PDF
... (Stewart, 1978), at different stages of development. The neuron trios lie immediately beneath the limiting membrane on the dorsal surface of the nervous system. If an embryo is freed from yolk and pinned out with its dorsal side uppermost, the neurons are easy to identify with a compound microscope ...
... (Stewart, 1978), at different stages of development. The neuron trios lie immediately beneath the limiting membrane on the dorsal surface of the nervous system. If an embryo is freed from yolk and pinned out with its dorsal side uppermost, the neurons are easy to identify with a compound microscope ...
Nervous System - s3.amazonaws.com
... – Nerve impulse causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane and release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. – Neurotransmitters diffuse across to the postsynaptic membrane – Neurotransmitters bind with postsynaptic receptors in a lock-and-key fit. – Neurotransmitters can res ...
... – Nerve impulse causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane and release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. – Neurotransmitters diffuse across to the postsynaptic membrane – Neurotransmitters bind with postsynaptic receptors in a lock-and-key fit. – Neurotransmitters can res ...
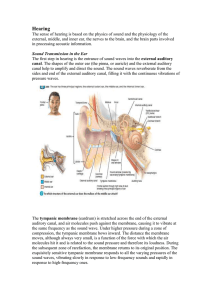
Ear
... The speed and magnitude of rotational head movements determine the direction in which the stereocilia are bent and the hair cells stimulated. Neurotransmitter is released from the hair cells at rest, and the release changes from this resting rate according to the direction in which the hairs are ben ...
... The speed and magnitude of rotational head movements determine the direction in which the stereocilia are bent and the hair cells stimulated. Neurotransmitter is released from the hair cells at rest, and the release changes from this resting rate according to the direction in which the hairs are ben ...
The Role of sema2a in the Neural Compensatory
... The Role of sema2a in the Neural Compensatory Growth of Gryllus bimaculatus Ana García-Moreno, Class of 2017 Nervous system growth and development is an intricate process and not yet fully understood. Because many factors that influence the growth of neurons are well conserved across a broad range o ...
... The Role of sema2a in the Neural Compensatory Growth of Gryllus bimaculatus Ana García-Moreno, Class of 2017 Nervous system growth and development is an intricate process and not yet fully understood. Because many factors that influence the growth of neurons are well conserved across a broad range o ...
Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... PKA recruits the mitogen-activated kinase (MAPK) and together they translocate to the nucleus (long-term pathway), where PKA phosphorylates the cAMP-response element binding (CREB) protein. One gene activated by CREB encodes a ubiquitin hydrolase, which in turn cause persistent activity of PKA. The ...
... PKA recruits the mitogen-activated kinase (MAPK) and together they translocate to the nucleus (long-term pathway), where PKA phosphorylates the cAMP-response element binding (CREB) protein. One gene activated by CREB encodes a ubiquitin hydrolase, which in turn cause persistent activity of PKA. The ...
Drug induced coma & Party drugs by Dr ML Tse
... • Typically pull out the ET tube and fully awake in 6 hrs • Flumazenil not consistent • Withdrawal? ...
... • Typically pull out the ET tube and fully awake in 6 hrs • Flumazenil not consistent • Withdrawal? ...
Introduction to Psychology - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse If the message is for arm movem ...
... chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse If the message is for arm movem ...
Additional Science B6 Module – What You Should Know
... I can recall that mammals have a complex brain of billions of neurons that allows learning by experience, including social behaviour I understand that during development the interaction between mammals and their environment results in neuron pathways forming in the brain I understand that learning i ...
... I can recall that mammals have a complex brain of billions of neurons that allows learning by experience, including social behaviour I understand that during development the interaction between mammals and their environment results in neuron pathways forming in the brain I understand that learning i ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... vesicles, and other parts of the cell membranes to and from the soma down the axon to the synapses and back up to the soma. Microtubules provide the structural basis for transport, axoplasmic flow. This mechanism of transport is not diffusion but rather retrograde axonal transport associated with th ...
... vesicles, and other parts of the cell membranes to and from the soma down the axon to the synapses and back up to the soma. Microtubules provide the structural basis for transport, axoplasmic flow. This mechanism of transport is not diffusion but rather retrograde axonal transport associated with th ...
Muscles
... Sensation is modulated from CNS by fusimotor system: - static gamma system for changes in length - dynamic gamma system for changes in speed. ...
... Sensation is modulated from CNS by fusimotor system: - static gamma system for changes in length - dynamic gamma system for changes in speed. ...
The Nervous System
... information about the threat passes the information directly to the motor neuron. ...
... information about the threat passes the information directly to the motor neuron. ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM REVIEW
... substances that are released by a transmitting neuron at the synapse and alters the activity of the receiving neuron. ...
... substances that are released by a transmitting neuron at the synapse and alters the activity of the receiving neuron. ...
Chapter 18: Senses - Johnston Community College
... The retina has three layers of neurons: rods and cones are near the retina, bipolar cells are in the middle, and the innermost layer contains ganglion cells that carry impulses to the optic nerve. The rod and cones synapse with the bipolar cells, which in turn synapse with ganglion cells that initia ...
... The retina has three layers of neurons: rods and cones are near the retina, bipolar cells are in the middle, and the innermost layer contains ganglion cells that carry impulses to the optic nerve. The rod and cones synapse with the bipolar cells, which in turn synapse with ganglion cells that initia ...
Review
... Role of acetylcholine, synaptic cleft, interstitial fluid Depolarization vs. repolarization Role of calcium during muscle contraction Role of acetylcholinesterase Energy sources for muscle contraction o Role of creatine phosphate o Purpose of glycolysis o Aerobic system Fate of pyruvic acid Prod ...
... Role of acetylcholine, synaptic cleft, interstitial fluid Depolarization vs. repolarization Role of calcium during muscle contraction Role of acetylcholinesterase Energy sources for muscle contraction o Role of creatine phosphate o Purpose of glycolysis o Aerobic system Fate of pyruvic acid Prod ...
Review
... What is saltatory propagation? Know the steps to transmission of an impulse from one neuron to another at a chemical synapse. What is the synaptic delay? What are the 3 main types of neurotransmitters? What are the 3 types of chemical synapses? How do they differ? What is the advantage of Excitator ...
... What is saltatory propagation? Know the steps to transmission of an impulse from one neuron to another at a chemical synapse. What is the synaptic delay? What are the 3 main types of neurotransmitters? What are the 3 types of chemical synapses? How do they differ? What is the advantage of Excitator ...
FinalStudyGuide
... What is a threshold stimulus? What is the all or none response? Does it occur with muscular contraction? With nerve impulses? Which muscle type causes peristalsis? Nervous How do motor neurons interact with the motor end plate of a muscle to initiate a muscle contraction? What are the func ...
... What is a threshold stimulus? What is the all or none response? Does it occur with muscular contraction? With nerve impulses? Which muscle type causes peristalsis? Nervous How do motor neurons interact with the motor end plate of a muscle to initiate a muscle contraction? What are the func ...
Resting Membrane Potential
... resting to firing? • The resting membrane potential of a neuron is -70 mV • In order for a neuron to fire a signal, the membrane potential must reach a certain threshold, around -55 mV. • This happens when another neuron stimulates it and allows a few Na+ channels to open and a few Na+ ions enter th ...
... resting to firing? • The resting membrane potential of a neuron is -70 mV • In order for a neuron to fire a signal, the membrane potential must reach a certain threshold, around -55 mV. • This happens when another neuron stimulates it and allows a few Na+ channels to open and a few Na+ ions enter th ...
Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity Orchestrates the Response of Pyramidal
... provide a feature upon which the relative timing of activity between cell classes can be examined. The neurons examined in Silberberg et al. (2004) were classified by the dynamics of the synapse received from the bursting layer V pyramidal population and comprised: layer V pyramidal cells receiving ...
... provide a feature upon which the relative timing of activity between cell classes can be examined. The neurons examined in Silberberg et al. (2004) were classified by the dynamics of the synapse received from the bursting layer V pyramidal population and comprised: layer V pyramidal cells receiving ...
Visual Field - Warren`s Science Page
... Brain projects pain back to missing part, past the healed region ...
... Brain projects pain back to missing part, past the healed region ...
Physiologic basis of EMG/NCS or what constitutes a waveform?
... • Predominant influx is Na, K blocked by electrochem gradient, Ca concentration gradient not that large • Na influx locally depolarizes muscle membrane= endplate potential reversal which is not propagated = EPP – Single packet of ACH from vesicle gives MEPP ...
... • Predominant influx is Na, K blocked by electrochem gradient, Ca concentration gradient not that large • Na influx locally depolarizes muscle membrane= endplate potential reversal which is not propagated = EPP – Single packet of ACH from vesicle gives MEPP ...
Tutorial 4: Shapes and Roles of Glial Cells Figure 4: Shapes and
... 3. calcium signaling (the use of slowly changing gradients of calcium as a means of cross-glial communication). Receptor sites for neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA have been identified on both astrocytes and Schwann cells. The functional significance of these receptors remains a mystery, ...
... 3. calcium signaling (the use of slowly changing gradients of calcium as a means of cross-glial communication). Receptor sites for neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA have been identified on both astrocytes and Schwann cells. The functional significance of these receptors remains a mystery, ...
Physiological Effects of a Warm Up on Skeletal Muscle
... Greater strength of contraction due to improved elasticity of muscle fibres. Faster speed of contraction due to an increased speed of nerve transmission to the muscle fibres. Faster speed of contraction and relaxation of the muscle fibres due to a higher muscle temperature. Increased speed o ...
... Greater strength of contraction due to improved elasticity of muscle fibres. Faster speed of contraction due to an increased speed of nerve transmission to the muscle fibres. Faster speed of contraction and relaxation of the muscle fibres due to a higher muscle temperature. Increased speed o ...