1. A particle of mass m is projected vertically upward at z=O, with an
... 3. Consider the system shown below, where mass m is a magnetic bar and is sliding in a solenoid that is mounted on a cart of mass M. Let XI and x2 be the absolute positions ofM and m, respectively. A force F is applied to m in the positive x 2 direction if a positive voltage V is applied to the sole ...
... 3. Consider the system shown below, where mass m is a magnetic bar and is sliding in a solenoid that is mounted on a cart of mass M. Let XI and x2 be the absolute positions ofM and m, respectively. A force F is applied to m in the positive x 2 direction if a positive voltage V is applied to the sole ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant Acceleration
... though 45m into a dip which has a radius of curvature of 78m. Assuming that air resistance & friction are negligible. Calculate: a. The speed of the car at the bottom of the dip b. The centripetal acceleration at the bottom of the dip c. The extra force on a person with a weight of 600N in the train ...
... though 45m into a dip which has a radius of curvature of 78m. Assuming that air resistance & friction are negligible. Calculate: a. The speed of the car at the bottom of the dip b. The centripetal acceleration at the bottom of the dip c. The extra force on a person with a weight of 600N in the train ...
Navier-Stokes - Northern Illinois University
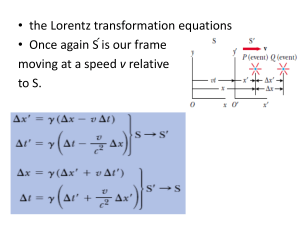
... pressure depends on the view. In the Lagrangian view the total time derivative depends on position and time. ...
... pressure depends on the view. In the Lagrangian view the total time derivative depends on position and time. ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: ____
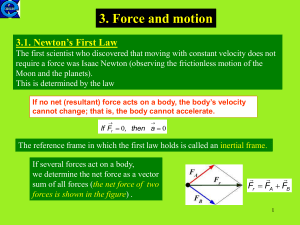
... 20. Why is Newton’s First Law commonly called Law of Inertia? 21. How is mass the measure of inertia? 22. What does acceleration depend on? 23. What happens to the mass if an objects acceleration decreases? Increases? 24. What happens to the force if an objects acceleration decreases? Increases? 25. ...
... 20. Why is Newton’s First Law commonly called Law of Inertia? 21. How is mass the measure of inertia? 22. What does acceleration depend on? 23. What happens to the mass if an objects acceleration decreases? Increases? 24. What happens to the force if an objects acceleration decreases? Increases? 25. ...
Advanced Physics Semester 2 Final Study Guide Momentum
... 2. How many times more intense is a sound of 120 dB compared to 60 dB? 1,000,000 times greater 3. What is resonance? Resonance occurs when an object is forced to vibrate at its natural frequency and an increase in amplitude occurs. What are some of the examples that we discussed in class? Breaking a ...
... 2. How many times more intense is a sound of 120 dB compared to 60 dB? 1,000,000 times greater 3. What is resonance? Resonance occurs when an object is forced to vibrate at its natural frequency and an increase in amplitude occurs. What are some of the examples that we discussed in class? Breaking a ...