![0pt20pt [1.44]Spike Train Correlations Induced [1ex] [1.44]by](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014522750_1-d16804f4edee9aca177facbeaf42eec6-300x300.png)
0pt20pt [1.44]Spike Train Correlations Induced [1ex] [1.44]by
... lly imaged plane (coloured according to their orientation preference, c, Three-dimensional rendering of the arbors and cell bodies of functionally recordings were carried out. (C) Connectivity diagram of neurons in D. (D) as in Fig. 1b), and the dendrites and cell bodies of all their characterized n ...
... lly imaged plane (coloured according to their orientation preference, c, Three-dimensional rendering of the arbors and cell bodies of functionally recordings were carried out. (C) Connectivity diagram of neurons in D. (D) as in Fig. 1b), and the dendrites and cell bodies of all their characterized n ...
SPINAL CORD II
... slow C type fibres. • Posterior root ganglion → Tip of posterior grey column → Poteriolateral tract of Lissauer → Synapse in posterior column → second order neuron axon cross obliquely to opposite side in ant: commissure ascend as lateral spinocerebellar tract → In medulla joined by ant: spinothalam ...
... slow C type fibres. • Posterior root ganglion → Tip of posterior grey column → Poteriolateral tract of Lissauer → Synapse in posterior column → second order neuron axon cross obliquely to opposite side in ant: commissure ascend as lateral spinocerebellar tract → In medulla joined by ant: spinothalam ...
SKZ Hx Ebefrenia Catatonia Demenza paranoide Demenza precox
... Thus, neurons in dlPFC can represent visual space in the absence of sensory stimulation Goldman Rakic, 1996 → behavioural inhibition and cognitive control depend on these ...
... Thus, neurons in dlPFC can represent visual space in the absence of sensory stimulation Goldman Rakic, 1996 → behavioural inhibition and cognitive control depend on these ...
O-Nervous System I
... Gray Matter – mostly nerve cell bodies. White Matter – mostly myelinated axons. Nerve fiber – a single axon of a neuron. Nerve – a bundle of axons in the PNS. Tract – a bundle of axons ins the CNS. Ganglion – a cluster of nerve cell bodies in PNS. Nucleus – gray matter in CNS with common function. ...
... Gray Matter – mostly nerve cell bodies. White Matter – mostly myelinated axons. Nerve fiber – a single axon of a neuron. Nerve – a bundle of axons in the PNS. Tract – a bundle of axons ins the CNS. Ganglion – a cluster of nerve cell bodies in PNS. Nucleus – gray matter in CNS with common function. ...
Multiple Choice - 32 points total In each of the questions, select the
... E) More than one of the above 7) _____ E_____Which of the following statements about the left ventricle is/are true? A) The left ventricle is more muscular than the right ventricle. B) The blood in the left ventricle has more oxygen than the blood in the right ventricle. C) The valves regulating the ...
... E) More than one of the above 7) _____ E_____Which of the following statements about the left ventricle is/are true? A) The left ventricle is more muscular than the right ventricle. B) The blood in the left ventricle has more oxygen than the blood in the right ventricle. C) The valves regulating the ...
Stochastic Model of Central Synapses: Slow Diffusion of Transmitter
... shown to agree well with experiments. Average open probabilities are computed from a novel kinetic model and are shown to agree with averages over many Monte Carlo runs. Our results suggest that post-synaptic currents are only weakly potentiated by clustering of post-synaptic receptors, but increase ...
... shown to agree well with experiments. Average open probabilities are computed from a novel kinetic model and are shown to agree with averages over many Monte Carlo runs. Our results suggest that post-synaptic currents are only weakly potentiated by clustering of post-synaptic receptors, but increase ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 25.1 Drawing of the auditory periphery
... superior olivary complex; SS, suprasylvian sulcus; VNLL, ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus. From Kiang and Peake (1988). FIGURE 25.17 Schematic of the main anatomical cell types of the cochlear nucleus and their corresponding poststimulus time (PST) histograms. (Left) An auditory nerve fiber ...
... superior olivary complex; SS, suprasylvian sulcus; VNLL, ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus. From Kiang and Peake (1988). FIGURE 25.17 Schematic of the main anatomical cell types of the cochlear nucleus and their corresponding poststimulus time (PST) histograms. (Left) An auditory nerve fiber ...
chapter_1
... The neuron activity is an all-or-nothing process, ie., the activation of the neuron is binary. A certain fixed number of synapses (>1) must be excited within a period of latent addition for a neuron to be excited. The only significant delay within the nervous system is synaptic delay. The activity o ...
... The neuron activity is an all-or-nothing process, ie., the activation of the neuron is binary. A certain fixed number of synapses (>1) must be excited within a period of latent addition for a neuron to be excited. The only significant delay within the nervous system is synaptic delay. The activity o ...
Ascending Tracts - Bell`s Palsy
... The axon crosses obliquely to the opposite side in the anterior grey and white commissures within several spinal segments. It ascends in the contralateral white column as the anterior spinothalamic tract (ASTT). As the ASTT ascends through the spinal cord new fibers are added to the anteromedial asp ...
... The axon crosses obliquely to the opposite side in the anterior grey and white commissures within several spinal segments. It ascends in the contralateral white column as the anterior spinothalamic tract (ASTT). As the ASTT ascends through the spinal cord new fibers are added to the anteromedial asp ...
Quick Quiz One
... Name _____________________________________________________________ Chapter 2 - Quick Quiz 2 1. The term neurotransmitter refers to __________ a) a chemical found in the synaptic vesicles that is released into the synapse. b) any one of a number of chemical compounds that increase the activity of the ...
... Name _____________________________________________________________ Chapter 2 - Quick Quiz 2 1. The term neurotransmitter refers to __________ a) a chemical found in the synaptic vesicles that is released into the synapse. b) any one of a number of chemical compounds that increase the activity of the ...
Quiz Answers
... sensory nerves, the ability of the neurons to transmit sensory information will be inhibited. This loss of sensory information would be experienced as a “numbness” in areas exposed to the toxin. 15. Paralysis is a term used to describe the loss of function of muscle. If tetrodotoxin ’s effect is on ...
... sensory nerves, the ability of the neurons to transmit sensory information will be inhibited. This loss of sensory information would be experienced as a “numbness” in areas exposed to the toxin. 15. Paralysis is a term used to describe the loss of function of muscle. If tetrodotoxin ’s effect is on ...
Synaptic receptors, neurotransmitters and brain modulators
... ionotropic receptors that form ion channels in cells' plasma membranes. they may be activated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh), but also by nicotine. Their action is inhibited by curare ...
... ionotropic receptors that form ion channels in cells' plasma membranes. they may be activated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh), but also by nicotine. Their action is inhibited by curare ...
Spinal cord- 2 - Weebly
... In the somatic nervous system (SNS), an upper motor neuron in the CNS controls a lower-motor neuron in the brain stem or spinal cord. The axon of the lower-motor neuron has direct control over skeletal muscle fibers. Stimulation of the lower- motor neuron always has an excitatory effect on the skele ...
... In the somatic nervous system (SNS), an upper motor neuron in the CNS controls a lower-motor neuron in the brain stem or spinal cord. The axon of the lower-motor neuron has direct control over skeletal muscle fibers. Stimulation of the lower- motor neuron always has an excitatory effect on the skele ...
Linear associator
... Introduction: The learning rules discussed in the previous tutorial can be applied to a number of models of human memory. In this tutorial, you will explore the properties of one of the more basic memory models, the linear associator. In the linear associator, two layers of neurons (layers “f “and “ ...
... Introduction: The learning rules discussed in the previous tutorial can be applied to a number of models of human memory. In this tutorial, you will explore the properties of one of the more basic memory models, the linear associator. In the linear associator, two layers of neurons (layers “f “and “ ...
The effect of neural synchronization on information transmission
... 20% of the neurons in the receiver layer. We assumed that the stimulus was a sequence of drifting gratings with random orientations. In response to stimuli, the network displayed transiently synchronized responses. Because similarly tuned LNP neurons projected to different subsets of neurons, the pa ...
... 20% of the neurons in the receiver layer. We assumed that the stimulus was a sequence of drifting gratings with random orientations. In response to stimuli, the network displayed transiently synchronized responses. Because similarly tuned LNP neurons projected to different subsets of neurons, the pa ...
Neuro 04 Brainstem Student
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
Excitatory amino acid receptors
... – mGluR 1-8 •Group I = mGluR 1&5 linked to PLC •Group II = mGluR 2&3 linked to adenylate cyclase •Group III = mGluR 4&6-8 linked to adenylate cyclase ...
... – mGluR 1-8 •Group I = mGluR 1&5 linked to PLC •Group II = mGluR 2&3 linked to adenylate cyclase •Group III = mGluR 4&6-8 linked to adenylate cyclase ...
The Nervous System
... synapse in the thalamus Impulses of similar function are sorted out, edited, and relayed as a group All inputs ascending to the cerebral cortex pass through the thalamus Plays a key role in mediating sensation, motor activities, cortical arousal, learning, and memory ...
... synapse in the thalamus Impulses of similar function are sorted out, edited, and relayed as a group All inputs ascending to the cerebral cortex pass through the thalamus Plays a key role in mediating sensation, motor activities, cortical arousal, learning, and memory ...
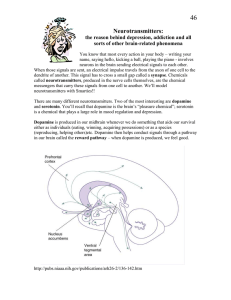
Neurotransmitters:
... name, saying hello, kicking a ball, playing the piano - involves neurons in the brain sending electrical signals to each other. When those signals are sent, an electrical impulse travels from the axon of one cell to the dendrite of another. This signal has to cross a small gap called a synapse. Chem ...
... name, saying hello, kicking a ball, playing the piano - involves neurons in the brain sending electrical signals to each other. When those signals are sent, an electrical impulse travels from the axon of one cell to the dendrite of another. This signal has to cross a small gap called a synapse. Chem ...
Abstract
... cortico-striatal boundary at E15. The axons then turn dorsally into the intermediate zone of the cerebral cortex, where they interact with cells of the cortical subplate before extending collateral branches to reach their final target in layer IV of the cerebral cortex [1]. The cellular and molecula ...
... cortico-striatal boundary at E15. The axons then turn dorsally into the intermediate zone of the cerebral cortex, where they interact with cells of the cortical subplate before extending collateral branches to reach their final target in layer IV of the cerebral cortex [1]. The cellular and molecula ...
amy-2a-2016-cryders-rmp-and-generation-of-action
... the diameter of the axon increases, the action potential travels faster because the internal resistance of flow of charge decreases. And the myelinated axons produce an AP by saltatory conduction. This is where the AP jumps from node to node, called the Nodes of Ranvier. ...
... the diameter of the axon increases, the action potential travels faster because the internal resistance of flow of charge decreases. And the myelinated axons produce an AP by saltatory conduction. This is where the AP jumps from node to node, called the Nodes of Ranvier. ...
Investigating the Effect of Knockout APP and Increased Calcium
... Perez M, Cuadros R, Benitez M, Jimenez J (2004). Interaction of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid β peptide fragment 25–35 with tau protein, and with a tau peptide containing the microtubule binding domain. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 6:461-467. (http://content.iospress.com/download/journal-ofalzheimer ...
... Perez M, Cuadros R, Benitez M, Jimenez J (2004). Interaction of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid β peptide fragment 25–35 with tau protein, and with a tau peptide containing the microtubule binding domain. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 6:461-467. (http://content.iospress.com/download/journal-ofalzheimer ...