neuro 04 brainstem student
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
Unit 2 Notes
... Chemical substances that mimic or enhance the effects of a neurotransmitter on the receptor sites of the next cell Increases or decreases the activity of that cell, depending on the effect of the original neurotransmitter (excitatory ...
... Chemical substances that mimic or enhance the effects of a neurotransmitter on the receptor sites of the next cell Increases or decreases the activity of that cell, depending on the effect of the original neurotransmitter (excitatory ...
File
... Both left and right tracts are needed to innervate both the left and right sides of the body. Pathways are composed of a series of two or three neurons that work together. ...
... Both left and right tracts are needed to innervate both the left and right sides of the body. Pathways are composed of a series of two or three neurons that work together. ...
Intro to the Biological Perspective
... sclerosis. This disease destroys the myelin sheaths of many neurons leaving them unable to operate at normal efficiency. As a result, individuals with multiple sclerosis have severe difficulties controlling their muscles and suffer serious vision problems. ...
... sclerosis. This disease destroys the myelin sheaths of many neurons leaving them unable to operate at normal efficiency. As a result, individuals with multiple sclerosis have severe difficulties controlling their muscles and suffer serious vision problems. ...
Intro to the Biological Perspective
... sclerosis. This disease destroys the myelin sheaths of many neurons leaving them unable to operate at normal efficiency. As a result, individuals with multiple sclerosis have severe difficulties controlling their muscles and suffer serious vision problems. ...
... sclerosis. This disease destroys the myelin sheaths of many neurons leaving them unable to operate at normal efficiency. As a result, individuals with multiple sclerosis have severe difficulties controlling their muscles and suffer serious vision problems. ...
PowerPoint Template
... A reduced number of discharging synaptic terminals in a motor endplate can result from a branch failure within the terminal arborization of the axon , as outlined previously. To a certain extent, this can be handled by the safety factory. The safety factor for type Ⅱ muscle fibers has been reporte ...
... A reduced number of discharging synaptic terminals in a motor endplate can result from a branch failure within the terminal arborization of the axon , as outlined previously. To a certain extent, this can be handled by the safety factory. The safety factor for type Ⅱ muscle fibers has been reporte ...
Note - Reza Shadmehr
... Slide 3. The exact content of the myosin molecule determines the functional characteristics of the extrafusal muscle fiber. In adults, we see three varieties of the myosin molecule. These isoforms are designated as type I, IIa, and IIx. Type I fibers are known as slow fibers, while type II are fast ...
... Slide 3. The exact content of the myosin molecule determines the functional characteristics of the extrafusal muscle fiber. In adults, we see three varieties of the myosin molecule. These isoforms are designated as type I, IIa, and IIx. Type I fibers are known as slow fibers, while type II are fast ...
Neurons and Glial Cells
... The nervous system is made up of neurons and glia. Neurons are specialized cells that are capable of sending electrical as well as chemical signals. Most neurons contain dendrites, which receive these signals, and axons that send signals to other neurons or tissues. multipolar, and pseudounipolar ne ...
... The nervous system is made up of neurons and glia. Neurons are specialized cells that are capable of sending electrical as well as chemical signals. Most neurons contain dendrites, which receive these signals, and axons that send signals to other neurons or tissues. multipolar, and pseudounipolar ne ...
FlyEM`s formal project plan
... three months and only stop when the sample imaging has been completed. This required addressing a variety of interrupt issues: ion source reheat, utility failure (water, power, air, and temperature fluctuation), and microscope failure (focus, electrical, software, vacuum). With improvements and back ...
... three months and only stop when the sample imaging has been completed. This required addressing a variety of interrupt issues: ion source reheat, utility failure (water, power, air, and temperature fluctuation), and microscope failure (focus, electrical, software, vacuum). With improvements and back ...
Slide ()
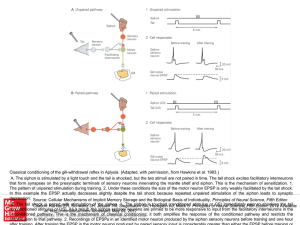
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
PowerPoint
... Discover significant patterns or features in the input data Discovery is done without a teacher Synaptic weights are changed according to local rules The changes affect a neuron’s immediate environment until a final configuration develops ...
... Discover significant patterns or features in the input data Discovery is done without a teacher Synaptic weights are changed according to local rules The changes affect a neuron’s immediate environment until a final configuration develops ...
The Nervous System - Florida International University
... Enhances the ability to perform several tasks at once ...
... Enhances the ability to perform several tasks at once ...
Lecture-29-2012-Bi
... b. Plasma membrane binding only? Possible with impermeant derivatives c. ER binding only? More challenging, especially for antagonists. 3. Better measurements of pathway-specific gene activation (RNA-Seq) 4. Analyze newly synthesized proteins ...
... b. Plasma membrane binding only? Possible with impermeant derivatives c. ER binding only? More challenging, especially for antagonists. 3. Better measurements of pathway-specific gene activation (RNA-Seq) 4. Analyze newly synthesized proteins ...
Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Changes that occur early in LTP are thought to tag activated synapses, allowing them to capture newly synthesized plasticity-related products (PRPs), which include scaffolding and cytoskeletal proteins. These PRPs are required to consolidate early LTP into late LTP; without them, synaptic strength d ...
... Changes that occur early in LTP are thought to tag activated synapses, allowing them to capture newly synthesized plasticity-related products (PRPs), which include scaffolding and cytoskeletal proteins. These PRPs are required to consolidate early LTP into late LTP; without them, synaptic strength d ...
Psychology Lecture 02 - Biological Basis
... ◦ Macula: A small patch of hair cells on both the saccule & utricle. Contains around 50 stereocilia & a single motile kinocilium. ◦ Otolithic Membrane: Thick, gelatin-like layer of glycoproteins weighted down by otoliths (calcium crystals). ◦ Shifting the head causes changes in these structures that ...
... ◦ Macula: A small patch of hair cells on both the saccule & utricle. Contains around 50 stereocilia & a single motile kinocilium. ◦ Otolithic Membrane: Thick, gelatin-like layer of glycoproteins weighted down by otoliths (calcium crystals). ◦ Shifting the head causes changes in these structures that ...
Biology 325 Fall 2004 - CSB | SJU Employees Personal Web Sites
... - supporting cells form bulk of taste buds; insulate receptor cells. - gustatory cells are the receptor cells. - both of the above have microvilli (gustatory hairs) that project from the tips and extend through taste pore to surface epithelium where they are bathed by saliva; gustatory hairs are the ...
... - supporting cells form bulk of taste buds; insulate receptor cells. - gustatory cells are the receptor cells. - both of the above have microvilli (gustatory hairs) that project from the tips and extend through taste pore to surface epithelium where they are bathed by saliva; gustatory hairs are the ...
Figure 8.12
... Air-filled cavity within the temporal bone Only involved in the sense of hearing Two tubes are associated with the inner ear › The opening from the auditory canal is covered by the tympanic membrane › The auditory tube connecting the middle ear with the throat Allows for equalizing pressure during ...
... Air-filled cavity within the temporal bone Only involved in the sense of hearing Two tubes are associated with the inner ear › The opening from the auditory canal is covered by the tympanic membrane › The auditory tube connecting the middle ear with the throat Allows for equalizing pressure during ...
Lecture 2: Structure and function of the NS
... neurons, as described in Chapters 7 and 8. The pink segments covering the axon represent the myelin sheath that coats many axons (see Figs. 1-24 and 1-30), and the gap in the axon represents a missing extent that might be as long as a meter in the longest axons. ...
... neurons, as described in Chapters 7 and 8. The pink segments covering the axon represent the myelin sheath that coats many axons (see Figs. 1-24 and 1-30), and the gap in the axon represents a missing extent that might be as long as a meter in the longest axons. ...
29.2 Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... make it effective in carrying out the functions of the nervous system? Neurons have long extensions called axons, which allow messages to be carried long distances without having to pass the signal to another cell. ...
... make it effective in carrying out the functions of the nervous system? Neurons have long extensions called axons, which allow messages to be carried long distances without having to pass the signal to another cell. ...
Document
... Processing a the perceptual level • When information gets to the brain it needs to decode it: • By the frequency of APs sent by one or more neurons (how loud you shout!) • By the number of neurons sending information from a narrow or broad area of the body (how many people are shouting) ...
... Processing a the perceptual level • When information gets to the brain it needs to decode it: • By the frequency of APs sent by one or more neurons (how loud you shout!) • By the number of neurons sending information from a narrow or broad area of the body (how many people are shouting) ...
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
... • Thoracolumbar division- Preganglionic neurons originate from the thoracic and lumbar levels of the spinal cord (T1-L2). • Sympathetic ganglia: Sympathetic trunk (vertebral chain) ganglia. Prevertebral (collateral) ganglia: celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric, aorticorenal and renal. ...
... • Thoracolumbar division- Preganglionic neurons originate from the thoracic and lumbar levels of the spinal cord (T1-L2). • Sympathetic ganglia: Sympathetic trunk (vertebral chain) ganglia. Prevertebral (collateral) ganglia: celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric, aorticorenal and renal. ...
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
... originate from the cranial nerves III, VII, IX and X and sacral spinal nerves S2-S4. • Parasympathetic ganglia: terminal ganglia. • Presynaptic neuron usually synapses with 4-5 postsynaptic neurons all of which supply a single visceral effector. ...
... originate from the cranial nerves III, VII, IX and X and sacral spinal nerves S2-S4. • Parasympathetic ganglia: terminal ganglia. • Presynaptic neuron usually synapses with 4-5 postsynaptic neurons all of which supply a single visceral effector. ...