which direction an ion will tend to move (into or out of a c ...
... • The sum of the two gradients, chemical and electrical. This “overall” gradient is valid for an individual ion (e.g. “the electrochemical gradient for Na+” or “the electrochemical gradient for K+”) • The electrochemical gradient tells you which direction an ion will tend to move (into or out of a c ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... 11. Describe the diversity of animal nervous systems and provide examples. Explain how the structure of the nervous system relates to the ways animals interact with their environment. 12. Describe the general structure of the brain, spinal cord, and associated nerves of vertebrates. Describe the for ...
... 11. Describe the diversity of animal nervous systems and provide examples. Explain how the structure of the nervous system relates to the ways animals interact with their environment. 12. Describe the general structure of the brain, spinal cord, and associated nerves of vertebrates. Describe the for ...
chapter 8 lecture ppt
... • Change resting membrane potential by activating gated ion channels • Local Current: movement of Na+ which causes inside of cell to be more positive (depolarize) ...
... • Change resting membrane potential by activating gated ion channels • Local Current: movement of Na+ which causes inside of cell to be more positive (depolarize) ...
Lecture 11b Neurophysiology
... • The sum of the two gradients, chemical and electrical. This “overall” gradient is valid for an individual ion (e.g. “the electrochemical gradient for Na+” or “the electrochemical gradient for K+”) • The electrochemical gradient tells you which direction an ion will tend to move (into or out of a c ...
... • The sum of the two gradients, chemical and electrical. This “overall” gradient is valid for an individual ion (e.g. “the electrochemical gradient for Na+” or “the electrochemical gradient for K+”) • The electrochemical gradient tells you which direction an ion will tend to move (into or out of a c ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... •ACh is NT for all preganglionic fibers of both sympathetic and _____________________ nervous systems. •Transmission at these synapses is termed cholinergic: •ACh is NT released by most postganglionic parasympathetic fibers at synapse with effector. ...
... •ACh is NT for all preganglionic fibers of both sympathetic and _____________________ nervous systems. •Transmission at these synapses is termed cholinergic: •ACh is NT released by most postganglionic parasympathetic fibers at synapse with effector. ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 1. Branching fibers extending out from the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
... 1. Branching fibers extending out from the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... • If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
... • If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
Simulating in vivo-like Synaptic Input Patterns in Multicompartmental
... (Edgerton and Reinhart 2003), and we concluded that in Purkinje neurons, SK channels are critical determinants of both the rate and regularity of spiking (Fig. 1). Our conclusions were well supported for Purkinje neurons in vitro; however, whether or not a blocker of SK channels would have similar e ...
... (Edgerton and Reinhart 2003), and we concluded that in Purkinje neurons, SK channels are critical determinants of both the rate and regularity of spiking (Fig. 1). Our conclusions were well supported for Purkinje neurons in vitro; however, whether or not a blocker of SK channels would have similar e ...
Unit II Practice Exam – Answer Key
... c. Of the variation in the trait within a group of people, 50 percent can be attributed to genes d. All of the above 56. Despite growing up in the same home environment, Karen and her brother John have personalities as different from each other as two people selected randomly from the population. Wh ...
... c. Of the variation in the trait within a group of people, 50 percent can be attributed to genes d. All of the above 56. Despite growing up in the same home environment, Karen and her brother John have personalities as different from each other as two people selected randomly from the population. Wh ...
OCR Document
... 10) Skeletal Muscle Contraction (p. 290 - 297) a) Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ, p. 290-292). Explain the following terms: i) motor neuron – ii) synapse – iii) neurotransmitters – iv) neuromuscular junction – v) motor end plate (list 3 special features) – vi) motor unit – vii) synaptic cleft – viii)sy ...
... 10) Skeletal Muscle Contraction (p. 290 - 297) a) Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ, p. 290-292). Explain the following terms: i) motor neuron – ii) synapse – iii) neurotransmitters – iv) neuromuscular junction – v) motor end plate (list 3 special features) – vi) motor unit – vii) synaptic cleft – viii)sy ...
Neuronal Regulation Implements Efficient Synaptic Pruning
... a near optimal strategy, maximizing memory capacity in the sparse connectivity levels observed in the brain. A fundamental requirement of central nervous system development is that the system should continuously function, while undergoing major structural and functional developmental changes. It has ...
... a near optimal strategy, maximizing memory capacity in the sparse connectivity levels observed in the brain. A fundamental requirement of central nervous system development is that the system should continuously function, while undergoing major structural and functional developmental changes. It has ...
Chapter 13
... Synaptic Plasticity: Long Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression • Long-Term Depression • Apparently, neural circuits that contain memories are established by strengthening some synapses and weakening others. • Dudek and Bear (1992) stimulated Schaffer collateral inputs to CA1 neurons in hippoc ...
... Synaptic Plasticity: Long Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression • Long-Term Depression • Apparently, neural circuits that contain memories are established by strengthening some synapses and weakening others. • Dudek and Bear (1992) stimulated Schaffer collateral inputs to CA1 neurons in hippoc ...
Know Your Neurons: How to Classify Different Types of Neurons in
... Besser named large, densely branching neurons "Purkinje cells" after their discoverer, Czech anatomist Jan Purkyně. Vladimir Alekseyevich Betz discovered the largest cells in the central nervous system, today known as Betz cells. Cajal tried out various names for different kinds of neurons, as well ...
... Besser named large, densely branching neurons "Purkinje cells" after their discoverer, Czech anatomist Jan Purkyně. Vladimir Alekseyevich Betz discovered the largest cells in the central nervous system, today known as Betz cells. Cajal tried out various names for different kinds of neurons, as well ...
Rexed`s Lamina
... Processing at the Perceptual Level Motor cortex Somatosensory cortex Thalamus ...
... Processing at the Perceptual Level Motor cortex Somatosensory cortex Thalamus ...
Slide 1
... Diverse molecular families control the growth and guidance of developing axons. A. A large family of classical cadherins promote cell and axonal adhesion, primarily through homophilic interactions between cadherin molecules on adjacent neurons. Adhesive interactions are mediated through interactions ...
... Diverse molecular families control the growth and guidance of developing axons. A. A large family of classical cadherins promote cell and axonal adhesion, primarily through homophilic interactions between cadherin molecules on adjacent neurons. Adhesive interactions are mediated through interactions ...
The Nervous System
... to Neuron • Virtually all nerve impulses must travel through many neurons before reaching their destinations: the brain, spinal cord, or effector. • However, the neurons don’t make a solid chain through the whole body. Instead, there are small fluid-filled spaces between the dendrites of one neuron ...
... to Neuron • Virtually all nerve impulses must travel through many neurons before reaching their destinations: the brain, spinal cord, or effector. • However, the neurons don’t make a solid chain through the whole body. Instead, there are small fluid-filled spaces between the dendrites of one neuron ...
IN SEARCH OF PRINCIPLES IN INTEGRATIVE BIOLOGY
... rocybernetics, and the rest. As zoologists we have much to contribute, much to learn, have a special interest, revolving about the and much to do, using our reservoir of forms of communication among nerve cells, animal types. Besides it's the best fun I including questions of coding. Call it the kno ...
... rocybernetics, and the rest. As zoologists we have much to contribute, much to learn, have a special interest, revolving about the and much to do, using our reservoir of forms of communication among nerve cells, animal types. Besides it's the best fun I including questions of coding. Call it the kno ...
Nervous System Review Power Point
... how does the action potential (or nerve impulse) get between the small space between the end of one nerve cell and the beginning of the next nerve cell? ...
... how does the action potential (or nerve impulse) get between the small space between the end of one nerve cell and the beginning of the next nerve cell? ...
Biological Impact
... Communication within neurons is electrical • Communication within neurons happens through the process of conduction • An electrical signal is sent down the length of the axon. This electrical signal is called an “action potential” • Some axons are myelinated (i.e., covered with a fatty tissue call ...
... Communication within neurons is electrical • Communication within neurons happens through the process of conduction • An electrical signal is sent down the length of the axon. This electrical signal is called an “action potential” • Some axons are myelinated (i.e., covered with a fatty tissue call ...
Glial cell - TheTruthAboutStuff.com
... Some glia function primarily as physical support for neurons. Others regulate the internal environment of the brain, especially the fluid surrounding neurons and their synapses, and provide nutrition to nerve cells. Glia have important developmental roles, guiding migration of neurons in early devel ...
... Some glia function primarily as physical support for neurons. Others regulate the internal environment of the brain, especially the fluid surrounding neurons and their synapses, and provide nutrition to nerve cells. Glia have important developmental roles, guiding migration of neurons in early devel ...
W7 Lecture
... scenario (a) generates a burst of action potentials as the muscle is lengthened; in scenario (b), the shortened spindle produces fewer action potentials from the spindle. ...
... scenario (a) generates a burst of action potentials as the muscle is lengthened; in scenario (b), the shortened spindle produces fewer action potentials from the spindle. ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
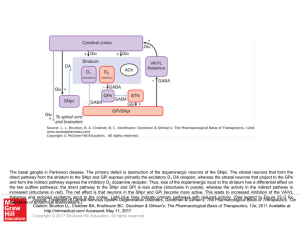
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
the electron microscopic localization of
... may be to define the pattern of possible synaptic transfer, since surfaces of adjoining axon branches are invariably closely applied to each other, unless they are separated by interpolated glial tendrils. Trujillo-Cen6z (1962) stressed that mere close apposition of axon surfaces is, however, of too ...
... may be to define the pattern of possible synaptic transfer, since surfaces of adjoining axon branches are invariably closely applied to each other, unless they are separated by interpolated glial tendrils. Trujillo-Cen6z (1962) stressed that mere close apposition of axon surfaces is, however, of too ...
Module overview
... stimulus causes receptor to change membrane potential (more later) ! leading to nerve impulse ...
... stimulus causes receptor to change membrane potential (more later) ! leading to nerve impulse ...
Lorem Ipsum - University of Western Australia
... While the somites are forming the neural tube closes The crest of the neural tube migrates off in to the body These cells form the dorsal root ganglia and contribute to many other tissues from the facial skeleton to the adrenals ...
... While the somites are forming the neural tube closes The crest of the neural tube migrates off in to the body These cells form the dorsal root ganglia and contribute to many other tissues from the facial skeleton to the adrenals ...