File
... Where are they located? The receptor cells are ________________ neurons with hairlike ________________ covering the dendrites. These project into the ____________________cavity. Nerve pathways: When olfactory receptors are stimulated, their fibers synapse with neurons in the ______________ _______ l ...
... Where are they located? The receptor cells are ________________ neurons with hairlike ________________ covering the dendrites. These project into the ____________________cavity. Nerve pathways: When olfactory receptors are stimulated, their fibers synapse with neurons in the ______________ _______ l ...
word - My eCoach
... amount of insulin in the blood. d. The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon at the same time and the same amount. ...
... amount of insulin in the blood. d. The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon at the same time and the same amount. ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... oxygen to neurons. They regulate chemical composition of extracellular space by removing excess ions, notably potassium. They regulate neurotransmission by recycling neurotransmitters released during synaptic transmission and by surrounding synapses and preventing diffusion of neurotransmitters. ...
... oxygen to neurons. They regulate chemical composition of extracellular space by removing excess ions, notably potassium. They regulate neurotransmission by recycling neurotransmitters released during synaptic transmission and by surrounding synapses and preventing diffusion of neurotransmitters. ...
important ascending tracts
... three neurons to convey sensory information from the periphery to conscious level at the cerebral cortex. Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion have axons that lead from the skin into the dorsal spinal cord where they ascend or descend one or two vertebral levels via Lissauer's tract an ...
... three neurons to convey sensory information from the periphery to conscious level at the cerebral cortex. Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion have axons that lead from the skin into the dorsal spinal cord where they ascend or descend one or two vertebral levels via Lissauer's tract an ...
Diseases of peripheral nervous system. Myasthenic, myopatic
... After immobilization – rapid development of fixed skeletal deformities and progressive skoliosis Patients die mostly before or around 20th year due to respiratory isufficiency (90%) Heart is often affected but asympomatic – cardial insufficiency is the cause of death only in 10% children ...
... After immobilization – rapid development of fixed skeletal deformities and progressive skoliosis Patients die mostly before or around 20th year due to respiratory isufficiency (90%) Heart is often affected but asympomatic – cardial insufficiency is the cause of death only in 10% children ...
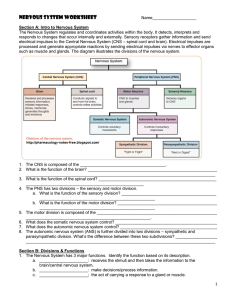
Nervous System Worksheet - Jackson County Faculty Sites!
... Neurotransmitters are chemicals which carrier the impulse from one neuron to the next neuron. These chemicals allow the transmission of signals across the synapse. Some neurotransmitters are excitatory or inhibitory. Here are a few examples of common neurotransmitters. Acetylcholine – stimulates m ...
... Neurotransmitters are chemicals which carrier the impulse from one neuron to the next neuron. These chemicals allow the transmission of signals across the synapse. Some neurotransmitters are excitatory or inhibitory. Here are a few examples of common neurotransmitters. Acetylcholine – stimulates m ...
Organization of Somatic Nervous system, Spinal nerve and Reflex arc
... 3, Axon hillock;Origin 4. No rough ER--No protein synthesis 5. Axon terminal 6. Chromatophilic-----no Nissl body ...
... 3, Axon hillock;Origin 4. No rough ER--No protein synthesis 5. Axon terminal 6. Chromatophilic-----no Nissl body ...
Lecture 5 Sensory and Motor Systems
... • One alpha motor neuron and all of its associated muscle fibers are collectively known as a motor unit. • Motor units can only fire as a unit, fiber contraction is all or nothing. • Strength of muscle contraction is controlled by the recruitment of varying numbers of motor units. ...
... • One alpha motor neuron and all of its associated muscle fibers are collectively known as a motor unit. • Motor units can only fire as a unit, fiber contraction is all or nothing. • Strength of muscle contraction is controlled by the recruitment of varying numbers of motor units. ...
22. ANS.Neuroscience
... autonomic, somatic and endocrine systems to preserve body homeostasis • Reflex activity is mediated by spinal cord and brain stem (medullary centers). ...
... autonomic, somatic and endocrine systems to preserve body homeostasis • Reflex activity is mediated by spinal cord and brain stem (medullary centers). ...
Nervous System Spinal Cord and Nerves Spinal Cord
... In a resting neuron the potential between the two sides of the cell membrane is called the “resting potential”. ...
... In a resting neuron the potential between the two sides of the cell membrane is called the “resting potential”. ...
news release - Institut de recherches cliniques de Montréal
... that form our nerves) in order to connect to their correct targets. Growing axons are, in turn, guided towards their targets by signals transmitted from molecules called “ligands,” which bind to special “receptors” on the surface of the axon. “What is really surprising is that our nerves develop usi ...
... that form our nerves) in order to connect to their correct targets. Growing axons are, in turn, guided towards their targets by signals transmitted from molecules called “ligands,” which bind to special “receptors” on the surface of the axon. “What is really surprising is that our nerves develop usi ...
ANS.Neuroscience.09
... autonomic, somatic and endocrine systems to preserve body homeostasis • Reflex activity is mediated by spinal cord and brain stem (medullary centers). ...
... autonomic, somatic and endocrine systems to preserve body homeostasis • Reflex activity is mediated by spinal cord and brain stem (medullary centers). ...
Exam I
... 20) If neuron X is excitatory and fires multiple action potentials to bring neuron W to threshold… A) spatial summation is occurring. B) temporal summation is occurring. C) inhibition shunting is occurring. D) All of the above are true. E) None of the above is true. 21) Based only on the location of ...
... 20) If neuron X is excitatory and fires multiple action potentials to bring neuron W to threshold… A) spatial summation is occurring. B) temporal summation is occurring. C) inhibition shunting is occurring. D) All of the above are true. E) None of the above is true. 21) Based only on the location of ...
Unit 08 Notes
... 1. Muscle contractions begin at the neuromuscular junction. 2. The axon of a motor neuron is attached to the motor end plate of a muscle fiber’s sarcolemma. 3. To create a muscle contraction, acetylcholine is released from the motor neuron axon. Acetylcholine will trigger a muscle impulse. 4. The m ...
... 1. Muscle contractions begin at the neuromuscular junction. 2. The axon of a motor neuron is attached to the motor end plate of a muscle fiber’s sarcolemma. 3. To create a muscle contraction, acetylcholine is released from the motor neuron axon. Acetylcholine will trigger a muscle impulse. 4. The m ...
GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE
... Clinical features • Isolated lesions of the glossopharyngeal nerve are rare. It is more common to see combined lesions of the IX and X • Patients with IX and X nerve lesions present with symptoms of hoarseness, dysphagia, and dyspnea. ...
... Clinical features • Isolated lesions of the glossopharyngeal nerve are rare. It is more common to see combined lesions of the IX and X • Patients with IX and X nerve lesions present with symptoms of hoarseness, dysphagia, and dyspnea. ...
DESCENDING TRACTS - University of Kansas
... Corticospinal Tract Lesions Reduced muscle tone Clumsiness Weakness Not complete paralysis Note: complete paralysis results if both pyramidal and extrapyramidal systems are involved (as is often the case). ...
... Corticospinal Tract Lesions Reduced muscle tone Clumsiness Weakness Not complete paralysis Note: complete paralysis results if both pyramidal and extrapyramidal systems are involved (as is often the case). ...
Taste and Smell
... fluid • The fluid may be saliva, mucous, or blood plasma • Rely on receptors that interact with specific molecules to generate an action potential • Receptors are integrated with two or more tissue types making them fit the definition of “organ” ...
... fluid • The fluid may be saliva, mucous, or blood plasma • Rely on receptors that interact with specific molecules to generate an action potential • Receptors are integrated with two or more tissue types making them fit the definition of “organ” ...
chapt10answers
... Do they adapt easily? no _visceral____ pain receptors are the only receptors in the organs that produce sensations. __referred____ pain occurs because of the common nerve pathways leading from skin and internal organs. An example would be a heart attack being felt as pain in the arm or as heartburn. ...
... Do they adapt easily? no _visceral____ pain receptors are the only receptors in the organs that produce sensations. __referred____ pain occurs because of the common nerve pathways leading from skin and internal organs. An example would be a heart attack being felt as pain in the arm or as heartburn. ...
Neuro_quiz3
... 23. Anterolateral horn = where neurons give rise to fibres that lead into the ________ nervous system, which controls many ________ ________. 24. What groups of vertebrae are concerned with #23? 25. Each spinal nerve connects with the spinal cord by way of 2 ________. 26. T/F Posterior roots are mad ...
... 23. Anterolateral horn = where neurons give rise to fibres that lead into the ________ nervous system, which controls many ________ ________. 24. What groups of vertebrae are concerned with #23? 25. Each spinal nerve connects with the spinal cord by way of 2 ________. 26. T/F Posterior roots are mad ...
Ch. 7 - The Nervous System
... (2) Axons - conduct impulses away from the cell body (a) Axons end in axonal terminals I. Axonal terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters II. Axonal terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap III. Synaptic cleft - gap between adjacent neurons IV. Synapse - junction between nerves ...
... (2) Axons - conduct impulses away from the cell body (a) Axons end in axonal terminals I. Axonal terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters II. Axonal terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap III. Synaptic cleft - gap between adjacent neurons IV. Synapse - junction between nerves ...
Copy of the full paper
... from studies of small circuits and their plasticity that generalizes to larger and more complex circuits in higher animals and humans? (1) Alterations in circuit function are often achieved by modifications of both intrinsic and synaptic properties. For example, in the pyloric rhythm of the lobster ...
... from studies of small circuits and their plasticity that generalizes to larger and more complex circuits in higher animals and humans? (1) Alterations in circuit function are often achieved by modifications of both intrinsic and synaptic properties. For example, in the pyloric rhythm of the lobster ...
Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment
... b. depolarization at the adjacent node of Ranvier. c. repolarization at the adjacent region of the membrane. d. depolarization at the adjacent region of the membrane. ____ 28. Multiple sclerosis is a disorder characterized by the breakdown of the myelin sheath around axons in the central nervous sys ...
... b. depolarization at the adjacent node of Ranvier. c. repolarization at the adjacent region of the membrane. d. depolarization at the adjacent region of the membrane. ____ 28. Multiple sclerosis is a disorder characterized by the breakdown of the myelin sheath around axons in the central nervous sys ...
Chapter 10 Somatic and Special Senses
... These include the senses of smell, taste, hearing, static equilibrium, dynamic equilibrium, and sight. Smell = Olfaction: Olfactory organs: what type of receptor are the olfactory receptors? Where are they located? The receptor cells are ________________ neurons with hair-like ________________ cover ...
... These include the senses of smell, taste, hearing, static equilibrium, dynamic equilibrium, and sight. Smell = Olfaction: Olfactory organs: what type of receptor are the olfactory receptors? Where are they located? The receptor cells are ________________ neurons with hair-like ________________ cover ...
Symposium Poster - uospur
... control, so we are using optogenetics to investigate this process. Using optogenetics, we can precisely control the timing and amplitude of activity in the glomeruli, in which OSNs form synapses with neurons of the olfactory bulb. Thus, we can ask whether mice can perceive bilateral differences in t ...
... control, so we are using optogenetics to investigate this process. Using optogenetics, we can precisely control the timing and amplitude of activity in the glomeruli, in which OSNs form synapses with neurons of the olfactory bulb. Thus, we can ask whether mice can perceive bilateral differences in t ...