Cells, Tissues
... -The part of the cell body where axon exits the soma is called the axon hillock and it lacks Nissl bodies. -Axon can be myelinated or unmyelinated. -Myelin sheath in CNS is provided by the oligodendrocyte , while in PNS by the Schwann cell -Axon diameter & myelin thickness determines the speed of ne ...
... -The part of the cell body where axon exits the soma is called the axon hillock and it lacks Nissl bodies. -Axon can be myelinated or unmyelinated. -Myelin sheath in CNS is provided by the oligodendrocyte , while in PNS by the Schwann cell -Axon diameter & myelin thickness determines the speed of ne ...
Auditory Aerobics
... ►The memory contains the meaning we most often associate with that set of sounds. ...
... ►The memory contains the meaning we most often associate with that set of sounds. ...
Airgas template
... Rationale: The tics and hyperkinesia that often accompany Tourette syndrome are typical of basal ganglia dysfunction (the function of the basal ganglia is movement control). ...
... Rationale: The tics and hyperkinesia that often accompany Tourette syndrome are typical of basal ganglia dysfunction (the function of the basal ganglia is movement control). ...
Animal Physiology, Chapter 10
... – Innervate smooth and cardiac muscle and glands – Make adjustments to ensure optimal support ...
... – Innervate smooth and cardiac muscle and glands – Make adjustments to ensure optimal support ...
Nervous System
... – Sensory neurons in your hand react to the pain by sending nerve impulses (signal) to the spinal cord – Interneurons relay the message to the motor neurons – Impulse travels to your arm which you lift quickly! ...
... – Sensory neurons in your hand react to the pain by sending nerve impulses (signal) to the spinal cord – Interneurons relay the message to the motor neurons – Impulse travels to your arm which you lift quickly! ...
Neurons and Circuits - UT Computer Science
... Now that we’ve covered neuron basics, its time to put them to use and give our cells something to do. One central neuronal job is that of coding the external world into symbols, so we’ll start here and see how that could be done. The model will be quite compelling so we’ll have to resist the urge to ...
... Now that we’ve covered neuron basics, its time to put them to use and give our cells something to do. One central neuronal job is that of coding the external world into symbols, so we’ll start here and see how that could be done. The model will be quite compelling so we’ll have to resist the urge to ...
R24Summary Statement - University of Illinois Archives
... requisite expertise. Although the phase I proposal itself does not present particularly novel ideas, there are compelling scientific reasons to encourage a "dendrite biology consortium" at this time. Dendrites are the major sites of input to individual neurons. The background material presented lays ...
... requisite expertise. Although the phase I proposal itself does not present particularly novel ideas, there are compelling scientific reasons to encourage a "dendrite biology consortium" at this time. Dendrites are the major sites of input to individual neurons. The background material presented lays ...
Drugs Acting on the Central and Peripheral Nervous
... Neurotransmitters stimulate postsynaptic cells either by exciting or by inhibiting them. The reaction that occurs when a neurotransmitter stimulates a receptor site depends on the specific neurotransmitter that it releases and the receptor site it activates. A nerve may produce only one type of neur ...
... Neurotransmitters stimulate postsynaptic cells either by exciting or by inhibiting them. The reaction that occurs when a neurotransmitter stimulates a receptor site depends on the specific neurotransmitter that it releases and the receptor site it activates. A nerve may produce only one type of neur ...
video slide - ScienceToGo
... Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) are hyperpolarizations that move the membrane potential farther from threshold After release, the neurotransmitter ...
... Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) are hyperpolarizations that move the membrane potential farther from threshold After release, the neurotransmitter ...
sms5
... that can develop increases linearly as length decreases because of the progressive increase in the number of binding sites for myosin heads. Around the muscle's optimal length (L0, between lengths b-c) the level of force remains constant because the central portion of the thick filaments is devoid o ...
... that can develop increases linearly as length decreases because of the progressive increase in the number of binding sites for myosin heads. Around the muscle's optimal length (L0, between lengths b-c) the level of force remains constant because the central portion of the thick filaments is devoid o ...
CNS: Brain and Spinal Cord
... apertures and median aperture in the 4th ventricle. It enters the subarachnoid space and circulates. At arachnoid villi, it enters dural sinuses and drains into the jugular veins. D. The blood brain barrier- capillaries that enter the neural part of the brain (as opposed to the choroid plexuses of t ...
... apertures and median aperture in the 4th ventricle. It enters the subarachnoid space and circulates. At arachnoid villi, it enters dural sinuses and drains into the jugular veins. D. The blood brain barrier- capillaries that enter the neural part of the brain (as opposed to the choroid plexuses of t ...
Neuroanatomy Part 2
... Photopigments: are made of two parts, a glycoprotein and a derivative of Vitamin A known as retinal (the light absorbing portion of all photopigments). Nyctalopia: night blindness (inability to see well in low light) causes by a deficiency in Vitamin A. Light immediately begins to degrade the photo ...
... Photopigments: are made of two parts, a glycoprotein and a derivative of Vitamin A known as retinal (the light absorbing portion of all photopigments). Nyctalopia: night blindness (inability to see well in low light) causes by a deficiency in Vitamin A. Light immediately begins to degrade the photo ...
full text pdf
... more Why do neurons build synapses or neurites just to degrade them again later on during development? For one, neurons (many billions in the mammalian brain) must make many highly specific synaptic connections (often thousands for a mammalian neuron in the brain). Accordingly, many specificity path ...
... more Why do neurons build synapses or neurites just to degrade them again later on during development? For one, neurons (many billions in the mammalian brain) must make many highly specific synaptic connections (often thousands for a mammalian neuron in the brain). Accordingly, many specificity path ...
A1990DM11000002
... late 1970s, one of the relatively few general princi- useful or not. ples that was emerging in integrative neurobiology The criteria we proposed (necessity and suffiwas that complex information may be encoded at ciency) had been long used in other contexts, but the level of individual neurons. On th ...
... late 1970s, one of the relatively few general princi- useful or not. ples that was emerging in integrative neurobiology The criteria we proposed (necessity and suffiwas that complex information may be encoded at ciency) had been long used in other contexts, but the level of individual neurons. On th ...
Sensory Systems
... • receptors synapse with –bipolar cells –horizontal cells • bipolar cells synapse with –ganglion cells –amacrine cells • ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve ...
... • receptors synapse with –bipolar cells –horizontal cells • bipolar cells synapse with –ganglion cells –amacrine cells • ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve ...
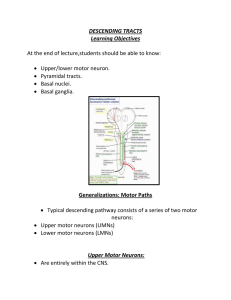
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Includes descending motor tracts that do not pass through medullary pyramids or corticobulbar tracts. Includes: Rubrospinal tracts Vestibulospinal tracts Reticulospinal tracts Rubrospinal Tract Begins in red nucleus. Decussates in midbrain. Descends in lateral funiculus (column). ...
... Includes descending motor tracts that do not pass through medullary pyramids or corticobulbar tracts. Includes: Rubrospinal tracts Vestibulospinal tracts Reticulospinal tracts Rubrospinal Tract Begins in red nucleus. Decussates in midbrain. Descends in lateral funiculus (column). ...
B. Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction
... to discuss the following: A. Excitation-Contraction Coupling a. Describe how wave of depolarization from the sarcolemma initiates muscle contraction. b. Describe relationship of DHP receptor and the Ryanodine receptor. c. Role of intracellular stores of Ca++ in SR/terminal cisternae B. Sliding Filam ...
... to discuss the following: A. Excitation-Contraction Coupling a. Describe how wave of depolarization from the sarcolemma initiates muscle contraction. b. Describe relationship of DHP receptor and the Ryanodine receptor. c. Role of intracellular stores of Ca++ in SR/terminal cisternae B. Sliding Filam ...
Conference Outline 1
... The cerebral hemispheres can be divided into four lobes (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). Some scientists though have added a fifth lobe that is the grouping of several medial structures that are involved in memory and emotions. This lobe is called the Limbic lobe. Carpenter in addition r ...
... The cerebral hemispheres can be divided into four lobes (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). Some scientists though have added a fifth lobe that is the grouping of several medial structures that are involved in memory and emotions. This lobe is called the Limbic lobe. Carpenter in addition r ...
item[`#file`]
... Tonically active in extensor muscles of the trunk and legs (antigravity muscles), but may be elicited from any skeletal muscle Receptor: the Muscle Spindle Small connective tissue capsule containing intrafusal muscle fibers Capsule is attached to connective tissue septae that are continuous with the ...
... Tonically active in extensor muscles of the trunk and legs (antigravity muscles), but may be elicited from any skeletal muscle Receptor: the Muscle Spindle Small connective tissue capsule containing intrafusal muscle fibers Capsule is attached to connective tissue septae that are continuous with the ...
Abstract - Iraqi Cultural Attache
... In the small intestine, dietary carbohydrate is hydrolysed ultimately by intestinal brush border membrane disaccharidases, sucrase, maltase and lactase, to glucose, galactose and fructose. Glucose and galactose are transported across the brush border membrane of enterocytes by the Na+/glucose cotran ...
... In the small intestine, dietary carbohydrate is hydrolysed ultimately by intestinal brush border membrane disaccharidases, sucrase, maltase and lactase, to glucose, galactose and fructose. Glucose and galactose are transported across the brush border membrane of enterocytes by the Na+/glucose cotran ...
Is a short duration interrupted direct currents with a pulse duration
... 2. Stimulation of the motor nerves: It occurs if the current is of a sufficient intensity, causing contraction of the muscles supplied by the nerve distal to the point of stimulus. A suitable faradic current applied to the muscle elicits a contraction of the muscle itself and may also spread to the ...
... 2. Stimulation of the motor nerves: It occurs if the current is of a sufficient intensity, causing contraction of the muscles supplied by the nerve distal to the point of stimulus. A suitable faradic current applied to the muscle elicits a contraction of the muscle itself and may also spread to the ...
Local Copy - Synthetic Neurobiology Group
... technique, the researchers discovered distinct pattern of dopamine cell activation that seemed to be able to disrupt alcohol-drinking behavior. Scientists at the California Institute of Technology found a neural circuit that connects the lateral septum (LS) with other brain structures in a manner th ...
... technique, the researchers discovered distinct pattern of dopamine cell activation that seemed to be able to disrupt alcohol-drinking behavior. Scientists at the California Institute of Technology found a neural circuit that connects the lateral septum (LS) with other brain structures in a manner th ...
Serotonin, also known as 5-HT (5
... stimulated neuron, and recognized by an adjacent neuron, causing it to fire and so on. In this way, the nerve impulse is propagated throughout the nervous system. Note that after a nerve fires at a synapse, the neurotransmitter must be taken back up by the original neuron. This so-called “re-uptake” ...
... stimulated neuron, and recognized by an adjacent neuron, causing it to fire and so on. In this way, the nerve impulse is propagated throughout the nervous system. Note that after a nerve fires at a synapse, the neurotransmitter must be taken back up by the original neuron. This so-called “re-uptake” ...


















![item[`#file`]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015956740_1-3f6ed5c9f9134adf505bbe94b8655b27-300x300.png)